A Graph is a non-linear information construction consisting of vertices and edges the place two vertices are related by an edge.
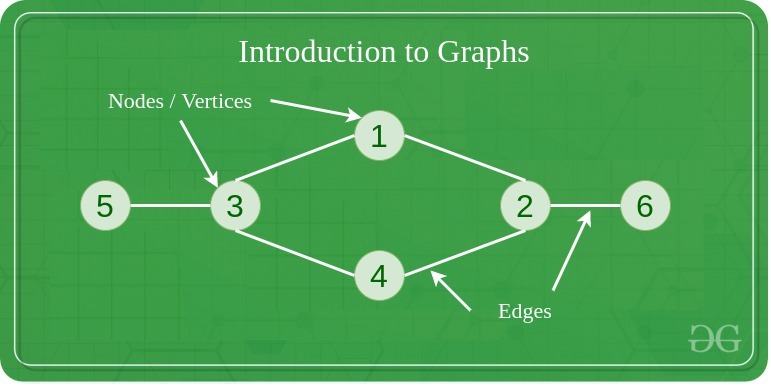
Instance of Graph
Properties of a Graph:
- Vertices (nodes): The factors the place edges meet in a graph are often known as vertices or nodes. A vertex can symbolize a bodily object, idea, or summary entity.
- Edges: The connections between vertices are often known as edges. They are often undirected (bidirectional) or directed (unidirectional).
- Diploma: The diploma of a vertex is the variety of edges that connect with it. In a directed graph, the in-degree of a vertex is the variety of edges that time to it, and the out-degree is the variety of edges that begin from it.
- Path: A path is a sequence of vertices which can be related by edges. A easy path doesn’t include any repeated vertices or edges.
- Cycle: A cycle is a path that begins and ends on the identical vertex. A easy cycle doesn’t include any repeated vertices or edges.
- Connectedness: A graph is claimed to be related if there’s a path between any two vertices. A disconnected graph is a graph that isn’t related.
- Planarity: A graph is claimed to be planar if it may be drawn on a aircraft with none edges crossing one another.
- Bipartiteness: A graph is claimed to be bipartite if its vertices could be divided into two disjoint units such that no two vertices in the identical set are related by an edge.
Sorts of Graph:
Primarily based on the instructions of edges, graphs could be divided into two classes:
- Directed Graph: If the perimeters of a graph have a path related to them, then it’s referred to as a directed graph.
- Undirected Graph: If the perimeters of the don’t have any path related to them, it’s referred to as an undirected graph.
Primarily based on the weights of edges, a graph will also be categorized into two classes:
- Weighted Graph: If the perimeters of the graph have some weight assigned to them, it’s referred to as a weighted graph.
- Unweighted Graph: If the perimeters don’t have any weight assigned to them, it’s an unweighted graph.
Utility of Graph:
- Social media evaluation: Social media platforms generate an enormous quantity of knowledge in actual time, which could be analyzed utilizing graphs to determine tendencies, sentiment, and key influencers.
- Community monitoring: Graphs can be utilized to watch community visitors in real-time, permitting community directors to determine potential bottlenecks, safety threats, and different points. That is important for guaranteeing the graceful operation of advanced networks.
- Monetary buying and selling: Graphs can be utilized to investigate real-time monetary information, akin to inventory costs and market tendencies, to determine patterns and make buying and selling choices. That is significantly essential for high-frequency buying and selling, the place even small delays can have a major affect on earnings.
- Autonomous autos: Graphs can be utilized to mannequin the real-time atmosphere round autonomous autos, permitting them to navigate safely and effectively. This requires real-time information from sensors and different sources, which could be processed utilizing graph algorithms.
To see extra functions of graphs, seek advice from this text.
Benefits of Graph:
- Representing advanced information: Graphs are efficient instruments for representing advanced information, particularly when the relationships between the info factors are usually not simple. They may also help to uncover patterns, tendencies, and insights which may be tough to see utilizing different strategies.
- Environment friendly information processing: Graphs could be processed effectively utilizing graph algorithms, that are particularly designed to work with graph information constructions. This makes it attainable to carry out advanced operations on massive datasets shortly and successfully.
- Visualization: Graphs are extremely visible, making it straightforward to speak advanced information and relationships in a transparent and concise manner. This makes them helpful for displays, experiences, and information evaluation.
- Machine studying: Graphs can be utilized in machine studying to mannequin advanced relationships between variables, akin to in suggestion methods or fraud detection.
To see extra benefits of graph, seek advice from this text.
Disadvantages of Graph:
- Restricted illustration: Graphs can solely symbolize relationships between objects, and never their properties or attributes. Because of this with a purpose to absolutely perceive the info, it could be essential to complement the graph with extra data.
- Problem in interpretation: Graphs could be tough to interpret, particularly if they’re massive or advanced. This could make it difficult to extract significant insights from the info, and should require superior analytical methods or area experience.
- Scalability points: Because the variety of nodes and edges in a graph will increase, the processing time and reminiscence required to investigate it additionally will increase. This could make it tough to work with massive or advanced graphs.
To be taught extra about disadvantages of graph, seek advice from this text.


