Rating is a core downside throughout a wide range of domains, resembling engines like google, advice programs, or query answering. As such, researchers typically make the most of learning-to-rank (LTR), a set of supervised machine studying methods that optimize for the utility of an whole listing of things (somewhat than a single merchandise at a time). A noticeable latest focus is on combining LTR with deep studying. Present libraries, most notably TF-Rating, provide researchers and practitioners the mandatory instruments to make use of LTR of their work. Nonetheless, not one of the present LTR libraries work natively with JAX, a brand new machine studying framework that gives an extensible system of perform transformations that compose: automated differentiation, JIT-compilation to GPU/TPU gadgets and extra.
Right now, we’re excited to introduce Rax, a library for LTR within the JAX ecosystem. Rax brings many years of LTR analysis to the JAX ecosystem, making it doable to use JAX to a wide range of rating issues and mix rating methods with latest advances in deep studying constructed upon JAX (e.g., T5X). Rax offers state-of-the-art rating losses, a variety of commonplace rating metrics, and a set of perform transformations to allow rating metric optimization. All this performance is supplied with a well-documented and simple to make use of API that can feel and look acquainted to JAX customers. Please try our paper for extra technical particulars.
Studying-to-Rank Utilizing Rax
Rax is designed to resolve LTR issues. To this finish, Rax offers loss and metric capabilities that function on batches of lists, not batches of particular person information factors as is widespread in different machine studying issues. An instance of such a listing is the a number of potential outcomes from a search engine question. The determine under illustrates how instruments from Rax can be utilized to coach neural networks on rating duties. On this instance, the inexperienced gadgets (B, F) are very related, the yellow gadgets (C, E) are considerably related and the purple gadgets (A, D) are usually not related. A neural community is used to foretell a relevancy rating for every merchandise, then this stuff are sorted by these scores to provide a rating. A Rax rating loss incorporates the whole listing of scores to optimize the neural community, bettering the general rating of the gadgets. After a number of iterations of stochastic gradient descent, the neural community learns to attain the gadgets such that the ensuing rating is perfect: related gadgets are positioned on the prime of the listing and non-relevant gadgets on the backside.
Approximate Metric Optimization
The standard of a rating is usually evaluated utilizing rating metrics, e.g., the normalized discounted cumulative acquire (NDCG). An vital goal of LTR is to optimize a neural community in order that it scores extremely on rating metrics. Nonetheless, rating metrics like NDCG can current challenges as a result of they’re typically discontinuous and flat, so stochastic gradient descent can’t immediately be utilized to those metrics. Rax offers state-of-the-art approximation methods that make it doable to provide differentiable surrogates to rating metrics that let optimization by way of gradient descent. The determine under illustrates using rax.approx_t12n, a perform transformation distinctive to Rax, which permits for the NDCG metric to be reworked into an approximate and differentiable kind.
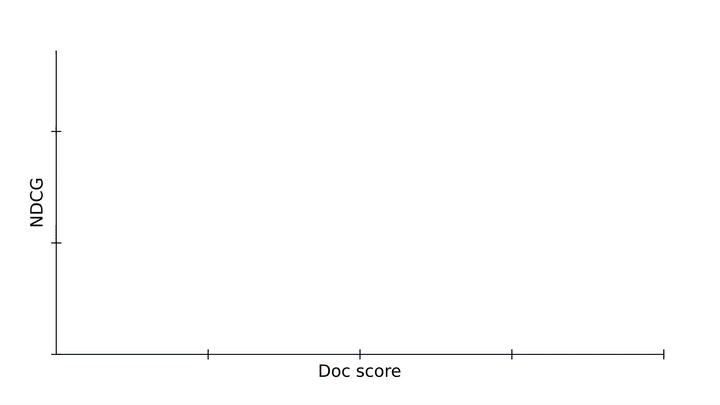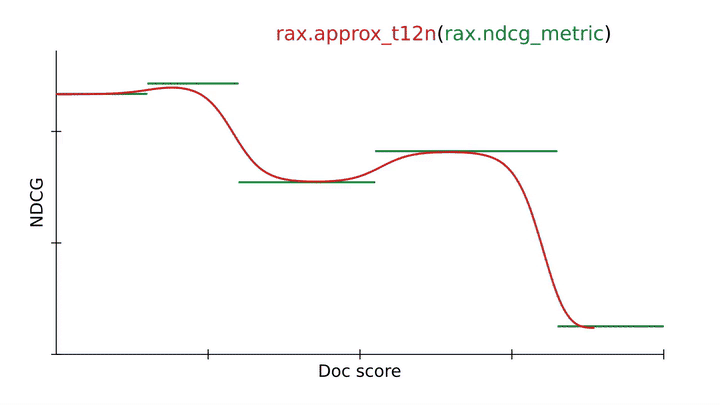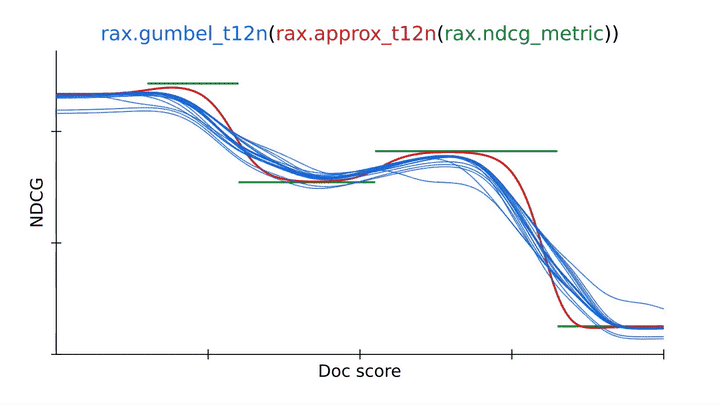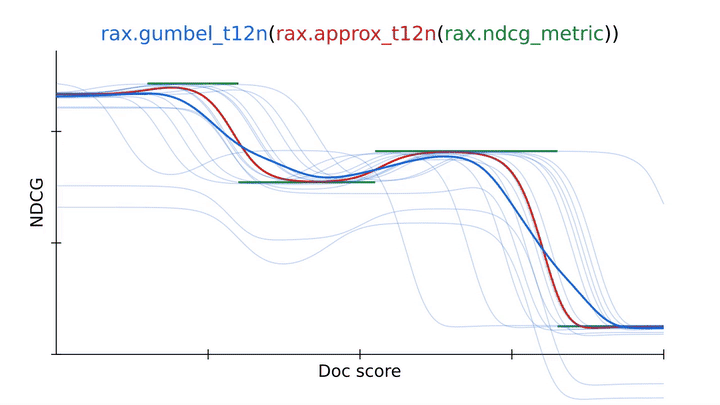 |
Utilizing an approximation method from Rax to rework the NDCG rating metric right into a differentiable and optimizable rating loss (approx_t12n and gumbel_t12n). |
First, discover how the NDCG metric (in inexperienced) is flat and discontinuous, making it exhausting to optimize utilizing stochastic gradient descent. By making use of the rax.approx_t12n transformation to the metric, we receive ApproxNDCG, an approximate metric that’s now differentiable with well-defined gradients (in purple). Nonetheless, it probably has many native optima — factors the place the loss is regionally optimum, however not globally optimum — through which the coaching course of can get caught. When the loss encounters such a neighborhood optimum, coaching procedures like stochastic gradient descent may have problem bettering the neural community additional.
To beat this, we will receive the gumbel-version of ApproxNDCG by utilizing the rax.gumbel_t12n transformation. This gumbel model introduces noise within the rating scores which causes the loss to pattern many alternative rankings that will incur a non-zero value (in blue). This stochastic remedy might assist the loss escape native optima and sometimes is a more sensible choice when coaching a neural community on a rating metric. Rax, by design, permits the approximate and gumbel transformations to be freely used with all metrics which are provided by the library, together with metrics with a top-k cutoff worth, like recall or precision. In reality, it’s even doable to implement your personal metrics and remodel them to acquire gumbel-approximate variations that let optimization with none additional effort.
Rating within the JAX Ecosystem
Rax is designed to combine properly within the JAX ecosystem and we prioritize interoperability with different JAX-based libraries. For instance, a standard workflow for researchers that use JAX is to make use of TensorFlow Datasets to load a dataset, Flax to construct a neural community, and Optax to optimize the parameters of the community. Every of those libraries composes properly with the others and the composition of those instruments is what makes working with JAX each versatile and highly effective. For researchers and practitioners of rating programs, the JAX ecosystem was beforehand lacking LTR performance, and Rax fills this hole by offering a group of rating losses and metrics. We now have rigorously constructed Rax to perform natively with commonplace JAX transformations resembling jax.jit and jax.grad and varied libraries like Flax and Optax. Which means customers can freely use their favourite JAX and Rax instruments collectively.
Rating with T5
Whereas big language fashions resembling T5 have proven nice efficiency on pure language duties, how you can leverage rating losses to enhance their efficiency on rating duties, resembling search or query answering, is under-explored. With Rax, it’s doable to completely faucet this potential. Rax is written as a JAX-first library, thus it’s straightforward to combine it with different JAX libraries. Since T5X is an implementation of T5 within the JAX ecosystem, Rax can work with it seamlessly.
To this finish, we have now an instance that demonstrates how Rax can be utilized in T5X. By incorporating rating losses and metrics, it’s now doable to fine-tune T5 for rating issues, and our outcomes point out that enhancing T5 with rating losses can provide vital efficiency enhancements. For instance, on the MS-MARCO QNA v2.1 benchmark we’re in a position to obtain a +1.2% NDCG and +1.7% MRR by fine-tuning a T5-Base mannequin utilizing the Rax listwise softmax cross-entropy loss as a substitute of a pointwise sigmoid cross-entropy loss.
 |
| Positive-tuning a T5-Base mannequin on MS-MARCO QNA v2.1 with a rating loss (softmax, in blue) versus a non-ranking loss (pointwise sigmoid, in purple). |
Conclusion
Total, Rax is a brand new addition to the rising ecosystem of JAX libraries. Rax is completely open supply and out there to everybody at github.com/google/rax. Extra technical particulars will also be present in our paper. We encourage everybody to discover the examples included within the github repository: (1) optimizing a neural community with Flax and Optax, (2) evaluating totally different approximate metric optimization methods, and (3) how you can combine Rax with T5X.
Acknowledgements
Many collaborators inside Google made this venture doable: Xuanhui Wang, Zhen Qin, Le Yan, Rama Kumar Pasumarthi, Michael Bendersky, Marc Najork, Fernando Diaz, Ryan Doherty, Afroz Mohiuddin, and Samer Hassan.



