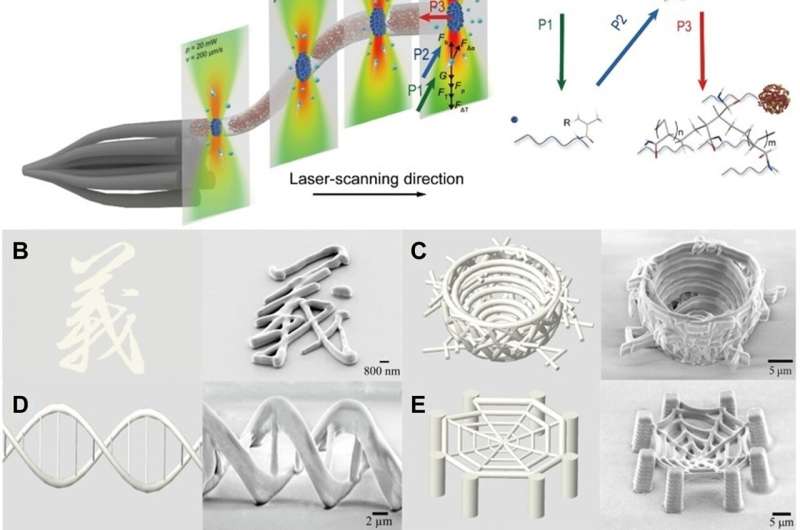
Two-photon polymerization is a possible technique for nanofabrication to combine nanomaterials based mostly on femtosecond laser-based strategies. Challenges within the area of 3D nanoprinting embody sluggish layer-by-layer printing and restricted materials choices because of laser-matter interactions.
In a brand new report now on Science Advances, Chenqi Yi and a staff of scientists in Know-how Sciences, Drugs, and Industrial Engineering on the Wuhan College China and the Purdue College U.S., confirmed a brand new 3D nanoprinting strategy often called free-space nanoprinting by utilizing an optical drive brush.
This idea allowed them to develop exact and spatial writing paths past optical limits to type 4D practical constructions. The strategy facilitated the speedy aggregation and solidification of radicals to facilitate polymerization with elevated sensitivity to laser vitality, to offer excessive accuracy, free-space portray very like Chinese language brush portray on paper.
Utilizing the tactic, they elevated the printing pace to efficiently print a wide range of bionic muscle fashions derived from 4D nanostructures with tunable mechanical properties in response to electrical alerts with glorious biocompatibility.
System engineering
Nanodevices and nanostructures may be engineered at excessive decision and pace to type next-generation merchandise. The semiconductor trade can use lithography, deposition and etching to create 3D constructions from a wide range of supplies, though the excessive processing price and restricted choice of supplies can have an effect on versatile fabrication of 3D constructions of practical supplies.
Supplies scientists have used two-photon polymerization-based femtosecond laser direct writing to create complicated 3D nanostructures utilizing micro/nanopolymers to type photonic quasicrystals, metamaterials, and nanoarchitectures.
Nonetheless, this technique continues to be restricted by a sluggish pace of printing, stairwise floor textures and restricted photocurable supplies. On this work, Yi et al. examined free-space laser writing to investigate the way it yields photochemical forces to perform optical drive brush-based nanopainting.
Free-space portray with a femtosecond laser
When timescales attain the femtosecond, molecules can take in the photon for excitation into an electronically larger state with a repulsive potential vitality floor, to generate free radicals.
Scientists can use multiphoton absorption mechanisms to soak up ultrashort pulse photon vitality in molecules and activate electron transition between the bottom and excited state. Yi and colleagues irradiated energetic radicals with a femtosecond laser for the optical forces to quickly mixture them and synthesize into macromolecules to shortly full solidification with out post-processing, whereas minimizing thermal movement of the solvent molecules.
The researchers developed a hydrogel-based ink as a photoswitch activated upon femtosecond laser writing via two-photon absorption, the place radicals within the gel absorbed photon vitality from the femtosecond laser. Whereas free radicals fashioned binding vitality within the molecules, the staff linked the long-chain molecules to totally different practical teams for a wide range of purposes.
The printable hydrogel-based ink supplied extremely biocompatible, elastic, and versatile situations for a number of purposes of free-space printable nanostructures in biomedicine.
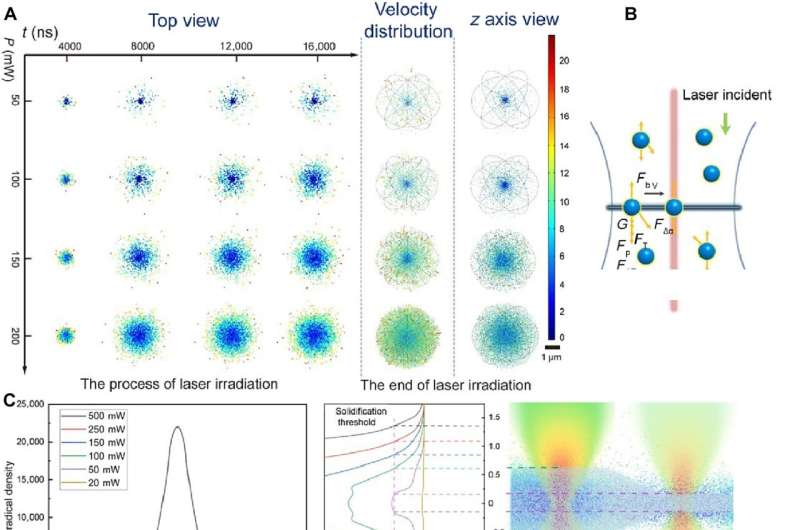
Mechanism-of-action
The laser beam moved freely in resolution very like a pen in house and concerned three steps: activation, aggregation, and solidification of free radicals. The scientists cultured the polymerization charges for two photon polymerization and optical drive brush individually with a multiphysics mannequin.
The strategy significantly improved the effectivity of the writing construction via a layer-by-layer, line-by-line printing technique, the place the variety of layers immediately correlated with the thickness decision. The strategy additionally facilitated significantly improved 3D nanostructure writing effectivity and accuracy. They refined the experimental outcomes to point out how the optical drive utilized to the free radicals have been immediately associated to the variety of pulses, the depth of the laser-field and its absorption coefficient.
Because the femtosecond laser irradiated the fabric, the kinetic vitality from the photons have been exchanged with the energetic free radicals to maneuver by the optical drive, finally leading to sharp and high-resolution 3D nanoprinting. The staff studied the elemental mechanisms underlying these processes via numerical simulations through multiphysics simulations to look at the movement and composite strategy of the radicals.
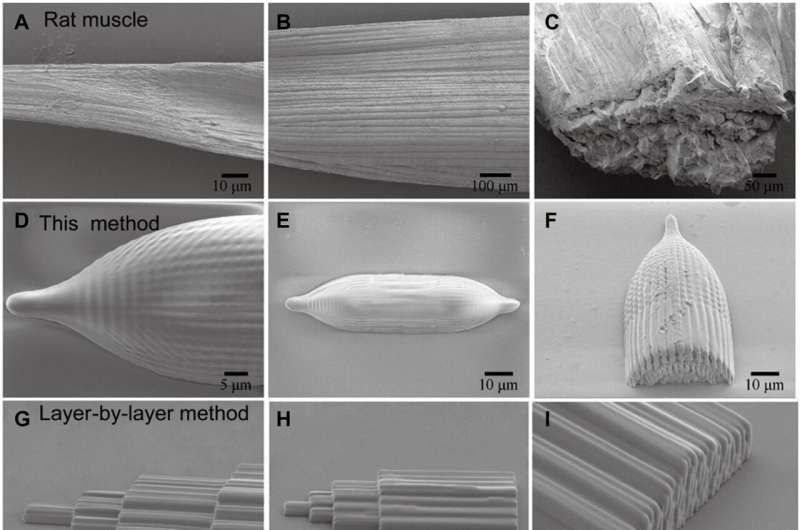
Engineering a nested muscle system
This technique allowed Yi and colleagues to print muscle, stomach, and tendon tissues composed of multilayered nesting of fibers and fiber bundles which might be troublesome to print through conventional 3D printing strategies. The staff printed the muscle’s inside and exterior form, whereas activating its motion through electrical stimulation with a practical hydrogel-based ink. This ends in the preliminary occasion of concurrently reaching each structural and practical bionic nanoprinting.
The scientists demonstrated the construction of rat hamstring’s tendon and stomach printed by optical drive brush and layer-by-layer technique. The strategies confirmed the potential to print multilayer constructions in 3D house, whereas the muscle fiber thickness turned skinny to thick to impart a wide range of functionalities.
The researchers confirmed the potential of utterly implanting the micro- and nanostructures into an organism to understand practical and structural biostructures at this scale. This free-space printing technique via the optical drive brush approach opens potentialities to use multifunctional micro and nanostructures in biology.
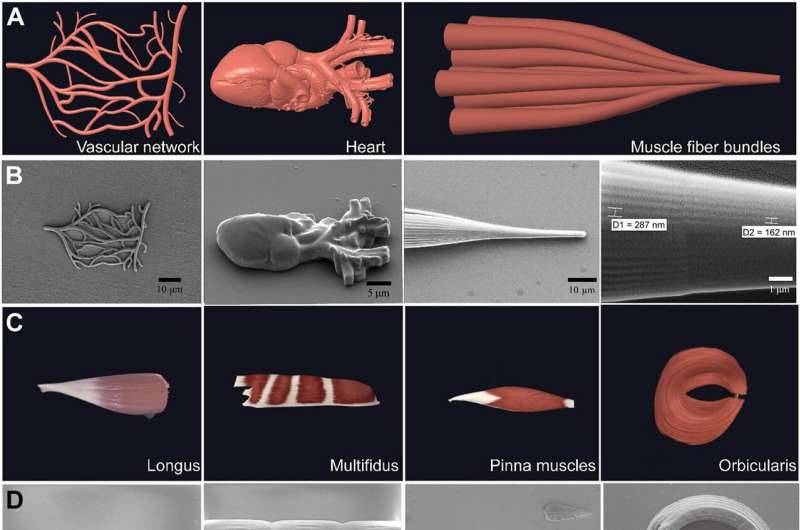
Outlook
On this means Chenqi Yi and colleagues used optical drive brush as a technique that built-in femtosecond laser paintbrush to print practical constructions with true 3D freedom. The optical drive brush has distinctive capabilities with an underlying strategy of optical drive enabled nanopainting, to facilitate an ultrahigh solidification charge, low solidification threshold, and excessive sensitivity to laser to exactly regulate the printing course of. The sensitivity allowed them to precisely regulate and create intricate constructions with fantastic particulars.
This resulted in true 3D printing freedom for steady printing and seamless transitions between totally different planes. The work additional explored the mechanisms of optical forces for nanoprinting in free house throughout optical drive brush use. This included interactions of the femtosecond laser with free radicals within the hydrogel ink photoswitch; a mechanism additionally explored via numerical simulations.
The analysis emphasised the capability of the optical drive brush to develop bionic practical constructions and pave the way in which for added research in tissue engineering and regenerative medication with breakthrough properties.
Extra info:
Yi C. et al, Optical drive brush enabled free-space portray of 4D practical constructions, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg0300
Ergin T. et al. Three-dimensional invisibility cloak at optical wavelengths, Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.1186351
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Free-space nanoprinting past optical limits to create 4D practical constructions (2023, October 7)
retrieved 7 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-free-space-nanoprinting-optical-limits-4d.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


