(Nanowerk Information) A collaborative group of experimental and computational bodily chemists from South Korea and america have made an vital discovery within the subject of electrochemistry, shedding gentle on the motion of water molecules close to metallic electrodes. This analysis holds profound implications for the development of next-generation batteries using aqueous electrolytes.
This analysis was printed within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (“The hydrogen-bonding dynamics of water to a nitrile functionalized electrode is modulated by voltage based on 2D IR spectroscopy”).
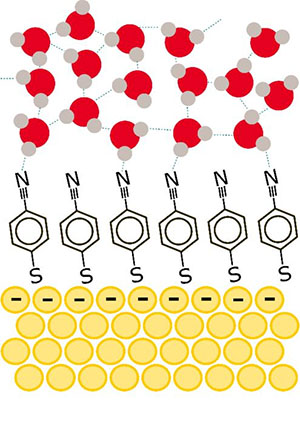 Schematic determine representing the natural molecules adsorbed on a gold floor and water molecules close to the gold electrode. (Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
Within the nanoscale realm, chemists sometimes make the most of laser gentle to light up molecules and measure spectroscopic properties to visualise molecules. Nevertheless, finding out the conduct of water molecules close to metallic electrodes proved difficult because of the overwhelming interference from metallic atoms within the electrode itself. Moreover, water molecules distant from the electrode floor additionally contribute to the response of the utilized gentle, complicating the selective remark of molecules on the liquid-metal electrode interface.
Led by Professor Martin Zanni from the College of Wisconsin at Madison and Director CHO Minhaeng from the Middle for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics throughout the Institute for Fundamental Science (IBS) addressed this problem with newly developed spectroscopic methods coupled with pc simulations. To be able to decrease the interference from the metals, the authors coated the floor of the electrode with specifically designed natural molecules. Then, surface-enhanced femtosecond (10-15 second) two-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy was employed to watch the modifications within the motion of water molecules close to the metallic electrode.
Schematic determine representing the natural molecules adsorbed on a gold floor and water molecules close to the gold electrode. (Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
Within the nanoscale realm, chemists sometimes make the most of laser gentle to light up molecules and measure spectroscopic properties to visualise molecules. Nevertheless, finding out the conduct of water molecules close to metallic electrodes proved difficult because of the overwhelming interference from metallic atoms within the electrode itself. Moreover, water molecules distant from the electrode floor additionally contribute to the response of the utilized gentle, complicating the selective remark of molecules on the liquid-metal electrode interface.
Led by Professor Martin Zanni from the College of Wisconsin at Madison and Director CHO Minhaeng from the Middle for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics throughout the Institute for Fundamental Science (IBS) addressed this problem with newly developed spectroscopic methods coupled with pc simulations. To be able to decrease the interference from the metals, the authors coated the floor of the electrode with specifically designed natural molecules. Then, surface-enhanced femtosecond (10-15 second) two-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy was employed to watch the modifications within the motion of water molecules close to the metallic electrode.
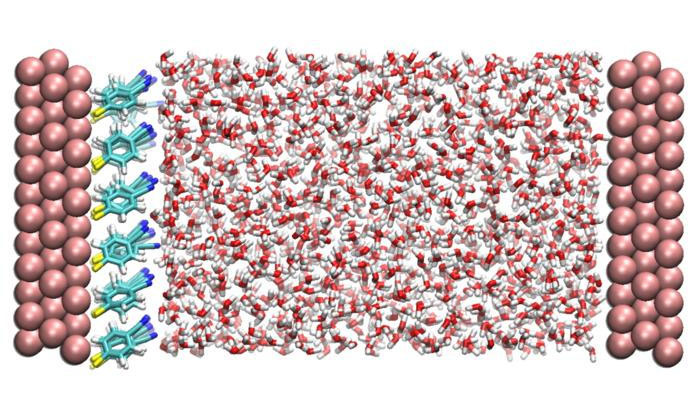 A snapshot taken from the pc simulation mannequin of the system on this examine. On each side are three layers of gold atoms representing the metallic electrode with adsorbed natural molecules on the left electrode. The house between the electrodes is stuffed with water molecules. (Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
Relying on the magnitude and polarity of the utilized voltage on the metallic electrode, the researchers noticed, for the primary time, both a deceleration or acceleration of the movement of water molecules close to the electrode. “When a optimistic voltage is utilized to the electrode, the motion of close by water molecules slows down. Conversely, when a destructive voltage is utilized, the other is noticed each in femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy and in pc simulations,” explains Dr. Kwac.
“The outcomes of this examine present essential info for understanding electrochemical reactions, providing important bodily insights obligatory for the analysis and growth of aqueous electrolyte batteries sooner or later,” feedback Director CHO Minhaeng of the IBS Middle for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics, a corresponding writer of the examine.
A snapshot taken from the pc simulation mannequin of the system on this examine. On each side are three layers of gold atoms representing the metallic electrode with adsorbed natural molecules on the left electrode. The house between the electrodes is stuffed with water molecules. (Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
Relying on the magnitude and polarity of the utilized voltage on the metallic electrode, the researchers noticed, for the primary time, both a deceleration or acceleration of the movement of water molecules close to the electrode. “When a optimistic voltage is utilized to the electrode, the motion of close by water molecules slows down. Conversely, when a destructive voltage is utilized, the other is noticed each in femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy and in pc simulations,” explains Dr. Kwac.
“The outcomes of this examine present essential info for understanding electrochemical reactions, providing important bodily insights obligatory for the analysis and growth of aqueous electrolyte batteries sooner or later,” feedback Director CHO Minhaeng of the IBS Middle for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics, a corresponding writer of the examine.
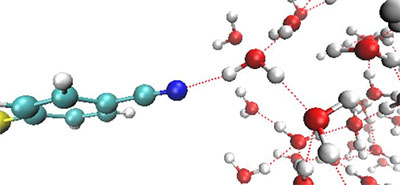 Determine representing the hydrogen bonding interplay between water molecules and an adsorbed natural molecule.(Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
This final result implies a detailed relationship between electrochemical reactions involving water on the floor of electrodes and the dynamics of interfacial water molecules. It’s anticipated to not solely advance our understanding of basic electrochemical processes but additionally pave the best way for the design of extra environment friendly and sustainable battery applied sciences.
Determine representing the hydrogen bonding interplay between water molecules and an adsorbed natural molecule.(Picture: Institute for Fundamental Science)
This final result implies a detailed relationship between electrochemical reactions involving water on the floor of electrodes and the dynamics of interfacial water molecules. It’s anticipated to not solely advance our understanding of basic electrochemical processes but additionally pave the best way for the design of extra environment friendly and sustainable battery applied sciences.