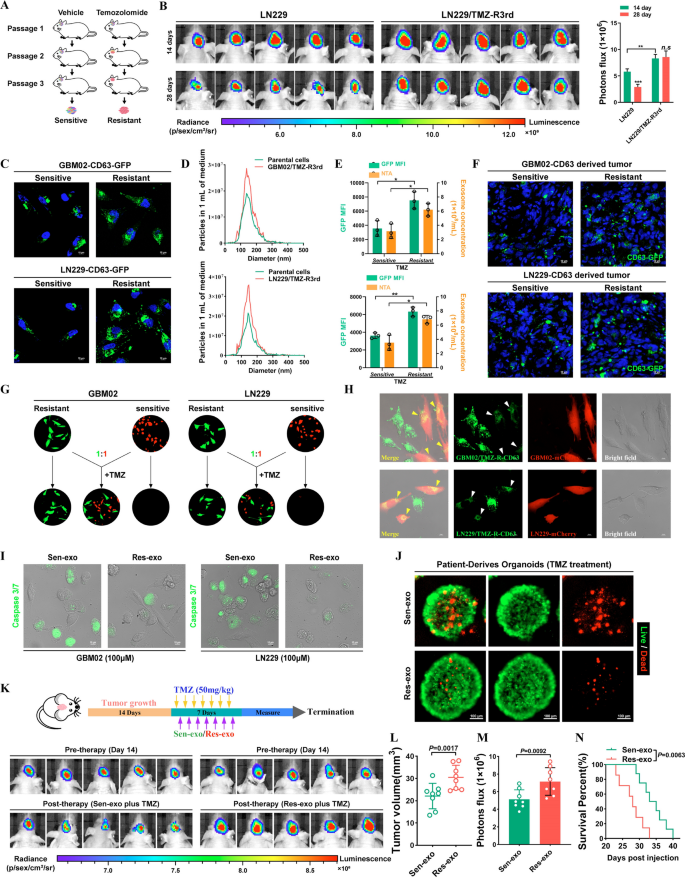
Exosomes derived from TMZ-resistant cells disseminates drug resistance traits to delicate cells
To generate TMZ-resistant GBM cells, we grafted GBM02 and LN229 cells into nude mice and carried out cycles of TMZ remedy together with serial passage in these orthotopic fashions (Fig. 1A). GBM xenografts from the third passage exhibited a poor response to TMZ remedy. Resistant GBM cells had been remoted from these xenografts and named LN229/TMZ-R3rd and GBM02/TMZ-R3rd cells. In contrast with the corresponding parental cells, LN229/TMZ-R3rd and GBM02/TMZ-R3rd cells exhibited extraordinarily poor responses to TMZ, as proven by the in vivo drug sensitivity take a look at (Fig. 1B and Extra file 1: Fig. S1A). Exosomes are membrane-bound extracellular vesicles which are produced within the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. Intercellular communication by way of exosomes is a vital mediator of organic processes. Not too long ago, accumulating research have reported that exosomes carry out vital organic capabilities in people, particularly within the incidence and growth of tumors [10, 22].
Temozolomide-resistant GBM cells transmit resistance to delicate cells by means of exosomes. A Schematic mannequin. Course of to accumulate Temozolomide-resistant cells. B Affirm the drug resistance of TMZ-resistant LN229 cells in vivo. Left, IVIS detects bioluminescence alerts. Proper, quantification of bioluminescent imaging sign intensities. C The expression of CD63 in TMZ-R cells and parental cells was detected by fusion expression of CD63-GFP protein. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. D Secretion of exosomes had been detected by nanoparticle monitoring evaluation. E GFP imply fluorescence depth (MFI; left y axis) and focus by NTA (proper y axis) of exosomes launched by delicate or resistant GBM cells. F Fluorescence photos of Mind frozen part of mind from orthotopic GBM xenograft mice. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. G TMZ resistant cells (GFP) co-cultured with parental cells (mCherry) at a ratio of 1:1 with TMZ remedy (100uM) for 4 days. H TMZ-resistant cells expressed CD63-GFP fusion protein co-cultured with parental cells (mCherry) at a ratio of 1:1 for 4 days. Scale bar, 10 μm. I GBM cells had been co-cultured with Res-exo or Sen-exo and TMZ (100 μM), and apoptosis was detected by caspase3/7 assay. Scale bar, 10 μm. J Affected person-derived organoids was to substantiate TMZ resistant after handled with Sen-exo / Res-exo. Scale bar, 50 μm. Okay–N Schematic mannequin. Strategy of animal examine. Nude mice had been orthotopically xenografted with GBM cells (2 × 106 cells) and handled intravenously with Res-exo or Sen-exo (200 μg per mouse) and intraperitoneally with TMZ (40 mg/kg) day by day. IVIS detects bioluminescence alerts. Quantification of tumor dimension (L), and quantification of bioluminescent imaging sign intensities (M), and survival charge (N) of mice in indicated teams are proven. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01. NS, not vital
We investigated whether or not TMZ can modulate exosome launch from most cancers cells. We then examined the consequences of chemotherapy-TMZ on exosome launch from most cancers cells. To hint exosomes, LN229 and GBM02 cells had been modified to precise a fluorescent CD63-GFP fusion protein focused to exosomal membranes (Fig. 1C). Nanoparticle monitoring evaluation (NTA) of conditioned medium demonstrated that TMZ-resistant cells launched a considerably greater variety of exosomes than TMZ-sensitive cells. As well as, CD63-GFP fluorescence was elevated in TMZ-resistant GBM cells (Fig. 1D, E). After cycles of TMZ remedy together with serial passage in these orthotopic fashions, we discovered that GFP fluorescence was elevated in resistant tumors in contrast with the parental tumors (Fig. 1F). Nonetheless, TMZ remedy didn’t alter the bodily options of resistant cell-derived exosomes, as demonstrated by transmission electron microscopy (Extra file 1: Fig. S1B).
Exosomes have an effect on tumor resistance to varied medicine, prompting us to discover whether or not TMZ-resistant cell-derived exosomes alter TMZ efficacy in delicate cells. In a co-culture assay, GFP-labeled parental cells grew to become insensitive to TMZ when cocultured with mCherry-labeled TMZ-resistant cells (1:1 ratio). The outcomes indicated that components secreted by TMZ-resistant GBM cells promoted the resistance phenotype in delicate GBM cells (Fig. 1G). To discover whether or not exosomes play a vital function on this impact, we diminished exosome manufacturing by means of interference with Rab27a/b expression by RNA interference (RNAi) or pharmacological inhibition of impartial sphingomyelinase-2 (nSMase) with GW4869. Curiously, CM from LN229/TMZ-R3rd cells with Rab27a/b knockdown or GW4869 remedy did not confer TMZ resistance on recipient cells, indicating the vital function of exosomes within the transmission of resistance (Extra file 1: Fig. S1C). Cell-secreted exosomes and capped cargoes could be internalized by neighboring cells. In a coculture system, CD63-GFP-labeled TMZ-resistant cells delivered exosomes to the adjoining mCherry-labeled TMZ-sensitive cells (Fig. 1H). Subsequent, we examined the impact of resistant cell-secreted exosomes on the therapeutic sensitivity of GBM cells and located that exosomes launched from resistant GBM cells (Res-exo), however not these launched from delicate GBM cells (Sen-exo), enhanced the resistance of recipient GBM cells to TMZ in vitro (Fig. 1I and Extra file 1: Fig. S1D).
Affected person-derived organoids (PDOs) can be utilized to foretell responses to chemotherapy. Right here, we efficiently established PDOs and used them to research drug responses after remedy. PDOs weren’t delicate to TMZ when pre-incubated with Res-exo (Fig. 1J). We administered mice with exosomes derived from TMZ-resistant and parental cells throughout chemotherapy. As proven in Fig. 1Okay, exosomes derived from TMZ-resistant cells however not parental cells considerably inhibited the response of GBM xenografts to TMZ, as decided by evaluating the tumor sizes and mouse survival occasions. As well as, exosome-conferred resistance was sustained for at the very least 7 days in recipient cells after the elimination of Res-exo and couldn’t be reversed by Sen-exo (Extra file 1: Fig. S1E, F). These knowledge recommend that the resistance of recipient cells conferred by Res-exo is sustainable.
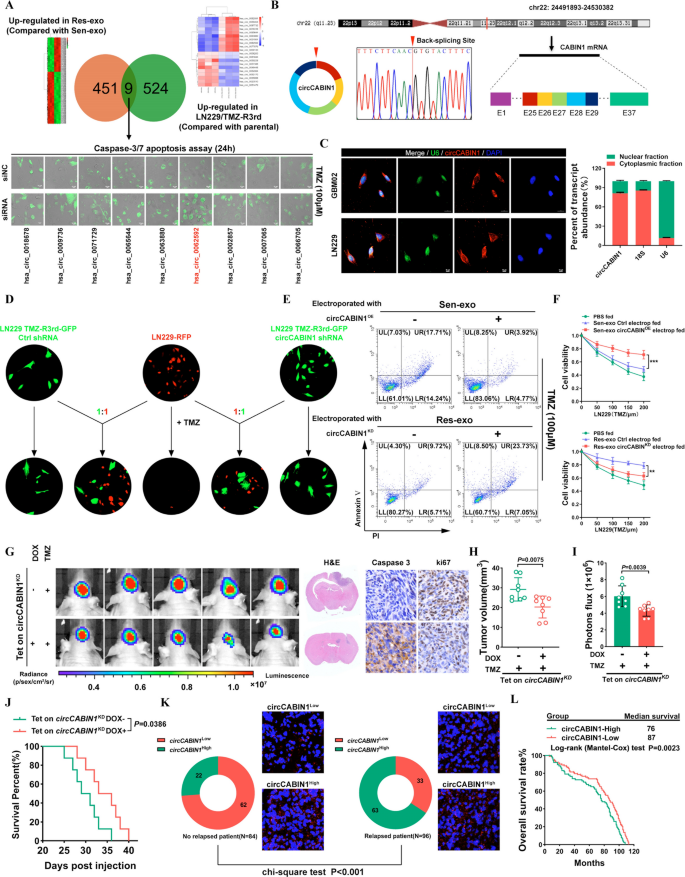
Intercellular transmission of circCABIN1 by exosomes considerably dampens the response of delicate cells to TMZ
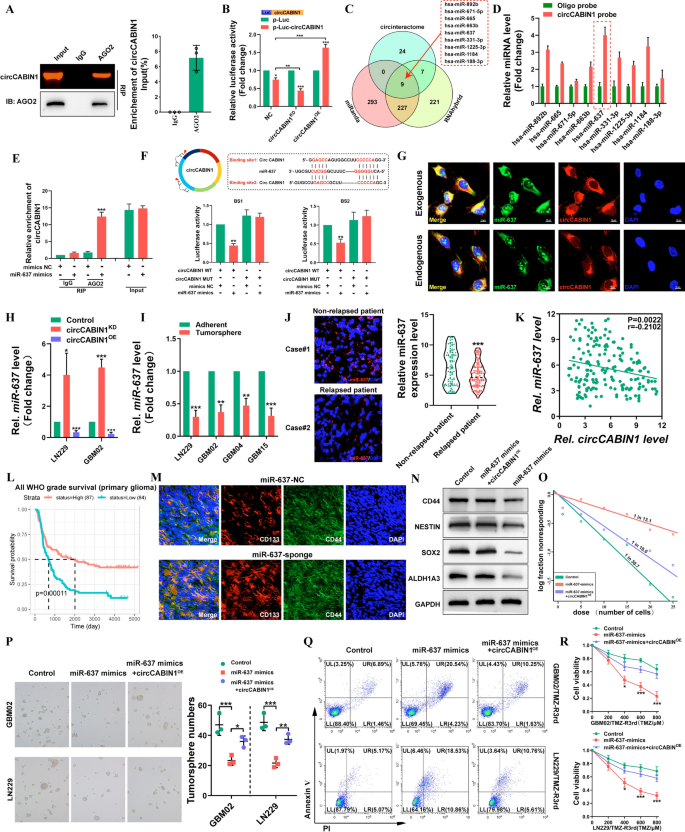
To establish the vital circRNAs that contribute to the dissemination of drug resistance traits, circRNA deep sequencing was carried out in LN229/TMZ-R3rd and parental cells. We additionally in contrast the circRNA transcriptome profiles of exosomes remoted from LN229/TMZ-R3rd cells (i.e., Res-exo) with these of exosomes derived from the parental LN229 cell line (i.e., Sen-exo). The circos plot and heatmap present the distribution and expression profiles of the detected and differentially expressed circRNAs on human chromosomes (Extra file 1: Fig. S2A, B). Comparative evaluation revealed that 9 circRNAs had been considerably upregulated in each LN229/TMZ-R3rd cells (in contrast with the parental cells) and Res-exo (in contrast with Sen-exo). The caspase-3/7 apoptosis assay revealed that the particular siRNA concentrating on hsa_circ_0062592 had essentially the most vital chemosensitizing impact on GBM cells (Fig. 2A). In response to circBase (http://www.circbase.org/), the circRNA hsa_circ_0062592 is derived from exons 25–29 of the CABIN1 transcript and kinds a 960 nt round transcript hereafter known as circCABIN1. The back-spliced junction of circCABIN1 was amplified and confirmed by Sanger sequencing, and the sequence was in line with that within the circBase database (Fig. 2B). We then additional examined the round traits of circCABIN1. Utilizing cDNA and genomic DNA as templates, reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) analyses utilizing convergent and divergent primers confirmed that circ CABIN1 was amplified by divergent primers in cDNA however not in genomic DNA (Extra file 1: Fig. S2C). As well as, circCABIN1 was extra secure than linear CABIN1 mRNA upon RNase-R/Actinomycin D remedy (Extra file 1: Fig. S2D, F). Furthermore, we utilized a Cy3-labeled circCABIN1-specific probe to focus on the junction area and RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) demonstrated that circCABIN1 was localized predominately within the cytoplasm. The nuclear/cytoplasm fractionation additional confirmed that circCABIN1 was expressed primarily within the cytoplasm (Fig. 2C).
Intercellular switch of circCABIN1 by exosomes disseminates temozolomide resistance. A Higher, Screening differentially expressed circRNA in TMZ-R cells and Res-exo by circRNA deep-sequencing. Decrease, LN229 cells had been transfected with siNC or siRNA and handled with TMZ (100 μM), and apoptosis was detected by caspase3/7 assay. Scale bar, 10 μm. B Clarification of the illustrated genomic loci of CABIN1, and the verification technique for the round exon 25–29 (circCABIN1). Sanger sequencing following PCR was used to indicate the “head-to-tail” splicing of circCABIN1 C Left, localization of circCABIN1 (purple) in cells utilizing fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). U6 probe coupled with Alexa Fluor™ 488 (inexperienced) and nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Proper, nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions had been remoted. circCABIN1 was primarily localized in cytoplasm. D TMZ-R3rd-GFP cells transfected with Ctrl shRNA or circCABIN1 shRNA co-cultured with parental cells (mCherry) at a ratio of 1:1 with TMZ remedy (100uM) for 4 days. Scale bar, 10 μm. E LN229 cells administrated with Sen-exo/Res-exo electroporated with circCABIN1OE/KD and TMZ had been subjected to FACS to detect apoptosis. F The impact of Sen-exo/Res-exo electroporated with circCABIN1OE/KD on LN229 cells by CCK-8 assay. G-J Nude mice had been orthotopically xenografted with Tet on circCABIN1 KD GBM cells (2 × 106 cells) and handled with DOX-diet and intraperitoneally with TMZ (40 mg/kg) day by day. Left, IVIS detects bioluminescence alerts. Proper, consultant photos of H&E and cleaved Caspase-3 and ki67 IHC in GBM sections of indicated teams. Quantification of tumor dimension (H), and quantification of bioluminescent imaging sign intensities (I), and survival charge (J) of mice in indicated teams. Okay Expression of circCABIN1 in relapsed or non-relapsed sufferers and consultant immunofluorescence photos in GBM part of indicated teams. L Kaplan–Meier evaluation of OS within the excessive and low circCABIN1 teams in accordance with the median circCABIN1 degree in pre-therapy plasma (p = 0.0023). Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
We additional examined whether or not exosome-transmitted circCABIN1 can confer a resistance phenotype on recipient GBM cells. Particularly, knockdown of circCABIN1 in resistant cells suppressed the flexibility of the cocultured parental cells to accumulate resistance (Fig. 2D). Furthermore, parental cells incubated immediately with exosomes derived from TMZ-resistant cells displayed diminished sensitivity to TMZ, which might be abrogated within the recipient cells by remedy with quick hairpin RNA (shRNA) in opposition to circCABIN1 (Extra file 1: Fig. S2G). GBM cells uncovered to Sen-exo electroporated with circCABIN1OE additionally exhibited a poor response to TMZ, excluding the involvement of things apart from circCABIN1 in exosomes. Res-exo electroporated with the circCABIN1KD assemble considerably decreased the flexibility of the cocultured parental cells to accumulate resistance (Fig. 2E, F).
To eradicate the impact of circCABIN1 on tumorigenesis, we constructed an LN229 cell line with Tet-on inducible circCABIN1 knockdown. Knockdown of circCABIN1 induced by doxycycline (DOX) remedy considerably sensitized GBM tumor-bearing mice to TMZ, as indicated by the decreases within the bioluminescence sign depth and tumor quantity. Survival evaluation confirmed that circCABIN1 knockdown considerably elevated the median survival time of mice from 30.0 (DOX-) to 34.5 (DOX +) days. The above findings revealed that downregulation of circCABIN1 promotes TMZ sensitivity. Ki-67 and caspase-3 staining confirmed that circCABIN1 knockdown inhibited tumor cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in tumor tissues (Fig. 2G–J).
Furthermore, circCABIN1 ranges had been elevated in GBM sufferers who ultimately skilled relapse. Once we divided the sufferers into the excessive and low circCABIN1 expression teams (with the median expression worth because the cutoff), the proportion of sufferers with excessive circCABIN1 expression was considerably decrease within the non-relapsed affected person group than within the relapsed affected person group (Fig. 2Okay). These knowledge recommend that circCABIN1 could also be related to recurrence in glioma sufferers. Kaplan‒Meier survival evaluation confirmed that prime circCABIN1 ranges in glioma sufferers had been correlated with diminished general survival (OS) (Fig. 2L). Furthermore, the extent of linear CABIN1 mRNA had no impact on OS in GBM sufferers, in accordance with evaluation of the CGGA, TCGA, Gravendeel and Rembrandt databases (Extra file 1: Fig. S2H).
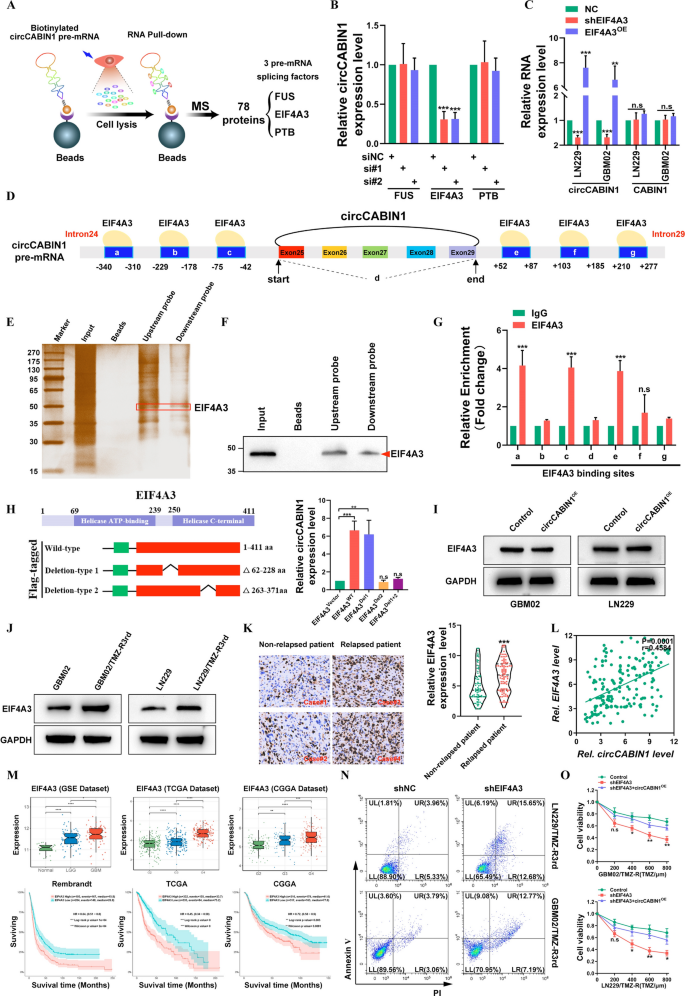
EIF4A3 will increase the biogenesis of circCABIN1 by juxtaposing the circularized exons
To establish the potential issue(s) concerned in circCABIN1 cyclization, an RNA pull-down assay was carried out utilizing circCABIN1 pre-mRNA, which was ready by way of in vitro transcription, and the merchandise had been then used for mass spectrometry-based proteomic evaluation. A complete of 78 proteins, together with 3 pre-mRNA splicing components (PTB, EIF4A3 and FUS), had been recognized as potent circCABIN1 pre-mRNA-interacting proteins (Fig. 3A). Additional qRT‒PCR evaluation revealed that silencing EIF4A3 considerably diminished however overexpressing EIF4A3 elevated circCABIN1 expression in GBM cells. Furthermore, overexpressing EIF4A3 didn’t have an effect on the expression degree of CABIN1, suggesting that EIF4A3 could be concerned in circCABIN1 cyclization (Fig. 3B, C).
EIF4A3 promotes the biogenesis of circCABIN1. A Schematic picture. Screening of RNA binding proteins by mass spectrometry. B The expression of circCABIN1 in LN229 cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR after indicated transfection. C The expression of circCABIN1 was analyzed by qRT-PCR after overexpress or knockdown EIF4A3. D Schematic picture. Binding website of EIF4A3 and circCABIN1 pre-mRNA. E–F Pull-down silver staining and western blotting had been used to reveal the interplay between EIF4A3 and the circCABIN1 pre-mRNA upstream and downstream area in LN229 cells. G RIP assay to confirm EIF4A3 binding on the putative websites. H Schematic picture. Development of wild-type and deletion mutant expression plasmids for EIF4A3, and the expression of circCABIN1 in LN229 cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR after indicated transfection. I The expression of EIF4A3 was analyzed by western blot after overexpressed circCABIN1. J The expression of EIF4A3 was analyzed by western blot in TMZ resistant and parental cells. Okay The expression of EIF4A3 in relapsed or non-relapsed sufferers and consultant EIF4A3 IHC photos in GBM part of indicated teams. L Pearson correlation evaluation of circCABIN1 and EIF4A3 (p = 0.0001). M The expression of EIF4A3 in numerous levels GBM and Kaplan–Meier evaluation of OS within the excessive and low EIF4A3 teams in public database. N TMZ resistant cells administrated with shNC or shEIF4A3 had been subjected to FACS to detect apoptosis. O The impact of shEIF4A3 and shEIF4A3 plus circCABIN1OE on TMZ resistant cells by CCK-8 assay. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. NS, not vital
We then examined whether or not EIF4A3 immediately interacts with circCABIN1 pre-mRNA. CircInteractome (https://circinteractome.nia.nih.gov/index.html) evaluation revealed 6 putative EIF4A3 binding websites within the upstream and downstream areas of circCABIN1 pre-mRNA (Fig. 3D). Then, we carried out an RNA pulldown assay utilizing particular biotinylated probes. As proven in Fig. 3E and F, EIF4A3 sure to each the upstream and downstream flanking sequences of circCABIN1. As well as, the RIP assay confirmed that endogenous EIF4A3 sure to 2 upstream putative binding websites (named a and c) and one downstream putative binding website (named e) however not the back-spliced junction website (named d) (Fig. 3G). Furthermore, we discovered that circCABIN1 has binding websites positioned in introns 24 and 29 of CABIN1 pre-mRNA. EIF4A3 could be inferred to advertise circCABIN1 biogenesis by bringing exons 25 and 29 into shut proximity. Due to this fact, these outcomes reveal that EIF4A3 immediately binds to circCABIN1 pre-mRNA and induces circCABIN1 cyclization.
To additional elucidate the binding websites of EIF4A3 within the circCABIN1 pre-mRNA transcript, we carried out a display screen with the catRAPID algorithm and recognized peptides containing aa 62–228 and aa 263–371 of EIF4A3 as two doable interplay areas. Consequently, we constructed wild-type EIF4A3 and EIF4A3 deletion mutant (Δ62-228 aa and Δ263-371 aa) expression plasmids. Ectopic expression of wild-type EIF4A3 or deletion-type 1 (Δ62-228 aa) however not deletion-type 2 (Δ263-371 aa) induced the expression of circCABIN1 in GBM cells (Fig. 3H). In distinction, silencing circCABIN1 didn’t change the EIF4A3 expression degree (Fig. 3I). These outcomes recommend that this area (aa 263–371) is indispensable for EIF4A3-mediated regulation of circCABIN1 cyclization.
As anticipated, EIF4A3 was upregulated in TMZ-resistant cell traces (Fig. 3J). As well as, elevated EIF4A3 expression was recognized in samples of relapsed glioma in comparison with samples of non-relapsed glioma, and a optimistic correlation between circCABIN1 and EIF4A3 expression was recognized in glioma samples (Fig. 3Okay–L). Furthermore, evaluation of the CGGA, TCGA and the GSE4290 dataset indicated that EIF4A3 expression was reasonably elevated in lower-grade glioma (LGG) tissues however strongly elevated in GBM tissues. Importantly, sufferers with excessive EIF4A3 expression had a shorter OS time than these with low EIF4A3 expression within the CGGA, TCGA and Rembrandt databases (Fig. 3M). An apoptosis assay confirmed that silencing EIF4A3 elevated the cytotoxicity of TMZ in LN229/TMZ-R3rd and GBM02/TMZ-R3rd cells, whereas ectopic expression of circCABIN1 promoted the TMZ resistance phenotype (Fig. 3N, O). Due to this fact, these outcomes reveal that EIF4A3 immediately binds to circCABNIN1 pre-mRNA and induces circCABNIN1 cyclization.
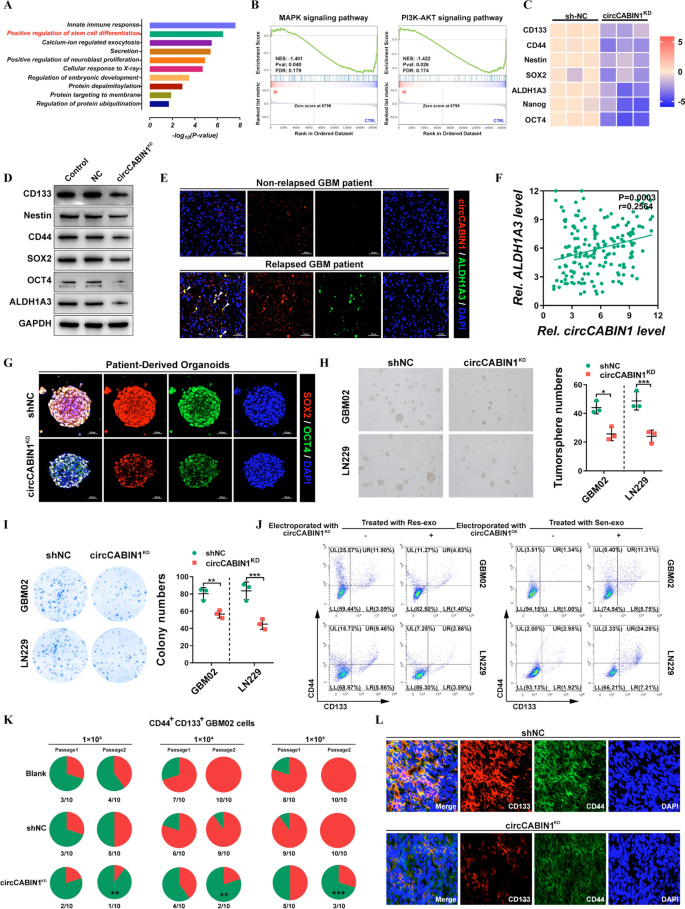
Management of most cancers stemness signature by way of circCABIN1
To discover the underlying mechanisms by which circCABIN1 KD promotes TMZ sensitivity, we carried out whole-transcriptome evaluation of LN229 cells upon circCABIN1 KD utilizing RNA sequencing. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment evaluation revealed that circCABIN1 KD affected the expression of genes enriched within the “pluripotency of stem cells” pathway (Fig. 4A). Moreover, Gene Set Enrichment Evaluation (GSEA) revealed that these differentially expressed genes had been enriched largely in a number of key stemness-related signaling pathways, such because the PI3K-AKT and MAPK pathways, which regulate dedifferentiation (Fig. 4B). The expression profiles of CD133, CD44, Nestin, SOX2, Nanog, ALDH1A3 and OCT4, that are related to glioma stem cell (GSC) signatures, had been visualized in a heatmap (Fig. 4C). Western blot evaluation confirmed that circCABIN1 KD diminished the expression of CD133, Nestin, CD44, SOX2, OCT4 and ALDH1A3 in GBM cells (Fig. 4D). Equally, we discovered that circCABIN1 preferentially expressed in GSCs (ALDH1A3+) in relapsed affected person tissues (Fig. 4E). Moreover, Pearson correlation evaluation revealed that the expression of circCABIN1 was positively correlated with the expression of ALDH1A3 in 180 glioma affected person tissues (Fig. 4F). Furthermore, circCABIN1 expression was upregulated in sorted CD44+CD133+ main GBM cells and in spheres shaped from main GBM cells (Extra file 1: Fig. S3A, B). Organoids type miniature replicas of the host organs by permitting the differentiation and self-organization of stem cells to accumulate organ-specific mobile capabilities and constructions. To judge circCABIN1 KD-mediated suppression of most cancers stemness, PDOs had been allowed to distinguish from stem cells within the presence or absence of a circCABIN1 shRNA adenovirus. circCABIN1 KD remedy suppressed the expression of each SOX2 and OCT4, displaying that circCABIN1 KD eliminates GSCs (Fig. 4G). The tumorsphere formation assay is a straightforward methodology to guage the self-renewal of GSCs in vitro. circCABIN1 KD additionally considerably inhibited the tumorsphere-forming skill of CD44+CD133+ GBM cells (Fig. 4H). Furthermore, the in vitro limiting dilution assay confirmed that circCABIN1 KD inhibited the sphere-forming skill of CD44+CD133+ GSCs (Extra file 1: Fig. S3C). The colony formation assay confirmed that circCABIN1 KD diminished colony numbers in contrast with these within the unfavourable management shRNA (shNC) group (Fig. 4I). Furthermore, GBM cells incubated immediately with exosomes derived from TMZ-resistant cells displayed enhanced expression of stem cell markers, which might be abrogated by publicity to Res-exo electroporated with siRNA in opposition to circCABIN1. GBM cells uncovered to Sen-exo electroporated with the circCABIN1OE assemble additionally elevated the proportion of CD44+CD133+ cells (Fig. 4J). As well as, exosomes derived from parental cells didn’t have an effect on the traits of GSCs (Extra file 1: Fig. S3D).
circCABIN1 promotes most cancers stemness. A KEGG pathway evaluation demonstrated that optimistic regulation of stem cell differentiation was concerned and could be the downstream of circCABIN1. B GSEA evaluation confirmed that differential genes had been primarily enriched in a number of key stem cell associated sign pathways, reminiscent of PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathway. C Warmth map was carried out to investigate the modified key stemness molecules after knockdown of circCABIN1. D The expression of key stemness molecules in LN229 cells had been analyzed by western blot after knockdown of circCABIN1. E Fluorescence photos confirmed the expression of circCABIN1 (Pink) and ALDH1A3 (Inexperienced) in affected person samples. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (Blue). Scale bar, 50 μm. F Pearson correlation evaluation of circCABIN1 and ALDH1A3 (p = 0.0003). G Fluorescence photos of patient-derived organoids was to substantiate the expression of SOX2 (purple) and OCT4 (inexperienced) after knockdown of circCABIN1. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm. H-I Tumorsphere formation assay and colony formation detected GSC’s self-renewal and proliferation skill after knockdown of circCABIN1. J GBM cells administrated with Sen-exo or Res-exo electroporated with circCABIN1OE/KD had been subjected to FACS to detect the proportion of CD44+CD133+ cells. Okay Incidences of tumorigenesis of CD45+CD133+ main GBM cells (GBM02) contaminated with circCABIN1KD in serial transplantation fashions. **P < 0.01 in contrast with untreated main GBM cells within the first inoculation by Fisher’s precise take a look at. L Fluorescence photos confirmed the expression of CD133 (purple) and CD44 (inexperienced) of mind frozen part from orthotopic GBM xenograft mice in indicated teams. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001
Moreover, serial transplantation was carried out by subcutaneous injection of CD44+CD133+ cells remoted from main GBM cells right into a second and a subsequent third batch of mice. circCABIN1 KD considerably suppressed tumorigenicity upon in vivo serial passaging of sorted CD44+CD133+ cells, suggesting that circCABIN1 KD impaired the tumor formation skill of GSCs (Fig. 4Okay). In line with this discovering, the variety of CD44+CD133+ tumor cells was considerably decreased in circCABIN1KD mice in contrast with shNC mice (Fig. 4L). Collectively, these outcomes point out that circCABIN1 KD impairs the self-renewal and upkeep of GSCs and suppresses tumor propagation.
CircCABIN1 immediately binds to miR-637 and acts as a competing endogenous RNA
Earlier research have proven that circRNAs can perform as miRNA sponges, bind to RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), act as transcription components, or be translated into proteins [23, 24]. As a result of circCABIN1 was proven to be localized within the cytoplasm, we first investigated whether or not circCABIN1 can act as a ceRNA for miRNAs. The RIP assay confirmed that circCABIN1 can immediately work together with Argonaute-2 (Ago2), a core element of the RNA-induced silencing complicated (Fig. 5A). A luciferase reporter gene with a circCABIN1 fragment was constructed and inserted. Subsequently, knockdown and overexpression of endogenous circCABIN1 expression additional decreased and elevated luciferase exercise, respectively (Fig. 5B). These outcomes recommend that circCABIN1 would possibly function a binding platform for Ago2 and miRNAs.
circCABIN1 acted as a sponge of miR-637 in GBM. A RIP assay verified AGO2 binding with circCABIN1. B A luciferase reporter assay was carried out to measure the luciferase exercise of p-luc circASAP1 in HEK-293 T cells cotransfected with the circCABIN1KD or circCABIN1OE. C The venn diagram confirmed that 9 miRNAs had been modified collectively in three teams. D Pull down and qRT-PCR assay verified 9 miRNA binding with circCABIN1 probe. E RIP assay verified miR-637 binding with AGO2. F Schematic diagram of the circCABIN1 and miR-637 binding websites and luciferase reporter assay verified circCABIN1 binding with miR-637 mimics. G The co-localization of circCABIN1 (purple) and exogenous / endogenous miR-637 (inexperienced) in LN229 cells utilizing fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. H The expression of miR-637 in GBM cells had been analyzed by qRT-PCR after knockdown or overexpression of circCABIN1. I The expression of miR-637 in TMZ-resistant and adherent cells by qRT-PCR. J The expression of miR-637 in relapsed or non-relapsed sufferers by fluorescence confocal and qRT-PCR. Okay Pearson correlation evaluation of circCABIN1 and miR-637 (p = 0.0022). L Kaplan–Meier evaluation of OS within the excessive and low miR-637 teams in CGGA (p = 0.00011). M Fluorescence photos confirmed the expression of CD133 (purple) and CD44 (inexperienced) of mind frozen part from orthotopic GBM xenograft mice in indicated teams. Nuclei had been counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. N-P Western blot, limiting dilution evaluation and tumorsphere formation assays detected the stem cell properties of cells transfected with management vector, miR-637 mimics alone or miR-637 mimics plus circCABIN1OE. Q-R GBM cells administrated with management vector, miR-637 mimics alone or miR-637 mimics plus circCABIN1OE had been subjected to FACS and CCK-8 assays. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001
To analyze novel downstream molecules, three bioinformatics databases, miRanda, RNAhybrid and CircInteractome had been used as instruments to foretell the candidate goal miRNAs probably binding to the circCABIN1 sequence (Fig. 5C). For a circRNA pulldown assay, a devoted biotinylated circCABIN1 probe was used, and circCABIN1-related RNAs had been purified previous to qRT–PCR. In contrast with management group samples, samples pulled down with the circCABIN1-specific probe confirmed notable enrichment of miR-637 (Fig. 5D). Subsequently, an anti-AGO2 RIP assay was carried out. In contrast with IgG, the anti-AGO2 antibody effectively pulled down miR-637 and circCABIN1; moreover, the quantity of immunoprecipitated circCABIN1 was considerably greater within the miR-637-overexpressing samples than within the NC samples (Fig. 5E). Moreover, bioinformatic evaluation confirmed that circCABIN1 accommodates two sequences complementary to the miR-637 seed areas. The luciferase reporter assay confirmed that solely the miR-637 mimic markedly suppressed psiCHECK2-circCABIN1 luciferase exercise, whereas luciferase exercise was not considerably modified when the miR-637 binding websites had been mutated (Fig. 5F). Furthermore, FISH indicated that miR-637 colocalized with each endogenous and exogenous circCABIN1 in GBM cells (Fig. 5G). Typically, these outcomes reveal that circCABIN1 bodily interacts with miR-637 in GBM cells. Knockdown or overexpression of circCABIN1 resulted in up- or downregulation of miR-637, respectively, in GBM cells (Fig. 5H). Notably, miR-637 expression was extra considerably decreased in TMZ-resistant GBM cells than within the corresponding parental cells, in tumorspheres than in non-spheroid cells, and in GSCs than in non-GSCs (Fig. 5Iand Extra file 1: Fig. S4A, B). Subsequently, we evaluated the expression degree of miR-637 in glioma tissues. miR-637 was downregulated in relapsed glioma tissues in contrast with non-relapsed glioma tissues (Fig. 5J). As well as, a unfavourable correlation between circCABIN1 and miR-637 expression was recognized (r = -− 0.2102, P = 0.0022, Fig. 5Okay). Furthermore, within the CGGA database, sufferers with greater expression ranges of miR-637 tended to have longer survival occasions (Fig. 5L). Sponge lentivirus for miR-637 knockdown elevated the proportion of CD44+CD133+ GSCs in GBM tumor-bearing mice (Fig. 5M).
To additional examine whether or not the binding of miR-637 and circCABIN1 regulates the capabilities of most cancers cells, we co-transfected GBM02 and LN229 cells with the circCABIN1 overexpression vector and miR-637 mimic. The outcomes of the limiting dilution, colony formation and tumorsphere formation assays revealed that the miR-637 mimic considerably reversed the enhancement of stem cell properties induced by circCABIN1 overexpression (Fig. 5N–P and Extra file 1: Fig. S4C). Furthermore, the miR-637 mimic accelerated TMZ-induced apoptosis, whereas mixed circCABINOE partially inhibited apoptosis in LN229/TMZ-R3rd and GBM02/TMZ-R3rd cells (Fig. 5Q, R). Taken collectively, these findings point out that circCABIN1 knockdown reduces the malignancy of GBM cells by concentrating on miR-637.
Olfactomedin-like 3 (OLFML3) is a downstream goal of the circCABIN1/miR-637 signaling axis
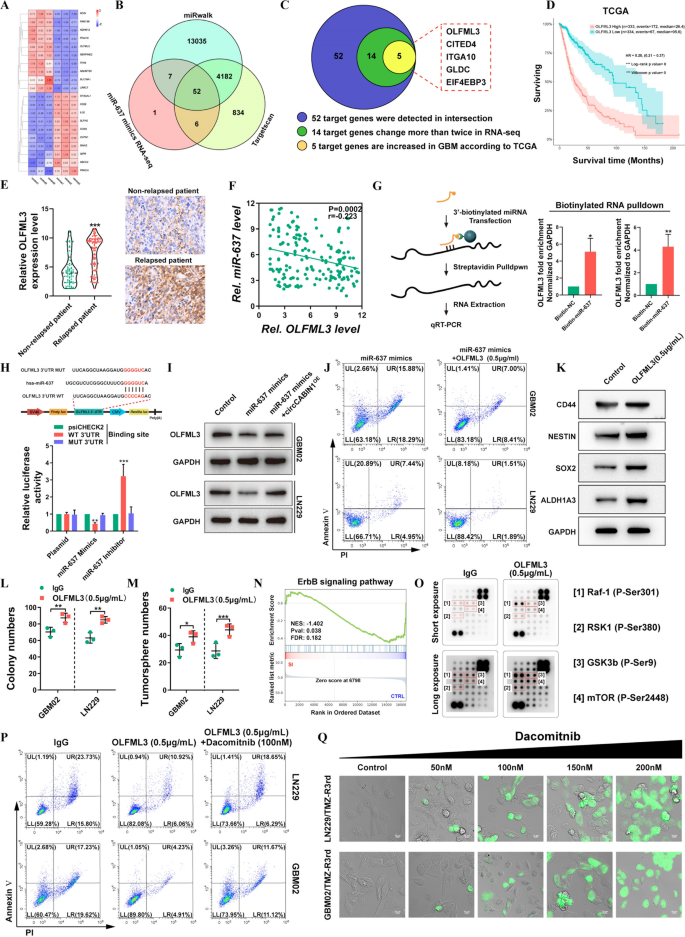
To find out the downstream goal genes of the circCABIN1/miR-637 signaling axis, RNA-seq mixed with bioinformatic evaluation utilizing TargetScan and miRWalk was carried out to investigate the downstream targets of miR-637 (Fig. 6A, B). The info revealed 52 doable genes focused by miR-637. After filtering out differentially expressed mRNAs with an expression fold change of lower than two within the RNA-seq knowledge and genes whose expression was not elevated in GBM tumor tissues in contrast with the corresponding regular tissues within the TCGA database, EIF4EP3, GLDC, ITGA10, CITED4 and OLFML3 had been chosen for additional evaluation (Fig. 6C). Survival evaluation in TGCA confirmed {that a} excessive degree of solely OLFML3 was correlated with poor prognosis in GBM sufferers (Fig. 6D and Extra file 1: Fig. S5A). Related outcomes had been noticed within the CGGA, Gravendeel and Rembrandt databases (Extra file 1: Fig. S5B). The upregulation of OLFML3 in GBM was verified within the GSE4290, GSE50161, GSE59612 and GSE11260 datasets (Extra file 1: Fig. S5C). Furthermore, OLFML3 was extremely expressed in glioma sufferers with relapse in contrast with glioma sufferers with out relapse (Fig. 6E). Correlation evaluation confirmed that the expression degree of OLFML3 in glioma tissues was negatively correlated with that of miR-637 (Fig. 6F).
OLFML3 was a downstream goal of the circCABIN1/miR-637 signalling axis. A-C 5 doable goal genes had been screened by means of RNA-seq, miRwalk, Targetscan and TCGA database. Warmth map was carried out to investigate the modified genes after transfected with miR-637 mimics (A). The venn diagram confirmed that 52 genes had been modified collectively in three teams (B). Schematic illustration of genes considerably elevated in GBM (C). D Kaplan–Meier evaluation of OS within the excessive and low OLFML3 teams in TCGA. (p < 0.001). E The expression of OLFML3 in relapsed or non-relapsed affected person and consultant photos of IHC in GBM sections of indicated teams. F Pearson correlation evaluation of OLFML3 and miR-637 (p = 0.0002). G Pull down and qRT-PCR assay verified miR-637 binding with OLFML3 mRNA. H Schematic diagram of the OLFML3 mRNA and miR-637 binding websites and luciferase reporter assay verified OLFML3 mRNA binding with miR-637. I The expression of OLFML3 after transfected with miR-637 mimics alone or miR-637 mimics plus circCABIN1OE had been analyzed by western blot in LN229 cells. J GBM cells administrated with miR-637 mimics alone or miR-637 mimics plus OLFML3 recombinant protein (0.5 μg/mL) had been subjected to FACS to detected apoptosis. Okay-M Western blot, colony formation and tumorsphere formation assays detected the stem cell properties after handled with OLFML3 recombinant protein (0.5 μg/mL). N GSEA evaluation confirmed that differential genes had been primarily enriched in ErbB sign pathway (p = 0.038). O Protein array assay detected ErbB-related signalings after OLFML3 recombinant protein remedy (0.5 μg/mL). P GBM cells administrated with OLFML3 recombinant protein (0.5 μg/mL) alone or OLFML3 recombinant protein plus Dacomitnib (100 nM) had been subjected to FACS to detected apoptosis. Q TMZ-resistance cells handled with dacomitnib with focus gradient, and apoptosis was detected by caspase3/7 experiment. Scale bar, 10 μm. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001
To acquire extra direct proof for the interplay of miR-637 with OLFML3 mRNA, we carried out a miRNA pulldown assay. OLFML3 mRNA was considerably enriched within the miR-637 mimics precipitate relative to the miR-NC precipitate (Fig. 6G). The miR-637 mimic considerably decreased and the miR-637 inhibitor considerably elevated the luciferase exercise in cells expressing the WT plasmid, however these results weren’t noticed in cells expressing the mutant plasmid (Fig. 6H). To additional make clear the regulatory function of circCABIN1 within the miR-637/OLFML3 axis, we overexpressed miR-637 in GBM02 and LN229 cells within the presence or absence of circCABIN1OE. miR-637 overexpression diminished OLFML3 expression, whereas transfection with the circCABIN1OE assemble abolished this impact (Fig. 6I). Additional research confirmed that the recombinant OLFML3 protein neutralized the flexibility of the miR-637 mimic to reinforce TMZ sensitivity (Fig. 6J). To make clear the mechanism of OLFML3-mediated TMZ resistance, we carried out RNA-seq to check the gene profiles of LN229 cells with excessive and low OLFML3 expression. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment evaluation confirmed that the differentially expressed mRNAs in OLFML3Excessive in contrast with OLFML3Low LN229 cells had been enriched in gene units associated to most cancers stem cell (CSC) upkeep, in line with the selling function of circCABIN1 in GSCs (Extra file 1: Fig. S5D). We searched the CGGA database to test the correlations between the expression of OLFML3 and that of those key stemness molecules, and the outcomes revealed optimistic correlations between OLFML3 and CD44, SOX2, Nestin, ALDH1A3 (Extra file 1: Fig. S5E). Subsequently, the expression ranges of GSC marker genes, together with CD44, SOX2, Nestin and ALDH1A3, had been examined and located to be markedly elevated after remedy with recombinant OLFML3 protein (Fig. 6Okay). Moreover, overexpression of OLFML3 promoted colony formation (Fig. 6L, M and Extra file 1: Fig. S5F). Nonetheless, the mechanism of OLFML3 in GSC upkeep stays unclear.
GSEA indicated that the differentially expressed genes induced by OLFML3 knockdown had been enriched within the ErbB signaling pathway (Fig. 6N). Given the essential function of the ErbB signaling pathway within the growth of GBM, we investigated whether or not OLFML3 can modulate the ErbB signaling pathway. ErbB-related signaling was analyzed utilizing a protein array after remedy with recombinant OLFML3 protein. The array contained 18 site-specific and phospho-specific antibodies. Within the array, the alerts, together with these for phospho-Raf-1 (Ser301), phospho-RSK1 (Ser380), phospho-GSK-3β (Ser9) and phospho-mTOR (Ser2448), had been markedly activated by remedy with OLFML3 (Fig. 6O). Earlier research confirmed that the activation of those pathways is said to self-renewal upkeep of GSCs and drug resistance [25,26,27]. To discover whether or not the ErbB pathway mediates the perform of OLFML3 in TMZ resistance, we used dacomitinib, an irreversible pan-ErbB inhibitor. Pharmacological inhibition of ErbB with dacomitinib blocked the impact of OLFML3 on TMZ resistance (Fig. 6P). Unsurprisingly, OLFML3 was extremely expressed in LN229/TMZ-R3rd and GBM02/TMZ-R3rd cells (Extra file 1: Fig. S5G). Dacomitinib promoted apoptosis in TMZ-resistant cells in a dose-dependent method (Fig. 6Q). These outcomes indicated that OLFML3 promote TMZ resistance in an ErbB pathway-dependent method.
Focused supply of chemically modified multi-siRNAs by engineered ANG-exo sensitizes GBM cells to TMZ
Our findings point out that EIF4A3-induced circCABIN1 capabilities in an vital underlying mechanism in TMZ resistance by means of modulation of the miR-637/OLFML3 signaling pathway, which may present pivotal potential therapeutic targets for GBM. Contemplating these findings, we sought to concurrently intervene with the expression and performance of those two genes (circCABIN1 and OLFML3). Then, we designed a multi-siRNA containing the sequences similar to si-circCABIN1 and si-OLFML3; the sequence “AUUGCAC” was used as a linker to attach si-circCABIN1 and si-OLFML3. The multi-siRNA was modified with ldl cholesterol to extend stability and matched to cy3 teams for tracing. Outcomes confirmed that this multi-siRNA may concurrently suppress circCABIN1 and OLFML3 expression (Extra file 1: Fig. S6A, B).
Chemical modification successfully improves the steadiness of siRNAs in blood, however the lack of concentrating on limits its software. Focused supply of siRNAs loaded in engineered exosomes was thus our first selection. Exosomes have change into the main target of drug supply analysis and are characterised by excessive biosafety, ease of preparation, and weak immunogenicity. Notably, angiopep-2 (ANG) is a promising ligand that binds particularly to the lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) receptor and might enhance the BBB transport effectivity of exosomes for drug supply into the mind [28, 29]. Due to this fact, we designed a focused supply scheme primarily based on engineered ANG-exo and the chemically modified multi-siRNA. We constructed an expression vector containing a fusion of ANG and LAMP2; LAMP2 carried the integrin-targeting ANG peptide to the exosomal membrane floor, permitting the exosomes to focus on GBM cells and cross the BBB (Fig. 7A).
Focused supply of chemically modifed multi-siRNAs by engineered ANG-exo sensitized GBM cells to temozolomide. A Schematic picture. Strategy of ANG-exo development, isolation, multi-siRNA loading, animal tail vein injection. B Schematic picture of the BBB mannequin in-vitro. C Immunofluorescence photos detected unmod-exo/ANG-exo uptake into LN229 cells after passing by means of a bEnd.3 monolayer. Scale bar, 10 μm. D In vivo florescence imaging of Orthotopic GBM xenograft mice at 0 h, 3 h, 6 h and 9 h time level after intravenous administration of unmod-exo / ANG-exo. E Left, ex vivo fluorescence photos of Mind, Liver, Spleen, Lung, Coronary heart, Kidney and frozen part of mind from mice sacrificed at 9 h post-injection. Proper, fluorescence quantitative evaluation of ex vivo organs of tumor-bearing mice after intravenous injection. F Schematic picture. Time line of nude mice receiving mixture remedy. G-J Confirm the impact of mixed remedy in vivo. IVIS detects bioluminescence alerts. Quantification of bioluminescent imaging sign intensities (H), quantification of tumor dimension (I), and survival charge (J) of mice in indicated teams. Okay Consultant photos of TUNEL assay and cleaved Caspase-3, ALDH1A3 and OLFML3 IHC in GBM sections of indicated teams. Scale bar, 20 μm. Outcomes are offered as imply ± SD. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001
On this examine, multi-siRNAs had been loaded into exosomes by electroporation. The sizes of exosomes had been measured to be between 100 and 150 nm, and the encapsulation of the multi-siRNA didn’t have a major impact on the dimensions of the exosomes (Extra file 1: Fig. S6C). The morphology of unmodified exosomes (unmod-exo) and multi-siRNA-loaded exosomes (multi-siRNA-exo) was evaluated by TEM imaging. There have been no vital variations between unmod-exo and multi-siRNA-exo (Extra file 1: Fig. S6D). Then, an in vitro BBB mannequin was established to check the transcytosis and BBB penetration skill of those exosomes (Fig. 7B). In consequence, unmod-exo confirmed minimal penetration, as slight fluorescence was noticed in LN229 cells within the decrease chamber. ANG modification enhanced the penetration of exosomes, whereas ANG-exo confirmed greater uptake by cells within the decrease chamber (Fig. 7C). As proven in Extra file 1: Fig. S6E, ANG-multi-siRNA-exo considerably decreased the expression ranges of circCABN1 and OLFML3. The impact of ANG-multi-siRNA-exo on TMZ sensitization was additional confirmed each in TMZ-resistant and parental cells by CCK8 and apoptosis assays (Extra file 1: Fig. S6F).
To judge the brain-targeting supply effectivity of ANG-exo by systemic injection, DiD-labeled exosomes had been injected into mice by means of the tail vein. As proven in Fig. 7D, the fluorescence depth in mind areas was considerably greater for ANG-exo than for unmod-exo at completely different time factors (3, 6, 9 h) after injection. An efficient tumor concentrating on impact focuses the drug on the tumor website, will increase the efficacy of the drug and reduces the antagonistic results on regular organs. First, we investigated whether or not the ANG-exo delivered the focused drug to the tumor. Fluorescence amassed primarily within the tumor after intravenous injection of ANG-exo. Extra importantly, ANG-exo had been distributed primarily inside the tumor boundary, suggesting their superior tumor concentrating on skill (Fig. 7E).
The in vivo antitumor results of Ang-multi-siRNA-exo had been evaluated in mice bearing orthotopic GBM tumors. Tumors had been allowed to develop for 14 days, and had been then handled with saline, TMZ, Ang-multi-siRNA-exo, or Ang-multi-siRNA-exo + TMZ. Luciferase bioluminescence alerts within the tumors had been then evaluated (Fig. 7F). Quantification of tumor bioluminescence revealed considerably higher inhibition of tumor progress by Ang-multi-siRNA-exo mixed with TMZ than by TMZ alone. Furthermore, notably, Ang-multi-siRNA-exo monotherapy had a slight remedy impact on GBM tumors. Importantly, mice administered each ANG-multi-siRNA-exo and TMZ survived considerably longer than these handled with ANG-multi-siRNA-exo or TMZ alone (Fig. 7G–J). Cleaved-Caspase3 staining and TUNEL within the orthotopic GBM mouse mannequin confirmed vital cell dying in mice receiving the mixture remedy. Moreover, immunohistochemical staining indicated that engineered ANG-exo that delivered the cholesterol-modified multi-siRNA successfully inhibited the expression of OLFML3. The expression degree of ALDH1A3 within the mixture remedy group was considerably decrease than that within the TMZ group, suggesting that ANG-exo-mediated knockdown of circCABIN1 and OLFML3 reduces the technology and self-renewal of GSCs (Fig. 7Okay).
Security has been a serious concern in the usage of nanocarriers for drug supply. To eradicate the affect of immunodeficiency, we carried out related experiments in BALB/c mice. In contrast with the saline group, the Ang-multi-siRNA-exo group confirmed no apparent will increase within the serum ranges of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Furthermore, the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr) ranges didn’t differ considerably among the many teams. As well as, H&E staining of main organs confirmed no injury (Extra file 1: Fig. S6G–I). These outcomes demonstrated the improved security of ANG-exo-mediated multi-siRNA supply for GBM remedy.