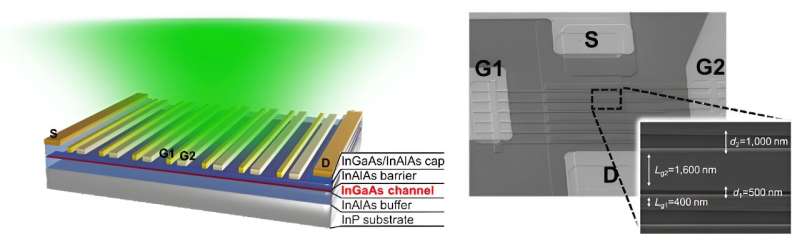
A analysis group from Tohoku College and RIKEN has developed a high-speed, high-sensitivity terahertz-wave detector working at room temperature, paving the best way for developments within the improvement of subsequent technology 6G/7G expertise.
Particulars of their breakthrough had been printed within the journal Nanophotonics on November 9, 2023.
The enhancement of present communications speeds will depend on terahertz (THz) waves. THz waves are electromagnetic waves inside the THz vary, which falls between the microwave and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, usually spanning frequencies from 300 gigahertz to three THz.
Nonetheless, the quick and delicate detection of THz waves at room temperature is difficult for standard electronic- or photonic-based semiconductor units.
That is the place two-dimensional plasmons are available in. In a semiconductor field-effect transistor, there’s a two-dimensional electron channel the place a collective charge-density quanta, i.e., two-dimensional plasmons, exist. These plasmons are excited states of electrons exhibiting fluid-like behaviors. Their nonlinear rectification results, originating from these fluid-like behaviors, and their speedy response (not constrained by electron transit time) make them a promising means to detect THz waves at room temperature.
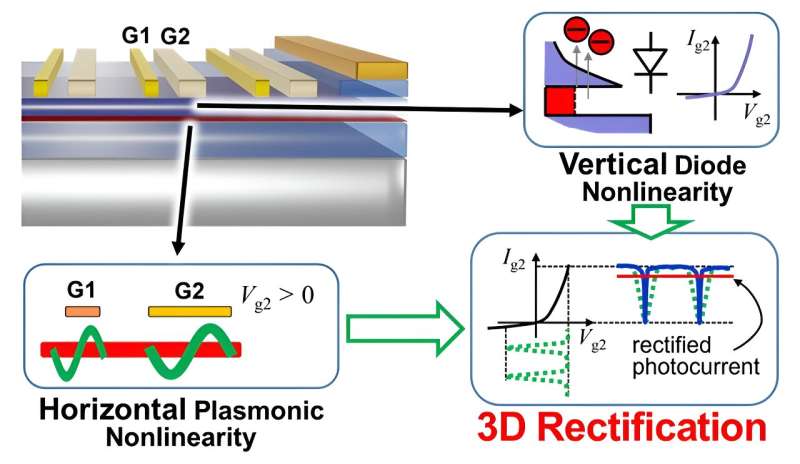
“We found a 3D plasmonic rectification impact in THz wave detector,” says Akira Satou, chief of the analysis group and affiliate professor at Tohoku College’s Analysis Institute for Electrical Communication (RIEC). “The detector was primarily based on an indium-phosphide high-electron mobility transistor and it enabled us to boost the detection sensitivity multiple order of magnitude greater than standard detectors primarily based on 2D plasmons.”
The brand new detection technique mixed the standard vertical hydrodynamic nonlinear rectification impact of 2D plasmons with the addition of a vertical diode-current nonlinearity.
It additionally dramatically resolved the waveform distortion attributable to a number of reflections of high-speed modulated alerts—a important challenge in standard detectors primarily based on 2D plasmons.
Main the group alongside Satou was Specifically Appointed Professor Tetsuya Suemitsu from Tohoku College’s New Trade Creation Hatchery Heart and Hiroaki Minamide from RIKEN Heart for Superior Photonics.
“Our new detection mechanism overcomes a lot of the bottlenecks in standard terahertz-wave detectors,” provides Satou. “Trying forward, we hope to construct on our achievement by enhancing the system efficiency.”
Extra data:
Akira Satou et al, Gate-readout and a 3D rectification impact for large responsivity enhancement of uneven dual-grating-gate plasmonic terahertz detectors, Nanophotonics (2023). DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0256
Supplied by
Tohoku College
Quotation:
Excessive-sensitivity terahertz detection by 2D plasmons in transistors (2023, December 27)
retrieved 27 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-high-sensitivity-terahertz-Second-plasmons-transistors.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


