
The European Union’s AI Act took a giant step towards changing into regulation right this moment when policymakers efficiently hammered out guidelines for the landmark regulation. The AI Act nonetheless requires votes from Parliament and the European Council earlier than changing into regulation, after which it will go into impact in 12 to 24 months.
The AI Act has been within the works since 2018, the identical 12 months that the EU’s Common Knowledge Safety Regulation (GDPR) went into impact, as European lawmakers search to guard the continent’s residents from the destructive impacts of synthetic intelligence.
As we’ve beforehand reported, the brand new regulation would create a standard regulatory and authorized framework for using AI know-how, together with the way it’s developed, what firms can use it for, and the implications of failing to stick to necessities.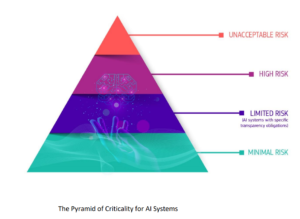
Earlier drafts of the regulation categorize AI by use instances in a four-level pyramid. On the backside are methods deemed a minimal threat which might be free from regulation. This would come with issues like search engines like google and yahoo. Above that may be methods with restricted dangers, reminiscent of chatbots, which might be topic to sure transparency necessities.
Organizations would want to achieve approval earlier than implementing AI within the high-risk class, which would come with issues reminiscent of self-driving automobiles, credit score scoring, regulation enforcement use instances, and security elements of merchandise like robot-assisted surgical procedure. The federal government would set minimal security requirements for these methods, and the federal government would preserve a database of all high-risk methods.
The EU Act would utterly ban sure AI makes use of deemed to have an unacceptable threat, reminiscent of real-time biometric identification methods, social scoring methods, and functions designed to control the habits or individuals or “particular susceptible teams.
The launch of ChatGPT one 12 months in the past and the rise of generative AI in 2023 has solidified regulators’ want to protect individuals from the dangerous features of AI. In line with an article within the New York Instances, EU policymakers tailored the AI Act to account for the emergence of GenAI by including necessities for big AI mannequin creators “to reveal details about how their methods work and to guage for ‘systemic threat.’”
In line with the Instances, policymakers lastly agreed on AI Act guidelines after three days of negotiations, together with a marathon 22-hour session on Wednesday. It’s not clear how quickly a draft of the finalized AI Act regulation can be accessible to the general public. If it’s accepted within the European Union’s legislative our bodies, it will possible go into power one to 2 years later.
One of many areas of the brand new regulation that had but to be hammered out earlier than this week’s rulemaking session included penalties. Violations of the GDPR can carry penalties equal to as much as 4% of an organization’s annual income or €20 million, whichever is larger.
Associated Gadgets:
Europe Strikes Ahead with AI Regulation
Europe’s New AI Act Places Ethics Within the Highlight
Europe’s AI Act Would Regulate Tech Globally


