The recognition of wearable biosensors has been growing with the event of smartphones and different cellular units, providing the outstanding functionality of steady and real-time assortment of physiological information, thereby offering worthwhile insights into people’ efficiency and well being [1, 2]. These biosensors, which incorporate organic recognition components into their design, maintain nice potential in managing continual situations and supporting distant monitoring. This functionality was not potential earlier than with conventional analytical strategies. Regardless of their excessive sensitivity and complexity, lab-based approaches typically lack real-time and point-of-care capabilities. For example, mass spectrometry [3, 4] can detect a variety of biomarkers concurrently. Nevertheless, its reliance on laboratories, educated technicians, excessive price, and time-consuming procedures makes it impractical from a decentralized medical perspective. Equally, ELISA [5, 6], which is extensively utilized in laboratory environments for medical analysis of biochemical species, suffers from prolonged evaluation time, restricted usability outdoors conventional diagnostic laboratories, reliance on cumbersome analytical devices [7], and the requirement for bigger pattern sizes [8].
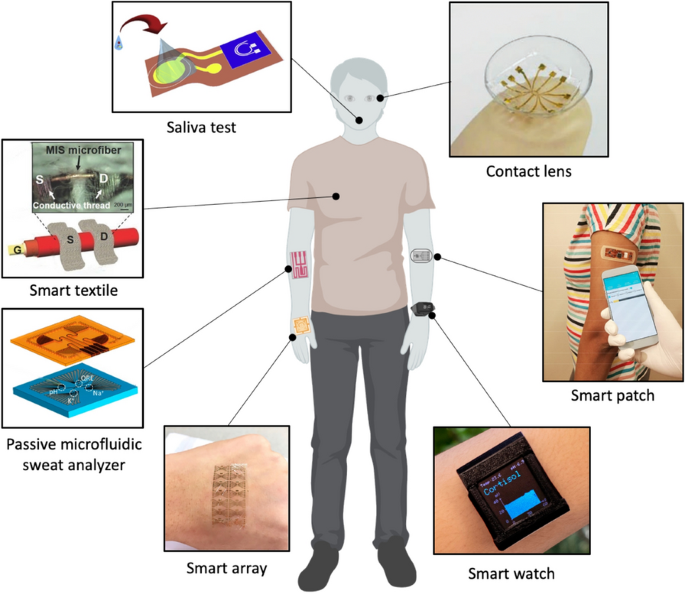
Thus far, appreciable efforts have been devoted to the event of next-generation wearable biosensors. Early research specializing in the non-invasive and dynamic measurement of biomarkers accessible in biofluids (e.g. interstitial fluid, saliva, tear, sweat). These wearable biosensors have been demonstrated for analytes collected from head-to-toe software websites, Fig. 1 [9]. Approaches for detecting biomolecules are for isntance electrochemical, micro-cantilever, fluorescence, colorimetric, chemoresistive and floor plasmon resonance (SPR) methods, which have their respective benefits and drawbacks [10, 11]. These sensors supply excessive specificity and might detect substances at low focus, making them appropriate for early detection and real-time evaluation. Electrochemical primarily based immunosensors, together with amperometric, impedimetric and potentiometric, have demonstrated novel and distinctive detection platform [12, 13]. Amongst these sensors, FETs have gained important curiosity as a result of their benefits reminiscent of fast pattern screening, label-free detection, vast dynamic vary, and cost-effective fabrication processes, significantly on versatile substrates surpassing the capabilities of present strategies [14, 15].
Wearable FET biosensors for diagnostics and well being monitoring functions. Clockwise from prime: Contact-lens biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [16] Copyright 2019 Wiley); Good patch biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [1] Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society); Good Watch biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [17] Copyright 2022 Science); Good array biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [18] Copyright 2020 Elsevier); Passive Microfludic Sweat Analyzer biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [19] Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society); Good textile biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [20] Copyright 2016 Wiley); Saliva check biosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [21] Copyright 2019 Elsevier)
Classical subject impact transistors (FET) have been the spine of recent digital units with gate-controlled present flowing by semiconducting channels. State-of-the-art micro/nanofabrication applied sciences make it potential to jam pack billions of transistors in a chip with measurement smaller than a human finger. This diploma of miniaturization has led to a considerable enhance in processing energy, however on the similar time a discount in energy consumption, and manufacturing price. A couple of excellent opinions exist on wearable FET sensors in numerous features. Li et al. [22] reviewed the current advances in wearable units primarily based on versatile field-effect transistors together with sensors for stress, temperature, chemical, and organic analytes. Chen et al. [23] offered important analysis on multidisciplinary technical particulars, together with sensing mechanism in detecting biomolecules, response sign kind, sensing efficiency optimization, and the combination technique. Dai et al. [24] assessment the current advances of field-effect transistor sensors primarily based on 2D supplies, from the fabric, working rules, fabrication applied sciences, proof-of-concept functions, and prototypes, to the challenges and alternatives for his or her commercialization.
The current assessment offers a complete overview on FET-based wearable biosensors from varied views together with sensing mechanisms, classification of system in accordance with gating mode, supplies, geometry, recognition components and sampling. Subsequent, we describe fabrication and floor modification methods of FET biosensors. Moreover, we define the varied rules of probe that may selectively detect the particular organic components by way of enzyme, antibody/nanobody, aptamer and ion-selective membrane. Moreover, we talk about physiological relevance of monitoring key biomarkers with wearable biosensors. Lastly, we critically assessment and talk about challenges that vastly have an effect on the long run growth of wearable FET biosensor.
Construction and dealing precept of FETs
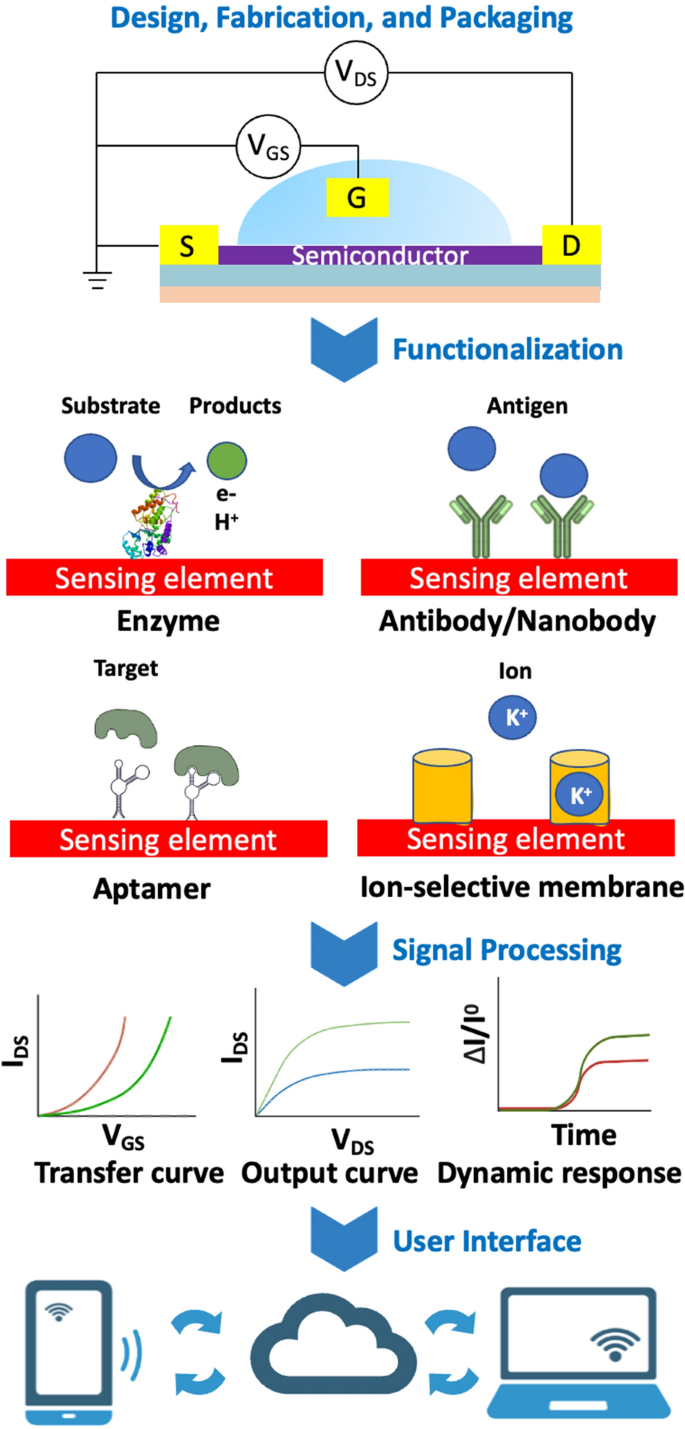
Discipline-effect transistor-based sensors (FET) are analytical units that may selectively detect the focus of a organic molecules. FET sensors sometimes comprise: a dielectric insulating layer, a semiconductor layer, and three electrodes (drain, supply, and gate), Fig. 2.
Illustration of a organic and chemical FET sensor platform. From prime to backside: Units are fabricated and packaged by micromachining processes; Sensing surfaces are functionalized with probes to seize biomarkers; Charged biomarkers causes potential modifications in sensing channels, then varied electrical traits are measured; Analog indicators are collected, reworked to digitals then logged to “cloud” information companies for distant accesses
The circulation of present (IDS) between drain and supply electrodes of a FET is regulated by a variable voltage (VGS) utilized between the gate and supply electrodes [22]. This utilized voltage prompts a redistribution of the electrical subject throughout the dielectric layer, resulting in the creation of a dual-electric layer. Consequently, cost carriers can transfer by the semiconductor layer near the interface adjoining to the dielectric layer [25, 26]. The conductive behaviors displayed by these cost carriers range relying on the connection in power ranges between the semiconductor and the drain/supply electrodes. Extra particularly, both holes (h+) or electrons (e−) can act as cost carriers within the semiconductor layer. In an n-type FET, when a optimistic voltage is utilized to the gate, a channel is generated, permitting electrons to journey from the supply to the drain, i.e., conduction [27]. Conversely, if a unfavorable gate voltage is utilized, the n-type channel is sealed off, stopping conduction by the carriers. With a p-type FET, the situation unfolds in reverse, whereby a optimistic (unfavorable) gate voltage deactivates (prompts) the transistor.
Charged molecules that bind to the lively layer, whether or not that be a gate electrode or a semiconductor channel, could cause the costs throughout the semiconductor materials to redistribute, thereby modifying the conductance of the FET channel. When the goal analyte interacts with the functionalized sensing layer of the FET system—sometimes both a semiconducting or a dielectric layer—it alters {the electrical} traits of this lively layer on the molecular degree. Consequently, the distribution of cost carriers inside this layer modifications, leading to fluctuations within the output present of the FET. These fluctuations which will be measured as electrical indicators, can both point out the presence of the goal analyte or modifications of its focus [22].
The Debye screening size, additionally referred to as Debye size (λD), is a bodily distance the place the charged analyte is electrically screened by the ions within the answer, strongly influences the sensitivity of immunosensor or electrochemical units in excessive ionic power media. The Debye size (λD) in an electrolyte is given as [28]:
$$lambda_{D} , = ,sqrt {frac{{varepsilon_{0} varepsilon_{r} K_{b} T}}{{2N_{A} q^{2} I}}} ,$$
The place ε0 corresponds to the vacuum permittivity; εr is the relative permittivity of the medium; okB is the Boltzmann fixed; T is absolutely the temperature; NA is the Avogadro quantity; q is the cost on an electron; and I is the ionic power of the answer. In keeping with this Debye principle, a rise in ion focus reduces the Debye size as a result of cost screening by counter-ions, reducing the sensitivity of the system.
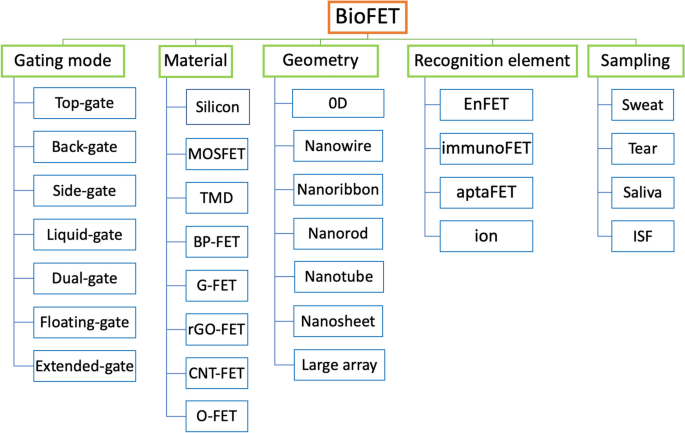
Classification of system
Determine 3 demonstrates totally different classification techniques for FET biosensors in accordance with structure, materials, geometry, recognition and sampling.
Structure
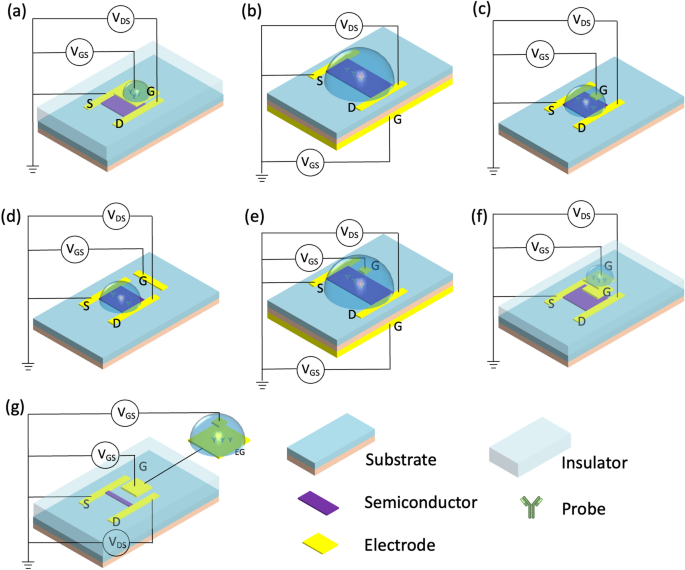
This classification technique divides the gate structure of FET biosensors into single gating (top-gate, back-gate, liquid-gate, side-gate) or complex-gating (dual-gate, floating-gate, extended-gate), Fig. 4. Moreover, FETs will be divided into top-contact and bottom-contact sorts in accordance with the contact positions of the semiconductor and supply/drain electrodes. Supply/drain electrodes are deposited on an insulating layer within the top-contact kind, whereas the supply/drain electrodes are positioned above semiconductor layers within the bottom-contact kind [29]. Typically, top-contact buildings have a decrease contact resistance and the next mobility as a result of expertise used to manufacture the sensors. Nevertheless, the bottom-contact sorts are inclined to have shorter channels.
Usually, top-gate biosensors are efficient detectors as the highest gate can be used because the sensing part as a substitute of semiconductor channel, Fig. 4a. Moreover, producing top-gate biosensors is comparatively easy, requiring solely contact lithography patterning and metallic lift-off expertise throughout the fabrication course of [30]. For example, Chu et al. [31] developed an electric-double-layer FET that may straight detect varied proteins in physiological excessive ionic power options. The gold prime gate on this system is separated from the lively channel. The probe is immobilized on the gate, leading to delicate detection of the analyte with a focus as little as 1 fM.
In comparison with top-gate configuration, back-gate biosensors typically have a bigger sensing space, Fig. 4b. In this sort of sensor, the silicon substrate is usually employed because the again gate, and silicon dioxide serves because the dielectric layer for the gate [30]. Guo et al. [32] developed a MoS2 FET, using a primary back-gate configuration straight fabricated onto a SiO2/Si substrate by the usual nanofabrication course of. This high-performance MoS2 transistor is massive in space and ultrathin, making it comparatively simple to combine right into a mushy, sensible contact lens the place photodetectors, glucose sensors, and temperature sensors monitor the tear fluid.
The liquid-gate (additionally referred to as solution-gate) is the most typical kind of FET because it presents the most effective simulation of the human physiological setting for binding biomolecules, Fig. 4c. When the FET operates in an electrolyte answer, reference electrodes are immersed in an answer, which offers bias voltage by a liquid gate. An electrical subject establishes on the interface between the electrolytes and the semiconductor. In consequence, an electrical double layer (EDL) kinds, and modulates the potential and conductivity of the channel [24]. This EDL on the semiconductor interface not solely makes the units extremely delicate to a spread of analytes, however it additionally permits for operation at low gate potentials. Wang et al. [17] developed a wearable liquid gate In2O3-FET, which depends on aptamers to measure cortisol degree in sweat. An Ag/AgCl reference electrode on the chip is fabricated just by depositing Ag/AgCl ink, which helps linear gate-source sweep voltage biasing.
One other FET structure is aspect gate (or co-planar gate). On this kind, the gate is positioned in the identical plan because the channel layer (Fig. 4d). On this case, the aspect gate can concurrently bias a number of close by semiconductor channels for multi-functional biosensing. For example, simultaneous monitoring of temperature, pH, and neurotransmitters (dopamine and serotonin) was achieved in a multiplexed platform utilizing this structure [33].
In a dual-gate FET, two insulated gates (bottom-gate and top-gate electrodes, or bottom-gate and liquid gate electrodes) supply two totally different VGS for unbiased modulation, Fig. 4e. This configuration will increase the sensor’s response, improves signal-to-noise ratio, and reduces sign drift and hysteresis [34]. Capua et al. [35] developed a SiNW FET utilizing this configuration to detect C-reactive protein. The sensor has glorious stability, low hysteresis, nice sensitivity, and a negligible shift over time. These properties are extremely advantageous in functions, the place the biomarkers in physique fluids must be repeatedly monitored.
Floating-gate kind FET sensors are designed to work in options, and are a comparatively current growth. An extra metallic floating management gate electrode is electrically remoted between the unique top-most gate (now referred to as the management gate) and the channel, making a floating node in direct present. This floating node can retailer the cost and management the channel’s conductivity, Fig. 4f. An oxide layer surrounding the floating gate retains the electrons trapped such that the system can retailer an electrical cost for an prolonged time period without having to connect with an influence provide. Liang et al. developed a wafer-scale uniform floating-gate carbon nanotube FET system [36]. An ultrathin Y2O3 high-κ dielectric layer within the floating-gate construction will increase the sensitivity and amplifies the response of the FET, as in comparison with counterparts and not using a Y2O3 layer. The advance is attributed to a dominant chemical gate-coupling impact within the response mechanism of the sensor [36]. The theoretical LOD is as little as 6 particles/mL.
Prolonged-gate FET (EG-FET) expands the gate electrode off-chip to implement separate moist and dry environments, Fig. 4g. Solely the detector portion is immersed into the answer, whereas the transducer stays in a totally dry setting. The sensor electrode is linked to a MOSFET gate and elongated with a metallic sign line. The benefit of this setup is that almost all of {the electrical} indicators is remoted from the measurement setting, making it an easy and reliable encapsulation method. This configuration additionally minimizes environmental interference, together with light-induced drift [37]. Fabricating this system can be considerably easy, permitting post-processing steps. On this class, Yang et al. [38] developed a low-cost and versatile ITO/PET EG-FET with roll-to-roll fabrication. The prolonged gate on this system has a easy enzyme functionalization for the detection of urea.
Semiconductor supplies
Varied semiconductor supplies have been used to manufacture FET, together with silicon [35], metallic oxides [18], III-V supplies [39], transition metallic dichalcogenides [39], natural semiconductors [40], graphene [2], carbon nanotubes [41], and black phosphorous [42]. A number of standards must be thought of for choosing the semiconductor for a bioFET sensor. These embody {the electrical} and mechanical stability of the measurement setting, the sensitivity of the fabric to mild and temperature, the provision of the fabric in business portions, and the compatibility is with large-scale fabrication on versatile substrates [43]. Desk 1 offers a abstract of the potential influence of fabric properties on biosensors.
FET-based wearable units have been efficiently utilized to supplies reminiscent of graphene, carbon nanotubes, silicon, In2O3, MoS2, ZnO, zinc titanium oxide, and natural semiconductors. These supplies are suitable with substrates reminiscent of Si/SiO2, polyimide, polyester PET, poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS), polyethylenenaphthalate (PEN). When deciding on a substrate, one should take into account the processing temperature concerned within the system fabrication, together with different bodily properties of the substrate such because the glass transition temperature, flexural modulus, Younger’s modulus, optical transparency, thermal growth, and adhesion to lively supplies.
Semiconductor geometry
Nanoscale semiconductor supplies have sometimes a thickness of a single atom or maybe a number of atoms. Measuring lower than 5 nm deep, their lateral measurement can vary from sub-micrometers to centimeters [24]. Desk 2 summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of a number of the widespread nanoscale supplies.
Different classifications
One other strategy to categorize FET sensors is predicated on the substance used to acknowledge the analyte. For instance, if a FET is designed to detect an analyte by an enzymatic response, the sensor is named an enzyme-FET or an EnFET. Different classes embody ISFETs, aptaFETs, immunological FETs, and DNA-FETs. For wearable units, a number of recognition components also referred to as probes have been used to watch biomarkers in physique fluids. Lastly, wearable FET system will be categorised primarily based on the biofluid samples, reminiscent of sweat, tear, saliva, ISF. Additional particulars about recognition factor and samples will likely be mentioned in different sections of this paper.
Fabrication of semiconductor supplies
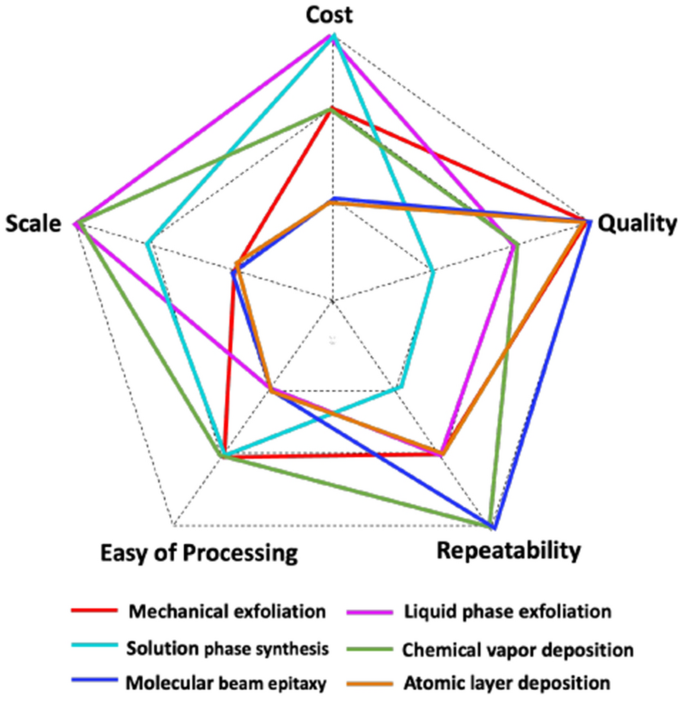
The principle perform of semiconductors in FET sensors is to facilitate the circulation of present, which critically impacts the sensitivity [43]. Varied approaches will be employed to manufacture FET sensors, together with top-down machining methods, bottom-up synthesis methods, and meeting methods. Determine 5 summarized widespread fabrication methods of skinny movies alongside 5 qualitative parameters, together with price, high quality, repeatability, scale, and ease of processing [24].
Qualitative comparability of widespread fabrication methods of skinny movies. Repaint with permission from Ref. [24].
The highest-down method is a strategy of breaking down the majority supplies into smaller, micro and nanoscale buildings. For silicon nanowire (SiNW)-FET sensors, top-down machining is nicely established with superior lithography and microfabrication methods to make microdevices in batch in a managed setting, permitting each cost-effective and simply scalable to provide massive portions [45]. Commencing with a silicon-on-isolator (SOI) substrate, the SiNW sensor construction is designated utilizing sample switch methodologies, together with electron-beam lithography, nanoimprint lithography, or sidewall switch lithography. The next etching course of encompasses reactive ion etching, moist chemical etching, or a hybrid method integrating each methods, facilitating the switch of the designed construction onto the uppermost silicon layer of the SOI substrate. Additional microfabrication methods are then employed to finalize the units with supply drain, ohmic contact institution, gate dielectric layer implementation, and passivation layer. For top-down machining of supplies apart from silicon, mechanical/liquid exfoliation is a standard approach. Mechanical exfoliation is reported to provide distinctive high quality with minimal defects by peeling-off atomically skinny layers from a bulk materials [46, 47]. Graphene, the primary 2D supplies found in a laboratory, was ready by this technique [48], merely with adhesive tapes. Nevertheless, the method is time-consuming and labour-intensive, particularly when aiming to acquire massive space of skinny flakes [45]. It is usually laborious to get uniform samples as there are many flakes with totally different variety of layers randomly dispersed on the substrates [49]. Mechanical exfoliation is without doubt one of the most used top-down methods for producing metallic oxide nanosheets with prime quality and diploma of crystallinity [50]. Lately, Zhang et al. reported a novel mechanical exfoliation course of to organize MoS2 nanoflakes with thermal remedy to enhance the scale and yield of fabric [51]. Liquid section exfoliation, however, presents another alternative to isolate and disperse skinny layers of nanomaterials from their bulk crystals in a liquid medium. The approach entails breaking down the majority crystals of the fabric into thinner layers by making use of mechanical or ultrasonic forces. The ensuing nanosheets or nanoparticles will be simply dispersed in a liquid solvent to kind a steady colloidal suspension [52]. Liquid exfoliation sometimes produces supplies with excessive yield, good high quality and slightly low price [49]. This method has been utilized to a variety of fabric together with carbon nanotube [53], graphene [54, 55], and black phosphorus [56, 57].
Backside-up synthesis entails assembling and rising supplies from atomic or molecular precursors to kind desired buildings. Following this method, SiNWs have been vertically grown on a silicon substrate utilizing varied strategies reminiscent of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [58], oxide assisted development [59] or metal-assisted chemical etching [60]. Within the case of metallic oxides, varied structural kinds reminiscent of nanoribbons, nanowires, nanorods, nanobelts, and nano skinny movies, will be created utilizing vapor-phased methods, which embody depositing chemical vapors and bodily vapors [43]. Whereas CVD synthesizes nanostructures by chemical reactions within the vapor section with the help of a noble metallic catalyst. In distinction, bodily vapor deposition (PVD) produces nanostructures by both thermal evaporation or plasma. CVD can be particularly helpful for transition metallic dichalcogenides reminiscent of MoS2 [61], as large-scale supplies will be grown on totally different substrates by CVD, and the supplies will be simply transferred to different substrates [62]. Nevertheless, this technique wants an correct management of experimental situations, so it’s nonetheless too difficult and costly for mass-production [49]. Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) is a bodily vapor deposition approach that may develop skinny movies of single crystals from varied supplies, together with gallium nitride [63], zinc oxide [64] and natural semiconductor [65]. This subtle approach presents atomic-level precision over the expansion of crystalline supplies in an ultra-high vacuum setting. Nevertheless, MBE has excessive tools and operation prices, and should face challenges in scaling up as a result of its comparatively sluggish development price [66]. Much like CVD, atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a skinny movie deposition approach counting on floor chemical reactions of gaseous precursors, however these floor reactions happen by self-saturating gas-surface response mechanisms [67]. ALD presents the capability for layer-by-layer deposition with distinctive management over movie thickness, excellent uniformity, and unparallel conformal protection on nanostructured surfaces [68], albeit on the expense of its excessive price and sluggish deposition price [69]. Resolution-phase synthesis routes, reminiscent of sol–gel and hydrothermal synthesis, will be employed to provide many metallic oxide nanostructures and skinny movies [43]. These solution-based strategies present a cheap method to create a various array of metallic oxide nanostructures with controllable properties [29].
Meeting methods are used to rearrange and place nanomaterials onto particular areas of the FET sensor. For instance, the floating-coffee-ring pushed meeting takes benefit of the self-assembly conduct of nanoparticles in evaporating liquid droplets, leading to a ring-like sample of the deposited nanoparticles [70]. Dynamic-template-assisted meniscus-guided coating is one other meeting technique the place the managed movement of a template or meniscus is used to information the deposition of supplies onto desired areas of the sensor floor [71, 72].
These fabrication methods contribute to the flexibility and performance of FET sensors, permitting for tailor-made sensor design and efficiency optimization in varied functions. You will need to observe that these methods aren’t exhaustive. Developments in nanotechnology and materials science proceed to broaden the repertoire of fabrication strategies for FET sensors.
Functionalization methods of semiconductor floor
Floor functionalization or immobilization entails attaching organic receptors onto a matrix or assist, both on the floor or inside it. This attachment can happen by bodily or chemical means, by direct or oblique methods, so long as in the end the bioreceptors are coupled to the lively layer of the sensor [73].
Whatever the particular technique used for immobilization, the approach must be easy to carry out, extremely reproducible, efficient at stopping non-specific bindings, and sturdy to excessive environmental situations [74]. Moreover, following the immobilization, the biomolecules ought to stay each simply accessible and chemically inert to the host construction. It will make sure the biosensor stays each purposeful and steady over time.
Bodily adsorption
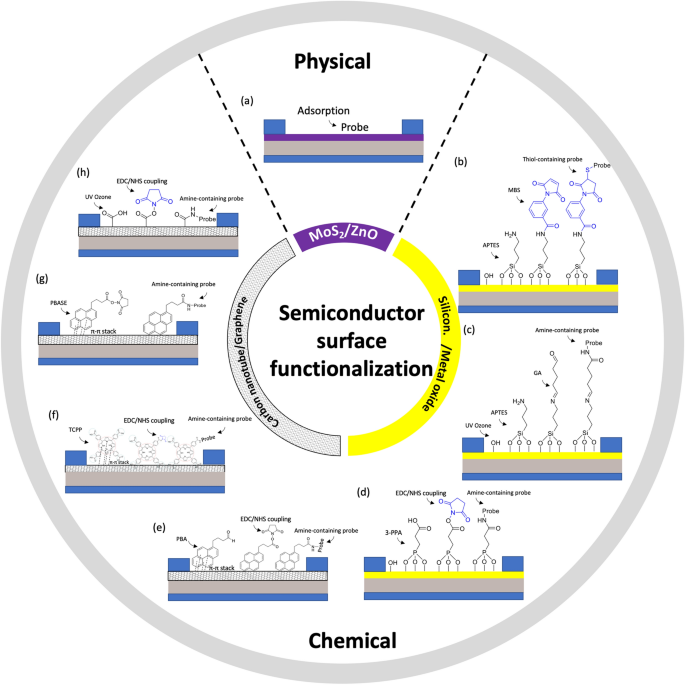
The best technique of immobilizing biomolecules on a floor is bodily adsorption (physisorption). This course of entails attaching the biomolecules to the floor utilizing weak and noncovalent binding or deposition forces, reminiscent of electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals forces, and hydrogen bonding interactions between the sensor floor and the goal analyte (Fig. 6a) [75]. Within the physisorption course of, biomolecules are sometimes immobilized on an electrode/semiconductor floor by immersing the floor into an answer containing the biomolecules and permitting them to bind to the floor throughout a hard and fast incubation interval. A minimal bulk receptor focus of 1 µM is required for a typical incubation time of 1 h to ensure most floor protection [76]. Subsequently, the floor is washed with a buffer answer to take away any unbound biomolecules [75].
Nevertheless, there are particular limitations related to physisorption. Because of the weak and noncovalent nature of the interactions, the efficiency, stability, and reusability of the sensor will be considerably affected by elements reminiscent of temperature, pH, focus, and ionic power. In consequence, this technique has not acquired in depth consideration. One main downside of immobilization by physisorption is the potential of desorption of the bioreceptors from the floor throughout measurements, resulting in decreased sensitivity. Moreover, non-specific adsorption of interfering molecules on the sensor floor is one other concern that may negatively influence the sensor’s accuracy and specificity [75].
Specifically, Guo et al. [32] fabricated a MoS2 FET immobilized with glucose oxidase through bodily adsorption. The measured glucose focus in phosphate buffer was from 0.1 mM to 0.6 mM, which is throughout the typical vary of human tear’s glucose degree. Equally, Zong et al. [44] developed a glucose sensor with ZnO FET. The FET sensor is fabricated through hydrothermal development of semiconducting ZnO nanorods between supply and drain microelectrodes. Following the fabrication course of, the semiconductor was incubated with glucose oxidase answer in a single day to maximise the adsorption. This method was capable of detect glucose with an LOD of 1 μM.
Chemical modification
Chemical approaches supply an answer to handle the constraints of physisorption and customarily obtain higher efficiency. These approaches contain creating a powerful and steady attachment between biomolecules and the electrode floor by covalent bonding, crosslinking, and bioconjugation affinity utilizing the purposeful teams current on the floor [73].
Within the case of FET sensors, the floor is functionalized with a chemical agent that makes use of covalent bonds to immobilize particular bioreceptors. Covalent immobilization offers a steady and everlasting attachment of the bioreceptor to the FET floor, enhancing the system’s sensitivity and specificity. This method ensures a dependable and environment friendly biosensing system able to precisely detecting the goal analyte [43].
Previous to functionalization, the semiconductor floor must be activated with both UV-ozone, oxygen plasma [38] or an ammonia/hydrogen peroxide combination. These remedies create − OH or − COOH teams on the floor, making it extra receptive to a response with any organosilanes throughout the subsequent functionalization step.
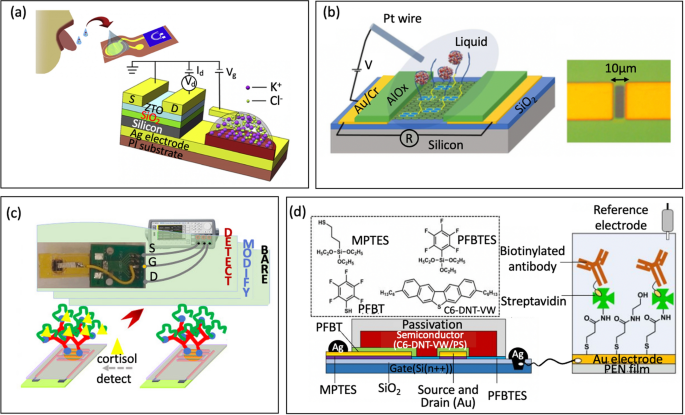
Relating to metallic oxide semiconductors, organo-silanization is a generally used approach for immobilizing biomolecules on the floor of oxides reminiscent of SiO2 and varied types of glass. This course of entails functionalizing the oxide floor with particular organosilane compounds. Two ceaselessly used alkoxysilanes for this objective are 3-aminopropyl-triethoxysilane (APTES) and 3-glycidyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GOPTS). Different alkoxysilanes like 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane and 3-trimethoxysilyl propyl aldehyde may additionally be used. Following APTES functionalization, the amine purposeful teams will be additional reacted with a linker reminiscent of m-Maleimidobenzoyl-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (MBS, Fig. 6b) or glutaraldehyde (GA, Fig. 6c). These linkers introduce purposeful teams that may be covalently certain to varied molecular thiol- or amine- containing probes, reminiscent of nucleotide probes, aptamers, antibodies, nanobodies, proteins, or enzymes. For example, Liu et al. [33] functionalized In2O3 FET platform with thiolated aptamer utilizing APTES and MBS linker. The platform was capable of concurrently detect neurotransmitters, reminiscent of serotonin and dopamine, in real-time with a detection vary from 10 fM to 1 μM. Equally, Hayashi et al. [77] used APTES and GA linker to immobilize Jacalin into the floor of SiO2 bioFET. The system might particularly detect secretory immunoglobulin A in sweat at concentrations starting from 0.1 μg/mL to 100 μg/mL. These research demonstrated the utility of FET biosensors in monitoring situation on psychological well being to stop melancholy.
Approaches with phosphonate chemistry supply some benefits over organosilanes [43, 78]. First, they are often utilized to a broader vary of metallic oxides in comparison with silane chemistry, making phosphonate chemistry relevant to a greater diversity of surfaces. Secondly, phosphonic acid-based monolayers are much less delicate to moisture than organosilanes. This attribute is necessary for sensible use reminiscent of storage, as a result of the soundness of a monolayer is much less affected by the humidity of the setting. Moreover, phosphonate chemistry is much less susceptible to self-condensation. In different phrases, phosphonic-acid-based reagents ought to reduce the quantity of undesirable byproducts in comparison with organosilanes, resulting in extra predictable and controllable biofunctionalization processes [29]. Specifically, Li et al. [79] submerged In2O3 nanowire into 3-phosphonopropionic acid, leading to binding of the phosphonic acid into the floor of the semiconductor. Subsequent, the carboxylic group was activated by carbodiimide chemistry, which served because the anchor for amine-containing probe reminiscent of monoclonal antibody (Fig. 6d). Actual-time detection in answer has additionally been demonstrated for analyte down to five ng/mL.
When it comes to carbon nanotube channel, the floor will be functionalized with 1-pyrenebutyric acid (PBA). PBA accommodates a pyrene group that may be hooked up to carbon nanotube through π-π* stacking, whereas the carboxyl group can be utilized to covalently anchor to amine-containing probe utilizing carbodiimide chemistry, which usually entails EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride) /NHS (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) coupling response, Fig. 6e. Throughout this coupling course of, the EDC creates a reactive O-acylisourea ester, rendering the floor quickly unstable. This O-acylisourea ester then reacts with the NHS to kind an amine-reactive NHS ester, whereas the floor stays semi-stable. Subsequent, amine group from probe reacts with the amine-reactive NHS ester to kind a steady amide bond that immobilizes the probe onto the NHS current on the floor of carbon nanotubes. Filipiak et al. [80] employed this technique to functionalize SWCNT-FET with nanobody receptor such that the system can detect antigen with excessive selectivity and sub-picomolar detection restrict with a dynamic vary exceeding 5 orders of magnitude. Lengthy-term stability measurements reveal a low drift of SWCNTs of 0.05 mV/h, making it promising for steady real-time monitoring of biomarkers.
Equally, for graphene semiconductors, the central macrocycle of Tetrakis (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin (TCPP) will be hooked up to the graphene’s honeycomb carbon community through π-π* stacking. Subsequently, amine-containing probe could possibly be immobilized through EDC/NHS coupling to the carboxyl teams surrounding the macrocycle of TCPP (Fig. 6f). Zhang et al. [81], for instance, used this method to functionalize a GFET with a cortisol aptamer for salivary cortisol exams. Notably, this TCPP ornament not solely enhances the sensitivity of liquid gate-GFETs to cortisol but in addition shields the oxygen-containing teams, thereby decreasing any response to pH variations within the samples [81].
Alternatively, a graphene channel will be biochemically functionalized through the use of 1-pyrenebutyric acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (PBSE). PBSE accommodates a pyrene group that interacts with graphene by π-π stacking, on the different finish, it has an ester group that reacts with major amines. Subsequent, a probe containing NH2 will be straight linked to the PBSE by forming amide bonds with out EDC/NHS chemistry (Fig. 6g). Zhuang Hao et al. [82] adopted this method to functionalize a GFET involving an aptamer to watch insulin. Initially, the sensor was submerged in a PBSE answer. It was then washed with dimethylformamide (DMF) to eradicate any unbound PBSE. Subsequent, the system was rinsed with PBS and uncovered to an aptamer answer. After PBS rinsing, ethanolamine was utilized to the graphene channel to deactivate and block any extra reactive teams left on the graphene floor. The authors, afterward, continued with this process for the immobilization of IL-6 aptamer to watch cytokine degree in saliva [83].
One other approach for activating the floor of graphene channel with a carboxylate group is using ultraviolet ozone (UVO). Nevertheless, extended publicity to UVO can excessively degrade the graphene’s resistance, so UVO publicity is usually restricted to 2 minutes [2]. As soon as UVO has been utilized, amine-containing probe will be immobilized by an EDC/NHS coupling response, Fig. 6h. Specifically, Ku et al. [2] used this technique to functionalize a GFET platform with cortisol monoclonal antibody. The platform was capable of measure cortisol concentrations in actual time with a detection restrict of 10 pg/mL.
Gate floor functionalization methods
Utilizing a gate as an lively layer is one other widespread method for FETs. In some instances, the floor of the gate electrode is functionalized with probes.
For instance, thiol-containing probes reminiscent of antibodies and aptamers can readily be used to functionalize top-gate gold electrodes by sturdy S–Au covalent binding to detect proteins [84], Fig. 7a. Proteins binding to those functionalized electrodes end in a drop in gate voltage, which redistributes the cost density regionally across the gate. This induces a change in cost density of the lively channel. Extra importantly, this detection technique doesn’t require any dilution or washing processes to cut back ionic power, but it stays extremely delicate. The whole detection course of solely takes about 5 min.
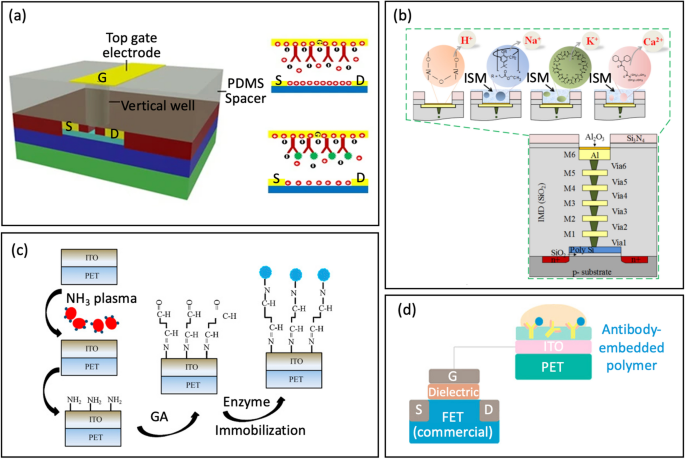
a Floor functionalization/immobilization on top-gate gold electrode with antibody through thiol-gold adsorption (reprinted with permission from Ref. [84] Copyright 2017 Springer Nature). b Cross-sectional view of the 3D-EMG-ISFET sensor functionalized with ion selective membranes sensing (reprinted with permission from Ref. [1] Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society). c Schematic of enzyme immobilization on indium tin oxide movies on versatile polyethylene terephthalate substrates (reprinted with permission from Ref [38. Copyright 2013 Elsevier). d Antibody-Embedded polymer coupled to extended gate (reprinted with permission from Ref. [85] Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society)
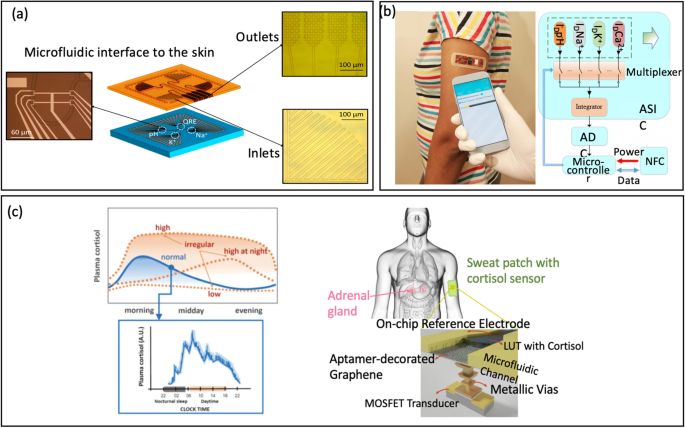
Zhang et al. [1] launched a Three-Dimensional Electrode-Steel-Gate Ion-Delicate FET (3D-EMG-ISFET) for monitoring electrolytes in sweat, Fig. 7b. An environment friendly functionalization materials for electrolyte-sensing is the ion-selective membrane (ISM). ISM has particular embedded ion receptor, often called an ionophore, in a polyvinyl chloride-based membrane ((PVC)/bis(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate (DOS)). This membrane is drop-casted onto the highest of the 3D-EMG-ISFET sensing dielectric. The ionophore within the membrane interacts poorly with interfering ions whereas selectively interacting with goal ion. Via these interactions, a junction potential is created, which modifications the gate bias of ISFETs and is straight correlated with the ion exercise on the liquid-to-ISM interface. On this explicit examine, three varieties of membranes have been deposited for sensing, ensuing within the creation of 3D-EMG-(Na+, Okay+, Ca2+) delicate FETs [1].
Yang et al. [38] developed indium tin oxide (ITO) movies on versatile polyethylene terephthalate substrates utilizing totally different NH3 plasma remedy situations. These ITO movies function sensing electrodes for extended-gate FETs, Fig. 7c. An NH3 plasma remedy was then launched to create amine teams on the ITO sensing membranes; thus, providing an easier various to the complicated procedures of inducing covalent bonding. Following the NH3 plasma remedy, a glutaraldehyde answer and urease have been dripped individually onto the ITO membrane for additional functionalization.
Another method entails embedding the probe inside a polymer, which is then coupled to the prolonged gate. Alongside these traces, Jang et al. [85] used an antibody-embedded PSMA sensing gate to detect cortisol, Fig. 7d. Incorporating the receptor into the polymer construction helped to bind the cortisol molecules in proximity to the membrane-substrate interface, successfully overcoming the issues related to the Debye size (λD). The reported LOD was 1 pg/mL in phosphate buffer saline, the place λD is 0.2 nm.
Probe
Enzyme (EnFET)
Enzyme-modified FET operates primarily based on enzymatic response, the place the enzyme catalyzes the conversion of a substrate into its product. This enzymatic response happens throughout the enzyme membrane, resulting in the change in gathered charged carriers on the gate floor, straight proportional to the quantity of analyte current within the pattern [86]. In consequence, protons are both generated or consumed, coupled with a change in pH ranges. This variation in pH will be measured utilizing a pH-electrode as a reference electrode [87]. Due to this fact, EnFET biosensors can quantify the presence of the goal analyte by correlating the modifications in pH with the focus of the analyte.
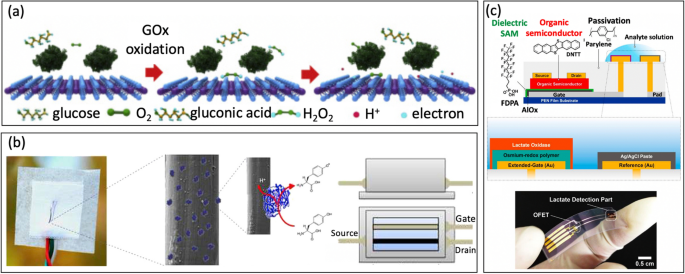
For example, Guo et al. [32] used glucose oxidase (GOD) because the bio-enzyme for making a MoS2 FET-based serpentine mesh sensor system to detect glucose on synthetic eyeballs. To reinforce glucose recognition and enhance conductance, the staff employed a big contact space with tear fluid to soak up and immobilize the enzyme. Initially, GOD (β-D-glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger) is immobilized onto the floor of MoS2 [88, 89], Fig. 8a. The next cost switch mechanism happens as a result of the glucose is oxidized by the GOD to kind H2O2, which then reacts with oxygen, producing hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons (e−):
a Illustration of the sensing mechanism of the system with oxidation of glucose (reprinted with permission from Ref. [32] Copyright 2021 Elsevier). b Tyrosine sensing mechanism of natural electrochemical transistor functionalized with laccase (reprinted with permission from Ref. [94] Copyright 2017 Elsevier). c Lactate detection with extended-gate natural FET functionalized with lactate oxidase and osmium-redox polymer (reprinted with permission from Ref. [95] Copyright 2019 Springer Nature)
$$D- Glucose + H2O2 + O2 stackrel{GOD}{to } D- gluconic acid + O2 + 2H+ + 2e-$$
This response generates free electrons, resulting in a rise in system present as a result of conduct of the n-type FET. GOD has a demonstrated excessive selectivity for glucose, with absolutely or quasi-reversible glucose conversion. Furthermore, it’s readily obtainable and has been confirmed to face up to situations of utmost pH, ionic power, and temperature [90,91,92]. This serpentine mesh sensor system will be positioned straight onto the lenses for direct contact with tears, in distinction to standard sensors and circuit chips embedded throughout the lens substrate. This design provided excessive detection sensitivity, mechanical robustness, and doesn’t intrude with blinking or imaginative and prescient. Moreover, in-vitro cytotoxicity exams have proven good biocompatibility, making it a promising candidate for the next-generation of sentimental electronics in healthcare functions.
In an identical examine, Kim et al. [93] developed a wearable contact lens able to selectively and sensitively detecting glucose. To realize this, the authors immobilized GOD on a graphene channel utilizing a pyrene linker by π-π stacking interactions. GOD is hooked up to pyrene linker by forming an amide bond ensuing from the nucleophilic substitution of N-hydroxysuccinimide. Of their experiments, the authors demonstrated in-vivo glucose detection functionality on a rabbit eye in real-time in addition to wi-fi in-vitro monitoring of the intraocular stress of a bovine eyeball. This progressive wearable contact lens holds important potential for biomedical functions.
Furthermore, Battista et al. [94] introduced a textile wearable natural electrochemical transistor the place the semiconducting polymer was fabricated on cotton fibers (the yarn). Recombinant fungal POXA1b laccase was immobilized by floor adsorption to detect Tyrosine (L-Tyr) (Fig. 8b). Lactate is a category of enzyme catalyzing the single-electron oxidation of phenolic compounds with related four-electron discount of oxygen to water. This direct electron switch with out mediator permits for the delicate detection of Tyrosine in aqueous options. This method permits for detecting Lactate with an LOD of 10 nM, making it a promising in depth utilization in sports activities, healthcare, and dealing security.
Equally, Minamiki et al. [95] developed an natural field-effect transistors utilizing extended-gate electrode modified with a lactate oxidase on an osmium-redox polymer [69], Fig. 8c. The biosensing functionality of the OFET is investigated by real-time measurement of lactate focus in an aqueous setting. The outcomes confirmed a restrict of detection of 10 mM for sweat, which falls throughout the vary of lactate ranges sometimes present in sweat. In one other instance, Joshi et al. [96] launched a novel glucose/lactate FET sensing platform by immobilizing enzymes on a polyimide substrate [97]. On this method, semiconductor materials was made out of carbon nanotubes, which randomly sprayed onto a Kapton membrane [98]. The drain present (IDS) for the p-type CNTFET elevated because the focus of lactate or glucose rised [99]. The units exhibited good shelf life and the flexibility to face up to repetitive mechanical deformations, making it promising for non-invasive monitoring of biomarkers on wearable units.
Antibody and nanobody (immunoFET)
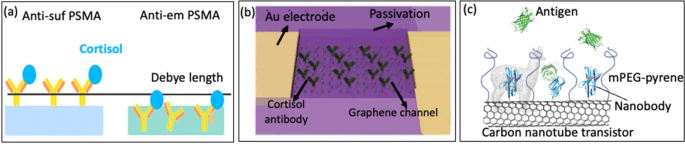
Antibodies are important protecting proteins secreted by B-lymphocytes. They’re characterised by their “Y” form and play an important position within the immune response of mammals. Moreover, Antibodies exhibit a outstanding capacity to bind to particular antigens with excessive selectivity, making them worthwhile for detecting target-specific analytes/antigens [93,94,95]. The popularity between antibodies and antigens will generate an electrical subject as they’re each charged molecules. This electrical subject alters the circulation of provider between the supply and the gate, making a sign that may be detected electrically [100, 101]. Due to this fact, the focus of the analyte will be measured by modifications in conductivity ensuing from the interplay of antigen–antibody bonds [102], making it promising for medical analysis functions. Nevertheless, antibodies nonetheless have limitations as a result of its attain over Debye size (λD), which might result in decreased sensitivity. Jang et al. [85] made important developments in overcoming the difficulty of λD by fabricating FET- primarily based sensor utilizing antibody- embedded poly (styrene-co-methacrylic acid) (PSMA) sensing gate to detect cortisol, Fig. 9a. The embedded construction of the receptor within the polymer allowed cortisol molecules to bind close to the membrane-substrate interface, successfully overcome the constraints posed by λD. The authors in contrast its sensing efficacy with the standard method of antibody functionalization on the PSMA floor. With the goal of evaluating the efficiency of PSMA built-in with embedded antibodies. The antibody-embedded PSMA achieved a restrict of detection (LOD) of 1 ng/mL in barely buffered synthetic sweat, demonstrating the potential to beat the limitation imposed by λD. The effectiveness of antibody-embedded PSMA was subsequently verified by a sandwich ELISA. This examine is the primary demonstration of FET-based cortisol sensing, the place cortisol is electrically detected utilizing polymers on a distant versatile gate platform. This creates alternatives for the detection of cortisol in saliva or sweat inside a medical setting.
a Presumed schematic picture of cortisol antibody-embedded geometric within the PSMA polymer matrix (reprinted with permission from Ref. [85] Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society). b Schematic picture of the graphene FET system functionalized with cortisol antibody on the floor of graphene channel (reprinted with permission from Ref. [2] Copyright 2020 American Affiliation for the Development of Science). c Consultant carbon nanotube FET functionalized with nanobody (reprinted with permission from Ref [80] Copyright 2018 Elsevier)
Equally, Chu et al. [103] developed a brand new kind of FET biosensor utilizing monoclonal antibodies (anti-CEA and anti-NT-pro BNP) to straight detect proteins past the discernable Debye size. Protein CEA was successfully detected through the use of antibodies immobilized on high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs). Initially, 2-Mercaptoethylamine (MEA) was utilized to interrupt the disulfide bond within the heavy chain of the IgG antibody. The ensuing cleaved thiol group then hooked up to the gold floor, aligning the antibody with a particular orientation. This coupling uncovered the binding web site upwards and lowered the space between the binding and the gate electrode [84]. This method managed to counteract the numerous charge-screening impact brought on by the excessive ionic power within the answer. As a result of sensing will not be depending on cost of goal proteins, it could possibly detect each charged and impartial proteins. Extra importantly, this course of doesn’t require dilution or washing, making it easier and extra environment friendly. The sensible approaches together with evaluating designs, measurement methodologies, and the working mechanism of enzyme FET promise direct protein detection in diagnostics.
Ku et al.[2] fabricated GFET biosensors for cortisol detection through the use of monoclonal antibody (C-Mab) chemically bonded to the floor of graphene. Determine 9b depicts FET biosensors built-in with contact lenses to noninvasively monitor tears in actual time. Of their examine, graphene serves as a transducer to show the antibody-cortisol interplay into electrical indicators. This method was capable of detect cortisol with an LOD of 10 pg/ml, which is throughout the typical vary of human tear’s cortisol degree from 1 to 40 ng/ml [104].
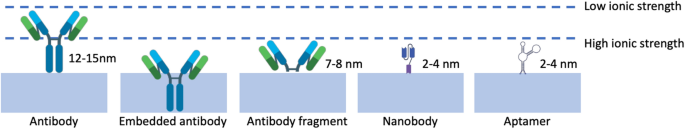
Extra lately, a novel method to immunoFETs has emerged, the place nanobodies are used to beat the constraints of the Debye size (λD). Nanobodies are steady and simply producible organic probes, characterised by their remarkably quick size of lower than 3 nm, which units them other than typical antibodies (15 nm) and even antibody fragments (7–8 nm). Their quick size means these nanobodies can assist analyte binding in proximities a lot nearer to the floor of the sensor. Furthermore, nanobodies exhibit spectacular physicochemical stability below numerous situations. In consequence, researchers have built-in nanobody receptors into carbon nanotube transistors, giving rise to extremely delicate, selective, and label-free protein detection in physiological options [105]. Despite the fact that nanobodies possess distinct attributes, they’ve not been extensively employed as probes in FET-based biosensors [106]. Among the many few to make use of them, Filipiak et al. [80] proposed a novel floor modification method to develop FET sensor through the use of a really quick nanobody receptors mixed with a polyethylene glycol layer to beat the difficulty of the Debye size, Fig. 9c. Nanomaterial-based FETs with inexperienced fluorescent protein was used because the mannequin antigen. FET sensors after being functionalized exhibited distinctive effectivity, delicate, selective, and label-free protein detection throughout a variety of concentrations. This functionality stays constant even in physiological options with a excessive ionic power (100 mM).
Aptamer
Aptamers are quick single-stranded oligo-nucleotide sequences of 15–40 nucleotides in size which were engineered by a range course of to exhibit an distinctive binding affinity in a fashion much like antibodies and nanobodies [107]. One of many key benefits of aptamers is their small measurement, which is roughly one-tenth that of an antibody. This makes them doubtlessly best for overcoming the Debye size restrict once they work together with the goal, enhancing sensitivity and decrease detection limits, Fig. 10.
Aptamers supply a number of superior benefits over antibodies as catch probes. First, they’re synthesized in vitro, decreasing the variation between batches. Moreover, aptamers will be designed to show various levels of affinity for a focused molecule [108, 109]. Furthermore, they show better resilience to temperature fluctuations and stay steady throughout long-term storage [110, 111]. Moreover, aptamers will be covalently immobilized on most surfaces by modifying both the 5′- or 3′-end [112].
Aptamers present a further benefit to apta-FET in comparison with immuno-FET. In contrast to conventional bio-FETs that require goal molecules to be charged, aptasensors can accommodate electroneutral targets by conformational modifications within the aptamer’s negatively charged phosphodiester backbones close to the semiconductor channel floor. Goal binding induces a secondary conformational shift, inflicting the aptamer to undertake a extra compact construction that positions the unfavorable prices nearer to the semiconductor floor, leading to a unfavorable prime gating impact on the system [113].
Whereas the sensing mechanism of aptamer-FETs hinges on altering aptamer conformations as a result of target-induced floor cost redistribution (aptaswitch), gate voltage manipulation may also affect aptamer configurations [32]. This enables for the modulation of aptamer states to launch targets and to realize efficient biosensor regeneration for steady analyte monitoring. [114, 115].
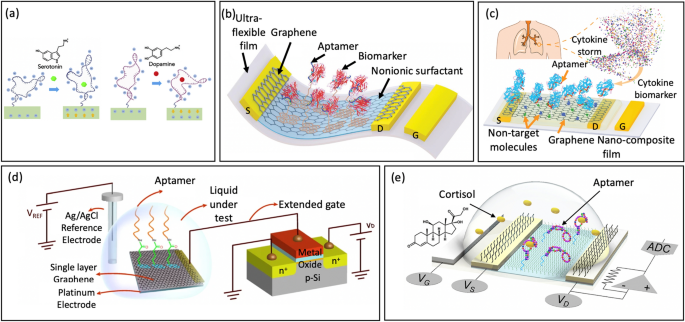
Liu et al. [33] launched a platform of nanoribbon In2O3 FETs, which have been functionalized with aptamers for monitoring serotonin and dopamine at various concentrations. When the aptamer captures the goal, a phase of the negatively charged spine of the serotonin aptamer strikes away from the In2O3 floor. Consequently, electrostatic repulsion between the electrons in an n-type semiconductor and the negatively charged aptamers would lower, resulting in a rise in channel conductance in response to affiliation between the aptamer and the goal. In distinction to the dopamine aptamer used within the examine, the authors hypothesized {that a} part of the negatively charged spine would transfer nearer to the n-type semiconductor upon dopamine binding. This variation elevated electrostatic repulsion and decreased In2O3 transconductance, Fig. 11a. The system detected serotonin and dopamine over a broad focus ranges, together with these occurring within the mind extracellular area [116, 117], in actual time, and in a multiplexed format that included temperature and pH sensing.
a Serotonin- and Dopamine-Aptamer-Functionalized FET sensors (reprinted with permission from Ref [33] Copyright 2020 Sciencedirect). b Schematic of the ultraflexible aptameric GFET nanosensor (reprinted with permission from Ref [16] Copyright 2019 Wiley). c Schematic of the aptameric GNFET biosensor for cytokine biomarker detection (reprinted with permission from Ref [118] Copyright 2020 Wiley). d Schematic of utilizing a single layer of graphene as a gate electrode functionalized with aptamer (reprinted with permission from Ref [108] Copyright 2021 Nature). e Schematic illustration of cortisol sensing by an aptaFET sensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [17] Copyright 2022 American Affiliation for the Development of Science)
Wang et al. [16] employed an identical method to manufacture an FET nanosensor by making a conducting channel with monolayer graphene functionalize aptamer. The sensor was designed to detect TNF-α, an inflammatory cytokine biomarker, Fig. 11b. The interplay between the aptamer and the biomarker results in a modification within the focus of graphene provider. An utilized voltage between the drain and supply terminals causes a present to circulation by the graphene channel. This present is measured through the FET to find out the focus of the biomarker. The nanosensor demonstrates constant excessive selectivity and low LOD (down to five × 10–12 M TNF-α), making it doubtlessly helpful in wearable sensors.
Subsequently, Wang et al. [118] developed a cytokine sensing platform to help hospitals in maximizing the advantages of anti-inflammatory therapies whereas avoiding cytokine storms, Fig. 11c. Current sensors face challenges in precisely measuring cytokine ranges in biofluids as a result of excessive background interference. To beat this concern, the authors created an aptameric FET sensor utilizing a composite graphene-Nafion movie. This composite movie minimizes nonspecific adsorption and will increase renewability within the biosensor. With these developments, the platform was able to constantly and sensitively monitoring cytokines in undiluted human sweat, with a detection vary from 0.015 to 250 nm and a powerful LOD all the way down to 740 fM. Furthermore, the system exhibited no seen mechanical injury and maintained a constant sensing response throughout regenerative exams and crumpling exams. These benefits make it promising for in depth utilization in sufferers with acute infectious illness in addition to situations that require each day monitoring.
Moreover, Sheibani et al. [108] made important progress in wearable EG-FET sensor growth to handle the Debye screening limitation of cost sensing, utilizing a single layer of graphene as a gate electrode and aptamers, Fig. 11d. Atomically skinny graphene chemically binds with the aptamer and permits for the popularity occasion of the analytes occurring throughout the Debye size. In the meantime, aptamers perform as the popularity elements, making the sensor remarkably delicate, particular, and enduring. The EG-FET sensor is hysteresis-free and displays excessive selectivity in direction of different comparable hormones with a detection restrict of 0.2 nM.
The truth is, the system integration of FET-based biosensors has not been considerably developed and prohibit their adaptation for wearable functions [85, 119, 120]. Wang et al. [17] fabricated a totally built-in sensing platform comprising novel cortisol aptamer binding with a nanometer-thin-film. The cortisol aptamer, which has a thiol modification on the 5′ finish, was covalently binded to amino-silanized In2O3 FET. The cortisol aptamer, which had a thiol modification on the 5′ finish, was covalently binded to amino-silanized In2O3 FET, Fig. 11e. The sensing system operates autonomously and wirelessly, label-free and remarkably low cortisol detection limits spotlight the potential of monitoring sweat cortisol for sensible functions [121, 122]. They are often reworked into wearable and cellular codecs to cater to different physiological biomarkers. That is particularly worthwhile for targets current with low concentrations in sweat, the place moveable measurement applied sciences are presently missing. This could contribute to the development of customized precision drugs.
Ion-sensitive membrane
Ion-selective membranes are a extremely efficient technique of chemical sensing. The membrane has particular ion receptors (ionophores). The membrane is positioned on prime of the gate stack of the sensing dielectric. The ionophore within the membrane selectively interacts with its goal ion, whereas displaying weaker interactions with interfering ions. A junction voltage is developed on account of these interactions. This voltage not solely impacts the gate bias of the ion-sensitive FET however is straight proportional to the ion exercise on the liquid-to-ISM interface [1].
To realize selective sensitivity to totally different ions, the sensing dielectric is functionalized with an ion-selective membrane for every ion species. Which means that solely the particular ion for which the membrane has been functionalized can cross by and supply its cost to the ion-sensitive FET’s gate [1]. On this means, ion-selective membranes enable totally different ions to be detected exactly and selectively for chemical sensing functions.
Ion-sensitive FETs (ISFETs) maintain nice promise for steady monitoring of biofluids in actual time. Nevertheless, the event of wearable sensors involving ISFETs has been hindered by the necessity for cumbersome reference electrodes. A steady reference electrode is important for ion detection because it should keep a relentless potential below various ion concentrations to make sure that the sensors perform correctly.
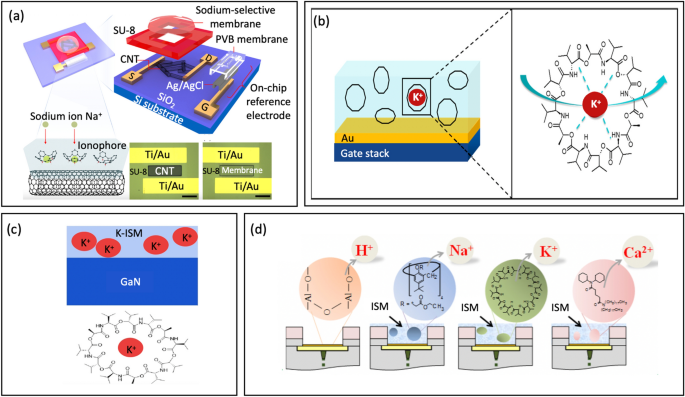
To deal with this limitation, Park et al. [123] launched a novel carbon nanotube FETs (CNT-FETs) platform utilizing ion-selective membrane and a miniaturized on-chip reference electrode for sodium sensing, Fig. 12a. The CNT floor is modified with a sodium-selective membrane made from polyvinyl chloride with a particular ionophore, which selectively captures sodium ions with excessive sensitivity. The electrochemical potential generated within the membrane is then transformed right into a channel present for the CNTs. A miniaturized reference electrode was built-in to realize a compact measurement for wearable units, which was not beforehand completed by business reference electrodes. The on-chip reference electrode has a steady efficiency, outperforming typical reference electrodes. The sodium sensor was able to selectively detecting sodium ions over a large focus vary from 0.1 to 100 mM. This vary covers typical human sweat sodium concentrations, even within the presence of interfering ions reminiscent of magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
a Schematic of CNT-FETs with the sodium-selective membrane and on-chip reference electrode (reprinted with permission from Ref. [123] Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society). b Functionalization chemistry of Au gates with a polymeric membrane for potassium sensing (reprinted with permission from Ref. [19] Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society). c Potassium ion-selective membrane modified on the GaN floor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [127] Copyright 2019 Wiley). d 3D-EMG-ISFETs with Al2O3 as pH sensing dielectric, functionalized with ion selective membranes for Na+,Okay+, and Ca2+ sensing (reprinted with permission from Ref. [1] Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society)
ISFET units have emerged as a promising various to different sensing applied sciences as a result of their capacity to combine with a spread of digital readouts. For that reason, these units are thought of to be extremely versatile and multifunctional. For example, Erick et al. [19] launched a fully-integrated on-chip sweat sensing system that’s each wearable and able to monitoring sodium and potassium ranges, Fig. 12b. These are important markers for figuring out hormonal modifications related to ovulation [124] and cystic fibrosis [125]. The ratio between potassium and sodium focus in sweat can be indicative of kidney failure [126]. On this system, valinomycin was blended with a PVC membrane to create a potassium ion-selective membrane, whereas Na ionophore X was blended with a PCV membrane to create a sodium ion-selective membrane. The concentrations of sodium and potassium exhibited almost Nernstian sensitivity, indicating that the purposeful membranes possess excessive sensitivity. Actual-time measurements additionally indicated steady and repeatable readings. Their response occasions align nicely with the physiological price of ion focus variations in sweat.
Moreover, the long-term steady and repeatable detection of ions has been a problem for FET biosensors – one which has restricted their adoption as a very efficacious health-monitoring platform. To deal with this concern, Liu et al. [127] launched a wearable platform primarily based on AlGaN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs) for repeatedly monitoring pH and potassium ions, Fig. 12c. The platform incorporates a sweatband that repeatedly collects sweat. Detecting models for pH and potassium ion are created by modifying the floor with totally different delicate movies. The GaN floor is embedded with Okay+ within the PVC movie to kind a potassium ion-selective membrane. The platform exhibited excessive sensitivity (45.72 μA/pH for pH 3–7, 51.073 μA/pH for pH 7.4–9, and 4.94 μA/lgαOkay+ for Okay+), strong stability (maintained over 28 days), and good repeatability (with a relative commonplace deviation (RSD) of two.6% for pH 3–7 sensitivity, an RSD of two.1% for pH 7.4–9 sensitivity, and an RSD of seven.3% for Okay+ sensitivity).
Notably, Zhang et al. [1] firstly introduced multianalyte sensing platform ISFET able to detecting 4 distinct analytes in sweat: pH, Na+, Okay+, and Ca2+ by integrating readout interface, NFC communications, and several other remotely powered 3D prolonged metallic gate ISFETs (3D-EMG-ISFETs), Fig. 12d. The whole platform occupies lower than 2.5 mm2. Moreover, extremely selective ion-selective membranes coupled with postprocessing integration steps eradicate important sensor hysteresis and parasitic, leading to excessive sensitivity of 58 mV/pH, -57 mV/dec (Na+), -48 mV/dec (Okay+), and -26 mV/dec (Ca2+). That is near the Nernstian restrict and excessive selectivity. The platform demonstrated in-vitro usability by measuring a number of analytes concurrently. Remarkably, the sensors boasted the bottom energy consumption ever reported at 2 pW/sensor. This ultralow energy consumption means the sensor, the readout interface, and the ISFET sensors can all be remotely powered by a radio frequency sign. As such, this platform demonstrates an ideal potential for predictive analytics and customized medical remedy, making it a promising candidate for wearable well being monitoring functions.
Biomarkers in physiological fluids
Desk 3 presents record of potential biomarkers together with tears, saliva, sweat, ISF, and related parameters.
Sweat-based sensors
Sweat accommodates quite a lot of biochemical compounds, together with ions [146], metabolites [147], acids [148, 149], hormones [150, 151], small proteins [152, 153] and peptides, together with a wealthy distribution of sweat glands (> 100 glands/cm2). Current research demonstrated that biomarkers in sweat are straight correlated with their concentrations in blood, rendering sweat a promising organic fluid for non-invasive diagnostics [1, 9, 154].
For example, Petrelli et al. [41] developed an ammonium sensing platform utilizing an electrolyte-gated carbon nanotube FET (EG-CNTFET). This platform offers a real-time profile of ammonium sweat dynamics, that are being explored as potential markers for the onset of muscular fatigue [155]. Whereas most research on ammonium sensing in sweat have used electrochemical sensors [156], the authors opted for a distinct method utilizing EG-CNTFETs functionalized with an ion-selective membrane as a substitute. That is as a result of distinctive properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), together with excessive surface-to-volume ratio, chemical stability, and the flexibility for solution-processing. Moreover, EG-FET platform is well-suited for detecting analytes in a liquid section [157]. The sensors yield a linear attribute of ammonium within the vary from 0.01 to 10 mM.
In one other examine, Garcia-Cordero et al. [19] demonstrated ion-sensitive FETs sensor to watch biochemical info in real-time from the pores and skin floor, Fig. 13a. This method collects a small quantity of sweat from an individual’s pores and skin. Subsequently, the collected sweat was passively transported to a bunch of functionalized ion-sensitive FETs (ISFETs) the place it was analyzed for its pH ranges and the concentrations of Na+ and Okay+ ions. The mixture of a microfluidic interface with an ISFET make it extra comfort to gather even in low-sweat-rate situations, or very small quantities of sweat. On this method, the system can analyze sweat even in periods of relaxation, rendering it an exceptionally sensible and handy technique for repeatedly monitoring biochemical markers.
a Consultant of lab-on-skin idea (reprinted with permission from Ref. [19] Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society). b Picture of the wearable system and Block diagram of the NFC powered sensing system (reprinted with permission from Ref. [1] Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society). c Qualitative depiction of standard and irregular circadian ranges of the cortisol produced by the adrenal glands in human physique by the day, displaying the necessity for prime time granularity measurements to seize the pulsatile nature of cortisol, and idea of 3D-integrated cortisol sensor built-in with a prime microfluidic channel that guides the sweat over a planar reference electrode and bio-functionalized graphene (reprinted with permission from Ref [108] Copyright 2021 Nature)
Furthermore, Hayashi et al. [77] developed wearable FET sensors for non-invasive detection of immunoglobulin A (s-IgA) in human sweat, a biomarker for sure psychological well being situations, significantly melancholy. The truth is, measuring by sweat face restrict as a result of non-specific binding of drugs reminiscent of sebum, mucin, proteins, and micro organism, resulting in a discount within the specificity of the sensor [152, 158, 159]. To beat this problem, the staff immobilized jacalin as a receptor, which particularly permits for s-IgA to be adsorbed by filtration course of, Fig. 13b. These jacalin-immobilized FET biosensors demonstrated increased sensitivity, working in a spread from 0.1 μg/mL to 100 μg/mL, making it a promising candidate for monitoring stress and analyzing s-IgA ranges in a non-invasive method. Lately, Sheibani et al. [108] developed a label-free FET sensor for detecting cortisol in a Debye screening time-frame inside a organic buffer, Fig. 13c. The wearable FET sensor employs an extended-gate aptamer primarily based on platinum/graphene (EG-FET) that’s hysteresis-free and possesses excessive voltage and present sensitivity. The outcomes indicated a detection restrict throughout the vary of cortisol concentrations in fluids, rendering it appropriate for steady real-time monitoring of cortisol in human sweat.
Tear-based sensors
Tears are complicated extracellular fluids comprising proteins, peptides, electrolytes, lipids, and metabolites that originate from quite a lot of sources such because the lacrimal glands, epithelial cells on the floor of the attention, Meibssomian glands, goblet cells, and blood [9]. As tears include a number of elements like these in blood, it’s potential to make use of tears to watch biomarkers. Nevertheless, the extraction and evaluation of tears in vitro pose a number of challenges, which have prevented tears from getting used as a diagnostic instrument. First, tear pattern will be evaporated throughout transport to a laboratory, considerably impacting the accuracy of centralized tear analyses. Second, the human eye is delicate, so nice warning is required when gathering samples. Moreover, biomarker concentrations typically range relying on the particular assortment technique in use, which can undermine any check findings [160, 161]. Thus, sensible contact lenses have garnered important curiosity, and the combination of biosensors with contact lenses is a promising method for real-time monitoring and evaluation of well being situation [93, 162,163,164].
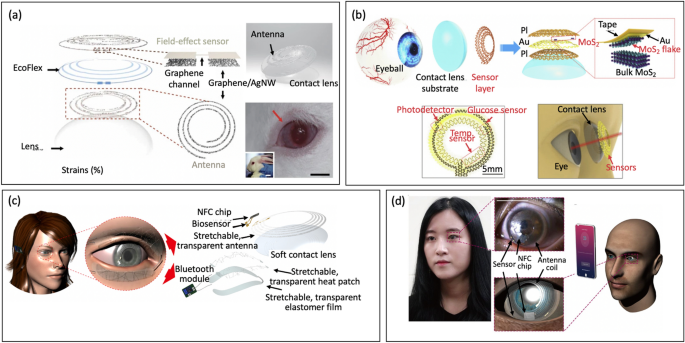
Nevertheless, contact lens sensors face some critical limitations reminiscent of obstructing person’s imaginative and prescient and missing functionality of multiplex evaluation. To beat a few of these shortcomings, Kim et al. [93] built-in a sensor into an precise ocular contact lens, Fig. 14a. The sensor includes of a clear graphene hybrid with metallic nanowires, which presents transparency and stretchability to make sure person consolation with out obstructing their line of sight to detect glucose in tears repeatedly and wirelessly. As a multifunctional system, the lens may also measure intraocular stress, which is linked to glaucoma. In-vivo and in-vitro exams on rabbits and bovine eyeballs show constant and reliable efficiency. Though this system permits for multifunctional sensing, the authors haven’t but demonstrated each capabilities working concurrently. Likewise, Guo et al. [32] developed a multifunctional contact lens outfitted with a versatile MoS2 FET mesh sensor to detect glucose, temperature, and UV mild, Fig. 14b. In contrast to conventional sensors embedded inside lens substrates, the authors straight affixed a serpentine mesh sensor system onto the lenses to keep up direct contact with tear fluid. This method permits for prime detection sensitivity, whereas guaranteeing mechanical robustness and no interference with blinking or imaginative and prescient. The outcomes confirmed good photo-detection response, high-sensitivity glucose detection, and correct temperature measurement, making it a promising candidate in healthcare functions.
a Schematic of the wearable contact lens sensor, integrating the glucose sensor and intra-ocular stress sensor (reproduced with permission from Ref. [93] Copyright 2017 Nature). b Structural design of a wise contact lens with ultrathin MoS2 transistor-based serpentine mesh sensor (reprinted with permission from Ref. [32] Copyright 2021 Elsevier). c Schematic illustration of the built-in system of the diagnostic and therapeutic units for the real-time monitoring and remedy of continual operational stress harm (reprinted with permission from Ref. [140] Copyright 2021 Science). d {Photograph} of an grownup carrying the sensible contact lens on her eye for cortisol degree monitoring (reprinted with permission from Ref. [2] Copyright 2020 Science)
Whereas nearly all of sensible contact lenses primarily deal with monitoring glucose ranges or intraocular stress, Jang et al. [140] developed a graphene FET biosensor to quantitatively diagnose ocular floor irritation (OSI) primarily based on the focus of MMP-9 in tears, Fig. 14c. By integrating a wise contact lens with a skin-attachable therapeutic system, the system can wirelessly monitor by tears. The FET biosensor is built-in with a wi-fi antenna, capacitors, resistors, and an NFC chip through stretchable interconnects to make sure that it doesn’t hinder the wearer’s field of regard. The outcomes are wirelessly transmitted to the person’s cellular system in real-time, permitting non-invasive analysis of OSI. Moreover, Ku et al. [2] developed a wise contact lens to detect cortisol in tear. The graphene FET sensor was fabricated by immobilizing a monoclonal antibody (C-Mab) onto the graphene floor, Fig. 14d. The platform was capable of measure cortisol concentrations in actual time with a detection restrict of 10 pg/ml, throughout the vary in human tears. Integration of cortisol sensor with a clear antenna and wi-fi communication circuitry allows smartphones remotely managed with out obstructing the person’s line of sight. In vivo exams utilizing reside rabbits and human topics confirmed the superb biocompatibility and reliability of the lens.
Saliva-based sensors
Saliva is an oral fluid primarily produced by the parotid gland. Saliva includes varied elements, reminiscent of metabolites, hormones, enzymes, microorganisms, proteins, and ions [165, 166]. Saliva is usually sampled by passive drooling straight into a tool [167] or with using a swab [168]. Integrating saliva sensors with units positioned within the mouth, reminiscent of toothbrushes [169], mouthguards [170], pacifiers [171], and even enamel, permits for in-situ sampling and detection of analytes. In-mouth biosensing platforms supply a painless and handy technique for acquiring real-time chemical info from saliva. Regardless of its potential for monitoring well being, not many developments of wearable oral biosensors have been reported in literature. Of their pioneering work, Bao et al. [21] launched an built-in wearable healthcare platform for monitoring ions, reminiscent of ammonium (NH4+), potassium (Okay+), and calcium (Ca2+). The platform was fabricated utilizing 3D printing strategies, which permits for a direct connection between the oxide FETs and ion-sensitive electrodes, ensuing within the formation of hybrid ISFETs, Fig. 15a. The check outcomes on synthetic saliva confirmed that reported ISFET displays excessive sensitivity and selectivity even in interfering ions environments.
a Schematic of the applying for selective ion detection in synthetic saliva ISFET (reprinted with permission from Ref. [21] Copyright 2019 Elsevier). b Schematic illustration of a G-FET system utilized for biosensing (reprinted with permission from Ref. [142] Copyright 2020 Willey). c The system fabrication processes and system exams for evaluating the digital options of the naked Lg-GFETs (reprinted with permission from Ref. [81] Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society). d Schematic illustration of the extended-gate-type OFET sensor for oxytocin detection (reprinted with permission from Ref. [40] Copyright 2022 RSC)
Equally, Kumar et al. [142] developed oral biosensing to detect human carbonic anhydrase 1 (CA1)—a biomarker for diagnosing a number of ailments reminiscent of diabetes, pancreatitis, cancers, and Sjogren’s syndrome, Fig. 15b. Graphene-based FETs functionalized with RNA aptamer have been employed with liquid gating to reduce voltage vary, preserving unique buildings and aptamers. The G-FET biosensors exhibited a low detection restrict of 10 pg/ml in simply 30 min. Likewise, Zhang et al. [81] launched a transportable salivary cortisol check utilizing liquid gate graphene FET (Lg-GFET), as proven in Fig. 15c. This sensor not solely has glorious dynamic vary of seven logs (0.01 to 104 nM), however it additionally has sturdy anti-interference capabilities to differentiate between substances with comparable chemical buildings. The mixture of the cortisol sensor platform, measuring block, and put in software on cellphones permits customers to conveniently use it at house. As well as, Ohshiro et al. [40] developed extended-gate natural FET sensor detect oxytocin in saliva, Fig. 15d. Via a functionalized extended-gate electrode, the system can discriminate between hormones with solely barely totally different chemical buildings, reaching correct oxytocin detection with a LOD worth of 0.57 pg/mL.
Pores and skin interstitial fluid-based sensors
Pores and skin interstitial fluid (ISF) is the fluid surrounding cells, by the method of diffusion, ISF maintains steady equilibrium with the blood capillaries, serving as a bridge between blood and cells [172]. ISF is probably the most accessible bodily fluid, primarily current within the subcutaneous tissue layer, constituting 70% of the amount [173]. ISF has been demonstrated to correlate with blood, containing important info for monitoring physiological indicators and will be collected non-invasively and repeatedly [174]. Essentially the most detected biomarker stays glucose for diabetes analysis over previous few a long time.
Usually, measuring the focus of drugs in ISF is carried out with microneedles. These microneedles have confirmed to be extremely environment friendly in measuring sodium ranges in ISFs, with out inflicting discomfort to the person [175,176,177]. Nevertheless, typical microneedles typically possess inflexible buildings, making them unsuitable for functions in units that require elasticity or flexibility. To deal with this limitation, Zheng et al. [144] developed an extended-gate FET biosensor able to stretching to detect sodium, a biomarker to minimal invasively analysis of dysnatremia. The FET sensor included an prolonged gate made from microneedles penetrating the pores and skin to entry ISF the place sodium is measured. The reported system exhibited excessive sensitivity, real-time monitoring, glorious biocompatibility, low detection limits, and mechanical stability on the physique. Lately, Capua et al. [35] developed an FET biosensor utilizing silicon nanowire arrays to detect C-reactive protein in ISF. The authors used SiNW arrays immobilized with antibody fragments to beat Debye screening and enabled label-free detection. Reference subtraction technique was utilized to make sure particular protein detection. The reported FET sensors facilitated real-time analysis and detected CRP throughout the vary of physiological focus 60 ng/mL to 100 μg/mL.
Challenges and alternative
Technical issues
Some FETs made from conventional supplies are dealing with issues reminiscent of leaking currents, when a channel’s floor will not be easy sufficient on the nanoscale [178,179,180,181]. To deal with these problem, Chhowalla et al. [182] listed three key options of FETs: (1) a really perfect insulator materials to stop leakage present between the gate, supply, and drain electrodes, (2) no leakage voltage drop between the contacts, and (3) a tool design that avoids electron scattering within the channel. Moreover, environmental stability, managed and steady doping, and uniform development are important for growing an efficient FET.
Standardization additionally performs a significant position within the fabrication, characterization, and efficiency analysis of FET biosensors. Standardization ensures the standard, reliability, and interoperability of those sensors. Presently, the shortage of standardization poses challenges for evaluating and reproducing FET sensors throughout totally different research and platforms. To deal with this concern, establishing commonplace protocols and pointers is important. This may be achieved by reference supplies, growing widespread metrics for analysis, and sharing information and finest practices amongst researchers [183]. By implementing standardization, researchers and builders can enhance the consistency, comparability, and reliability of FET biosensors to advance sensible functions in a spread of fields.
One other problem with epidermal electronics is that they sometimes contain difficult information processing circuits and want to speak wirelessly, that are each tough to implement [183]. One promising answer on the horizon are microwave sensors, that are primarily based on modifications within the electromagnetic properties of the sensing supplies at ultrahigh frequencies (ca. > 1 GHz). Moreover, novel bioenergy options are important to transition from typical laboratory-based sensing to environment friendly wearable biosensing. These might embody self-powered wearable biosensing techniques built-in with biofuel cells or battery-free choices using NFC expertise [13].
Organic challenges
There are a number of challenges related to analyzing biofluid with a small quantity, which tends to evaporate rapidly. Moreover, there’s a nice danger of contamination, significantly when saliva is concerned and could also be blended with meals or drink residues. Moreover, the variability in assortment time poses a problem [9]. To deal with these points, microfluidic techniques have emerged, which not solely supply exact management over pattern manipulation but in addition decreasing evaporation. Moreover, incorporating permselective protecting sensor coatings may help stop the presence of macromolecules on the sensor floor.
Tear, saliva, sweat, interstitial fluids sometimes have decrease concentrations of analytes than in blood samples, thereby requiring ultrasensitive biosensors to make sure correct detection. It is usually essential to think about the biocompatibility of supplies included in these biosensors, significantly when coping with tear and saliva samples, to make sure their security to be used within the human physique. Lastly, it could be essential to undertake a complete examine involving numerous medical samples to validate the leads to non-traditional fluids [184].
Challenges in system integration and {hardware}
The event and implementation of wearable FET biosensor units entails integrating varied elements, together with sensors, sign processors, information transmitters, and a few type of energy administration, with the final word purpose of enabling non-invasive, steady, and correct monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. A number of approaches have been taken to construct dependable, snug, and user-friendly wearable biosensor techniques, reminiscent of versatile printed circuit boards, stretchable interconnects, wi-fi communication modules, and power harvesting or storage units [24]. Nevertheless, there are a number of challenges and trade-offs that must be addressed to realize the specified reliability, consolation, and user-friendliness of wearable biosensor techniques. First, a steadiness is required between the scale, weight, energy consumption, and efficiency of the system elements. This entails optimizing the design and deciding on the elements to make sure an optimum steadiness between these elements. Second, guaranteeing the biocompatibility and sturdiness of the supplies and sensors utilized in wearable biosensor techniques is essential. The supplies must be suitable with the human physique to stop any opposed reactions, whereas additionally being sturdy sufficient to face up to on a regular basis use and potential environmental elements. Third, sustaining the soundness and accuracy of biosensing indicators in numerous environmental and physiological situations is a problem. Wearable biosensor techniques ought to have the ability to present dependable measurements no matter variations in temperature, humidity, movement, and different elements which will have an effect on the indicators. Lastly, guaranteeing the safety and privateness of the info transmission and processing is of the utmost significance. Wearable biosensor techniques ought to incorporate sturdy encryption and authentication measures to safeguard the transmitted information and shield the person’s privateness [184].
Challenges in system stretchability
Relating to growing wearable biosensors, a key facet to think about is the mechanical mismatch between inflexible lively supplies and mushy human tissues/pores and skin. Lyu et al. [12, 13] have offered a complete assessment on mushy wearable units, highlighting two predominant methods for reaching stretchable units: deformable architectures and intrinsically stretchable supplies. Deformable architectures contain designing buildings that may deform or buckle below pressure. Some examples of deformable architectures embody buckling, microbelts, serpentine, holey, nanomesh, and kirigami. These designs enable the system to stretch and conform to the form of the human physique. Then again, intrinsically stretchable supplies are supplies that possess inherent stretchability. Generally used stretchable supplies for wearable units embody PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane), eco-flex, polyurethane, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polyimide. Leveraging deformable architectures and intrinsically stretchable supplies, researchers and engineers can develop wearable biosensors which can be versatile, snug to put on, and able to precisely monitoring varied physiological parameters.
Commercialization challenges and alternatives
Business sensors are anticipated to satisfy a spread of calls for, together with sensitivity, reliability, scalability, affordability, information safety, and real-time communication functionality [24]. These elements are important for the profitable adoption and commercialization of sensors throughout varied industries. As well as, future prospects of wearable FET biosensor units by way of commercialization is determined by the prevailing merchandise and firms concerned of their growth. It performs a big position in advancing wearable FET biosensor applied sciences and translating them into business markets. Regulatory approval is a vital hurdle that should be overcome to make sure compliance with related laws and requirements. Medical validation can be important to show the accuracy and effectiveness of wearable FET biosensors in medical settings, and to achieve acceptance from healthcare professionals and regulatory our bodies. Person acceptance is one other necessary consideration, as wearable FET biosensors must be designed with user-friendly interfaces and cozy kind elements to advertise engagement and adherence to monitoring protocols. Efficient information administration methods are essential to deal with the substantial quantity of knowledge generated by wearable FET biosensors, whereas on the similar time guaranteeing information privateness, integrity, and accessibility. Furthermore, the wearable biosensor market is extremely aggressive. Corporations have to differentiate themselves by distinctive options, superior efficiency, and aggressive pricing to achieve a foothold and thrive out there. In conclusion, wearable biosensors maintain nice potential to revolutionize healthcare and wellness [24]. Nevertheless, their profitable integration and widespread adoption necessitate multidisciplinary collaboration and innovation to beat technical, medical, and business boundaries. By addressing these challenges and leveraging rising alternatives, wearable FET biosensors can drive transformative developments in healthcare, contributing to improved affected person outcomes and total well-being.