Cybersecurity researchers have found beforehand undocumented payloads related to a Romanian risk actor named Diicot, revealing its potential for launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults.
“The Diicot title is important, as it is also the title of the Romanian organized crime and anti-terrorism policing unit,” Cado Safety mentioned in a technical report. “As well as, artifacts from the group’s campaigns include messaging and imagery associated to this group.”
Diicot (née Mexals) was first documented by Bitdefender in July 2021, uncovering the actor’s use of a Go-based SSH brute-forcer instrument referred to as Diicot Brute to breach Linux hosts as a part of a cryptojacking marketing campaign.
Then earlier this April, Akamai disclosed what it described as a “resurgence” of the 2021 exercise that is believed to have began round October 2022, netting the actor about $10,000 in illicit income.
“The attackers use an extended chain of payloads earlier than ultimately dropping a Monero cryptominer,” Akamai researcher Stiv Kupchik mentioned on the time. “New capabilities embody utilization of a Safe Shell Protocol (SSH) worm module, elevated reporting, higher payload obfuscation, and a brand new LAN spreader module.”
The most recent evaluation from Cado Safety exhibits that the group can also be deploying an off-the-shelf botnet known as Cayosin, a malware household that shares traits with Qbot and Mirai.
The event is an indication that the risk actor now possesses the power to mount DDoS assaults. Different actions carried out by the group embody doxxing of rival hacking teams and its reliance on Discord for command-and-control and information exfiltration.
“Deployment of this agent was focused at routers operating the Linux-based embedded gadgets working system, OpenWrt,” the cybersecurity firm mentioned. “The usage of Cayosin demonstrates Diicot’s willingness to conduct quite a lot of assaults (not simply cryptojacking) relying on the kind of targets they encounter.”
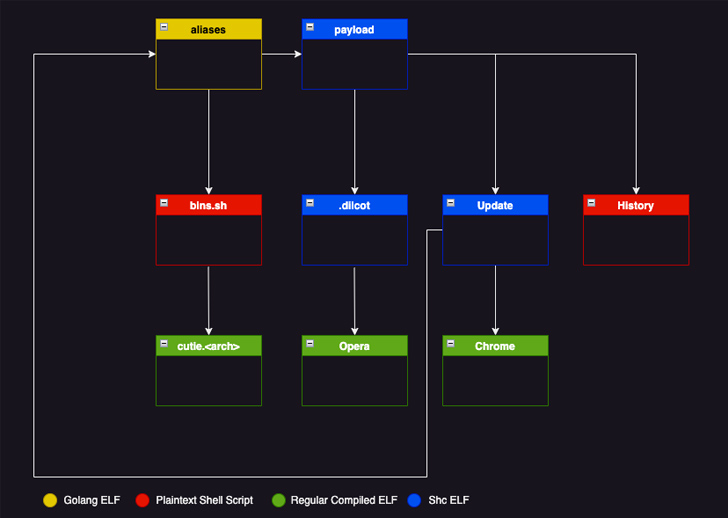
Diicot’s compromise chains have remained largely constant, leveraging the customized SSH brute-forcing utility to realize a foothold and drop further malware such because the Mirai variant and the crypto miner.
Among the different instruments utilized by the actor are as follows –
- Chrome – An web scanner based mostly on Zmap that may write the outcomes of the operation to a textual content file (“bios.txt”).
- Replace – An executable that fetches and executes the SSH brute-forcer and Chrome if they do not exist within the system.
- Historical past – A shell script that is designed to run Replace
The SSH brute-forcer instrument (aka aliases), for its half, parses the textual content file output of Chrome to interrupt into every of the recognized IP addresses, and if profitable, establishes distant connection to the IP handle.
🔐 Mastering API Safety: Understanding Your True Assault Floor
Uncover the untapped vulnerabilities in your API ecosystem and take proactive steps in the direction of ironclad safety. Be a part of our insightful webinar!
That is then adopted by operating a sequence of instructions to profile the contaminated host and utilizing it to both deploy a cryptominer or make it act as a spreader if the machine’s CPU has lower than 4 cores.
To mitigate such assaults, organizations are really useful to implement SSH hardening and firewall guidelines to restrict SSH entry to particular IP addresses.
“This marketing campaign particularly targets SSH servers uncovered to the web with password authentication enabled,” Cado Safety mentioned. “The username/password record they use is comparatively restricted and consists of default and easily-guessed credential pairs.”