MspA engineered nanopore permits for high-resolution detection of modifications on RNA.
Organic macromolecules (DNA, RNA, and proteins) after synthesis endure varied chemical modifications within the type of chemical teams being added onto their residues. These modifications act as markers and carry further data for exactly regulating gene expression. Protein post-translational modifications have been the main focus for a few years owing to their pharmacological roles in mobile modulation, thus making them engaging targets for drug discovery. Nevertheless, the function of RNA modifications has gained a whole lot of momentum lately as modified non-coding RNAs (microRNA, lincRNA, and many others.) have emerged as key gamers in mobile processes and illness development1,2. Amongst all RNA species, essentially the most closely modified are rRNA and tRNA, and to this point greater than 170 such modifications have been recognized3. Conventional strategies to establish RNA modifications have been chromatography methods and mass spectrophotometry4, and much more modifications have been newly found on account of developments in chemical strategies mixed with high-throughput sequencing. Nonetheless, on account of restricted availability of methods to sensitively and precisely establish these modifications, the rising discipline of RNA epitransciptomics stays troublesome to discover; primarily given the problem in discriminating between their comparable chemical constructions. Within the newest situation of Nature Nanotechnology, Wang et. al. report a nanopore-based technique that allows high-resolution detection of modifications on RNA5. Utilizing this technique, the authors have been in a position to distinguish eleven totally different modified nucleoside monophosphates (NMPs) with their customized base caller that studies a 99.6% accuracy.
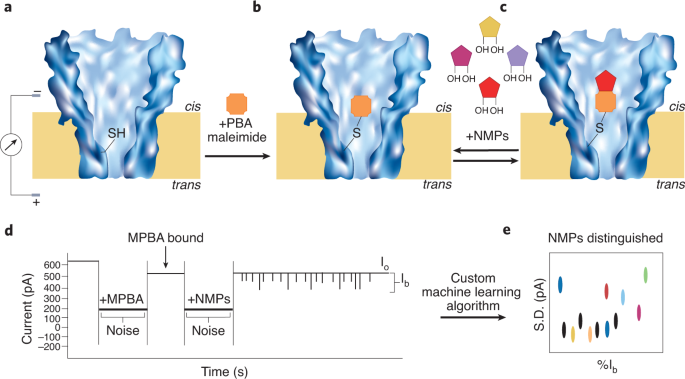
Organic nanopores provide a platform for tuneable sensing and real-time detection of single-molecules. On this proof-of-concept examine, Wang and associates report the design of a Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A (MspA) protein the place they engineered a single cysteine in its slim pore constriction. The one cysteine residue then served as an adapter for phenylboronic acid (PBA), a compound that may covalently react with cis-diols, thus appearing as an environment friendly sensor for reacting with the cis-diols current within the ribose of NMPs. Single-channel present recordings confirmed a ~100 pA drop in present as in comparison with the open channel present, instantly upon the addition of PBA. This instructed the binding of PBA with the cysteine, thereby occupying the pore. The authors first examined if the 4 canonical nucleotides might be individually detected with this MspA-PBA system. When a 200 mV voltage bias was repeatedly utilized to the nanopore, consultant present pulses have been noticed for the NMPs examined and simultaneous detection of all 4 nucleotides (AMP, CMP, UMP, GMP) produced distinct present blockade occasions for every NMP (Fig. 1).
a, MspA porin with a single cysteine engineered in its pore constriction. b, Upon the addition of 3-maleimide PBA, it reacts with the thiol of the cysteine residue, which leads to a ~100 pA drop within the present. This now represents the open channel present (Io), as proven in d. c, When NMPs are added to the cis aspect of the pore, it will probably reversibly bind with the PBA. d, This binding is noticed as stochastic sensing occasions. e, Uncooked present blockage knowledge is then fed into the customized machine studying algorithm and the present blockage ranges (Ib) vs noise (as commonplace deviation) are plotted to acquire a scatter plot of all of the NMP occasions.
Aside from essentially the most considerable N6-methyladenosine (M6A) modification discovered on mRNA, another related RNA modifications embody 5-methylcytosine (m5C), 7-methylguanosine (m7G), N1-methyladenosine(m1A), pseudouridine (Ψ), inosine (I) and dihydrouracil (D) (ref. 6). The authors subsequent examined seven of those epigenetic RNA modified compounds (m5C, m6A, m7G, m1A, I, Ψ and D) together with the 4 canonical NMPs. Nanopore present blockade occasions confirmed clear variations amongst all of the eleven kinds of NMPs, apart from UMP and m5C, which confirmed some overlap. Nevertheless, to additional discriminate all populations, plotting the noise (as commonplace deviation) versus the proportion blockage ranges resulted in full decision of all moieties. This factors to the sensitivity of the MspA-PBA system in having the ability to distinguish all eleven kinds of NMPs examined and discriminate structural variations among the many canonical counterparts.
The principle problem was to precisely detect and establish the delicate variations within the modifications. The authors constructed a customized machine studying algorithm which used consultant knowledge occasions that have been generated for every NMP and used this data-set for coaching right into a machine studying algorithm. The classifier algorithm was in a position to distinguish every of the NMP moieties with a powerful near 100% accuracy.
The feasibility of this MspA-PBA system mixed with the machine studying algorithm was put to check by detecting naturally occurring RNAs resembling microRNA and likewise tRNA, which is understood to have some of the complicated modifications6. In separate experiments, every of those RNAs have been first enzymatically degraded after which added onto the cis aspect of the nanopore. NMP compositions obtained from the uncooked occasions from every of the RNA subsets have been per the precise sequence, suggesting that every sort of occasion is identifiable and quantifiable by the algorithm.
This nanopore-based PBA sensor might function a place to begin for exonuclease-based sequencing the place cleaved nucleotides could be sequentially fed into the nanopore sensor for detection. This sensor coupled with a direct RNA sequencing strategy, resembling that of Oxford Nanopore Applied sciences sequencing technique7,8, might allow full-length epitrancriptome profiling of RNAs.
The results of viral RNA modifications have been within the limelight extra not too long ago9, given their significance in SARS-CoV-2 an infection the place the SARS-CoV-2 RNA incorporates a number of modifications resembling m6A, Ψ and a pair of′-O-methylation. Nevertheless, one of many limitations of this MspA-PBA system is that it can not detect ribose modified NMPs, resembling 2′-O-methylcytidine.
This MspA-PBA system presents a promising strategy for nanopore primarily based sequencing of epigenetic RNA modifications. Nonetheless, there are some things to bear in mind, transferring ahead with this method: library preparation would possibly require further purification steps to take away sure reagents current within the combination that would contribute to the noise throughout electrophysiological recordings. Extracting RNA from organic samples, for instance, microRNA from tissues, is troublesome due to their low abundance. Additionally, additional mannequin coaching of the algorithm can be required as newer kinds of modifications get recognized.
References
-
Ontiveros, R. J., Stoute, J. & Liu, Okay. F. Biochem. J. 476, 1227–1245 (2019).
-
Rong, D. et al. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids. 25, 67–82 (2021).
-
Boccaletto, P. et al. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 46, D303–D307 (2018).
-
Helm, M. & Motorin, Y. Nat. Rev. Genet. 18, 275–291 (2017).
-
Wang, Y. et al. Nat. Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01169-2 (2022).
-
Roundtree, I. A., Evans, M. E., Pan, T. & He, C. Cell 169, 1187–1200 (2017).
-
Leger, A., Amaral, P. P. & Pandolfini, L. et al. Nat. Commun. 12, 7198 (2021).
-
Xu, L. & Seki, M. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 25–33 (2020).
-
Izadpanah, A., Rappaport, J. & Datta, P. Okay. Entrance. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 849298 (2022).
Creator data
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding creator
About this text
Cite this text
Punthambaker, S. Detection of modified RNA with an engineered nanopore.
Nat. Nanotechnol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01210-4