Lately, the Division of Homeland Safety (DHS) recognized the necessity to encourage hands-on studying by cybersecurity competitions to deal with a scarcity of expert cyber defenders. Likewise, in 2019, Govt Order 13870 addressed the necessity to establish, problem, and reward america authorities’s greatest cybersecurity practitioners and groups throughout offensive and defensive cybersecurity disciplines. Properly-developed cybersecurity competitions provide a manner for presidency organizations to satisfy that order.
The Software program Engineering Institute (SEI) has been working with the DHS Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) to deliver distinctive cybersecurity challenges to the federal cyber workforce. This weblog put up highlights the SEI’s expertise growing cybersecurity challenges for the President’s Cup Cybersecurity Competitors and general-purpose tips and greatest practices for growing efficient challenges. It additionally discusses instruments the SEI has developed and made freely out there to help the event of cybersecurity challenges. The SEI technical report Problem Improvement Pointers for Cybersecurity Competitions explores these concepts in larger element.
The Objective and Worth of Cybersecurity Challenges
Cybersecurity challenges are the center of cybersecurity competitions. They supply the hands-on duties opponents carry out as a part of the competitors. Cybersecurity challenges can take a number of types and might contain totally different responses, resembling performing actions on one or many digital machines (VM), analyzing varied kinds of information or information, or writing code. A single cybersecurity competitors would possibly comprise a number of totally different challenges.
The objective of those cybersecurity challenges is to show or assess cybersecurity expertise by hands-on workouts. Consequently, when constructing challenges, builders choose mission-critical work roles and duties from the Nationwide Initiative for Cybersecurity Training Workforce Framework for Cybersecurity (NICE Framework), a doc printed by the Nationwide Institute of Requirements in Know-how (NIST) and the Nationwide Initiative for Cybersecurity Careers and Research (NICCS). The NICE Framework defines 52 work roles and supplies detailed details about the particular data, expertise, and skills (KSAs) required to carry out duties in every.
Utilizing the NICE Framework helps builders focus challenges on essential expertise that greatest symbolize the cybersecurity workforce. Every problem clearly states which NICE work position and duties it targets. By figuring out the data and expertise every problem targets, opponents can simply give attention to challenges that handle their strengths through the competitors and isolate studying alternatives when utilizing challenges for coaching.
Problem Planning
Creating profitable cybersecurity challenges begins with complete planning to find out the extent of issue for every problem, assessing the factors out there for every problem, and figuring out the instruments required to unravel the challenges. By way of issue, competitors organizers need contributors to really feel engaged and challenged. Challenges which can be too straightforward will make extra superior contributors lose curiosity, and challenges which can be too arduous will frustrate opponents. Competitions usually ought to embrace challenges which can be appropriate for all ranges—newbie, intermediate, and superior.
Scoring
Factors programs are used to reward opponents for the effort and time they spend fixing every problem. Furthermore, competitors organizers can use factors to find out competitor placement—opponents with increased scores can advance to future rounds, and organizers can acknowledge these with the very best factors as winners. Factors ought to be commensurate with the issue posed by the problem and energy required to unravel it. Level allocation is usually a subjective course of, a matter we are going to return to within the part Problem Testing and Overview part beneath.
Problem Tooling
Figuring out the instruments required to unravel a problem is a vital step within the improvement course of for 2 causes:
- It ensures that problem builders set up all required instruments within the problem atmosphere.
- It’s good follow to supply opponents a listing instruments out there within the problem atmosphere, particularly for competitions during which organizers present opponents with the evaluation atmosphere.
Builders ought to be cautious to construct challenges that don’t require using paid or licensed software program. Open supply or free instruments, purposes, and working programs are very important as a result of some opponents won’t have entry to sure software program licenses, which might put them at a drawback and even stop them from finishing altogether.
Problem Improvement
Builders have to be well-versed in cybersecurity material to plot revolutionary approaches to check opponents. Not solely should builders establish the talents the problem will goal and the state of affairs it can simulate, they need to additionally develop the technical facets of the problem, implement an automatic and auditable grading system, incorporate variability, and write documentation for each the testers and the opponents.
Pre-Improvement Concerns
Builders ought to start by figuring out the work roles and expertise their problem goals to evaluate. By so doing, they will construct extra exact challenges and keep away from together with duties that don’t assess relevant expertise or that take a look at too broad an array of expertise. After they’ve outlined the work position related to a given problem, builders can type a problem concept.
The problem concept contains the technical duties opponents should full and the placement during which the problem state of affairs will happen. All problem duties ought to resemble the duties that professionals undertake as a part of their jobs. Builders are free to be as artistic as they want when constructing the state of affairs. Topical challenges based mostly on real-world cybersecurity occasions provide one other manner so as to add distinctive and artistic situations to challenges.
Technical Part Concerns
The technical elements of problem improvement usually contain VM, community, and repair configuration. This configuration ensures the problem atmosphere deploys appropriately when opponents try the problem. Improvement of technical elements would possibly embrace:
- Configuring VMs or providers to include recognized vulnerabilities
- Configuring routers, firewalls, providers, and so forth., to the state builders need
- Staging assault artifacts or proof all through networks or logs
- Finishing different actions that put together the atmosphere for the problem
Builders may additionally purposefully misconfigure facets of the atmosphere if the problem targets figuring out and fixing misconfigurations.
Finest Practices for Growing Challenges
Every problem targets totally different expertise, so there isn’t any customary course of for growing a cybersecurity problem. Nevertheless, builders ought to apply the next greatest practices:
- Make sure the technical expertise assessed by the problem are relevant in the actual world.
- Make sure the instruments required to unravel the problem are free to make use of and out there to the opponents.
- Make a listing of the instruments out there to opponents within the hosted atmosphere.
- Guarantee challenges don’t power opponents down a single answer path. Opponents ought to be capable of clear up challenges in any sensible method.
- Take away pointless hints or shortcuts from the problem, together with command historical past, searching information, and different information that would permit opponents a shortcut to fixing the problem.
Problem Grading
Basically, builders ought to automate grading by an authoritative server that receives solutions from the opponents and determines what number of factors to award the submission. The submission system ought to usually ignore variations in capitalization, white area, particular characters, and different variations which can be in the end irrelevant to correctness. Doing so ensures opponents aren’t unfairly penalized for immaterial errors.
Ignoring these errors may appear to contradict an evaluation of operational readiness in instances the place precise precision is required. Nevertheless, cybersecurity competitions have targets and concerns past evaluating operational proficiency, resembling making certain a good competitors and inspiring broad participation.
Builders could apply totally different grading strategies, together with the next:
- Token discovery. In token-discovery grading, opponents should discover a string or token that follows an outlined format (these tokens will also be referred to as “flags”). Builders can place the token in any a part of the problem the place the competitor will discover it by finishing the problem duties.
- Query-and-answer issues. For question-and-answer issues, the competitor should discover the right reply to a number of questions by performing problem duties. The solutions to the problem questions can take a number of types, resembling coming into file paths, IP addresses, hostnames, usernames, or different fields and codecs which can be clearly outlined.
- Atmosphere verification. In atmosphere verification grading, the system grades opponents based mostly on adjustments they make to the problem atmosphere. Challenges can process opponents with fixing a misconfiguration, mitigating a vulnerability, attacking a service, or some other exercise the place success may be measured dynamically. When the grading system verifies adjustments to the atmosphere state, it supplies opponents with a hit token.
Problem Variation
Builders ought to embrace some degree of variation between totally different deployments of a problem to permit for various right solutions to the identical problem. Doing so is necessary for 2 causes. First, it helps promote a good competitors by discouraging opponents from sharing solutions. Second, it permits competitors organizers to reuse challenges with out dropping academic worth. Challenges that may be accomplished quite a few occasions with out leading to the identical reply allow opponents to be taught and hone their expertise by repeated follow of the identical problem.
Builders can introduce variation into challenges in a number of methods, relying on the kind of grading that they use:
- Token-based variation. Challenges utilizing token-discovery or environment-verification grading can randomly generate distinctive tokens for every competitor when the problem is deployed. Builders can insert dynamically generated submission tokens into the problem atmosphere (e.g., inserting guestinfo variables into VMs), and so they can copy them to the places the place they anticipate opponents to obtain the problem solutions.
- Query-and-answer variation. In question-and-answer challenges, builders can introduce variation by configuring totally different solutions to the identical questions or by asking totally different questions.
Problem Documentation
The 2 key paperwork builders should create in help of their problem are the problem information and the answer information.
The problem information, which is seen to the opponents, supplies a brief description of the problem, the talents and duties the problem assesses, the state of affairs and any background data that’s required to grasp the atmosphere, machine credentials, and the submission space or areas.
The problem doc ought to describe the state of affairs in a manner that opponents can simply comply with and perceive. The problem state of affairs and background data ought to keep away from logical leaps and the issue degree shouldn’t hinge on data internationally omitted of the information.
The answer information supplies a walk-through of 1 option to full the problem. Throughout testing, builders use the answer information to make sure the problem may be solved. Builders may also launch the answer information to the general public after the conclusion of the competitors to function a neighborhood studying useful resource.
The meant viewers for this information is the overall cybersecurity neighborhood. Consequently, builders ought to assume the reader is aware of fundamental IT and cybersecurity expertise, however is just not an knowledgeable within the discipline. Screenshots and different photographs are useful additions to those guides.
Problem Testing and Overview
After builders construct a problem, it ought to undergo a number of rounds of testing and evaluate. Builders take a look at challenges to make sure high quality, and so they evaluate them to estimate the problem’s issue.
Builders ought to carry out an preliminary spherical of testing to catch any errors that come up through the problem deployment and initialization course of. They need to additionally be sure that opponents can totally clear up the problem in not less than a method. A second spherical of testing ought to be carried out by certified technical employees unfamiliar with the problem. Testers ought to be inspired to aim fixing the problem on their very own however could also be supplied the developer’s answer information for assist.
The testers ought to guarantee every problem meets the next high quality assurance standards:
- The problem deploys as anticipated and with out errors.
- The problem VMs are accessible.
- The problem is solvable.
- There aren’t any unintentional shortcuts to fixing the problem.
- Problem directions and questions are correctly formatted and provides a transparent indication of what opponents should do.
Of their evaluate of the problem, testers ought to take notes concerning the content material, together with estimates of issue and size of time it might take opponents to unravel. After testers full their evaluate, competitors organizers can look at the issue assessments and examine every problem with others. This comparability ensures that simpler challenges stay in earlier rounds and are value fewer factors than challenges judged as harder.
When deciding problem level allocations, organizers can use a base or customary rating allotment as a place to begin (e.g., all challenges are value 1,000 factors initially of the method). Organizers can then improve or lower level allocations based mostly on the out there issue information, conserving in thoughts that the principle objective is for the variety of factors they allocate to a problem to straight correspond with the trouble required for fixing it. Level allocations ought to take into account each the issue and the time it takes to unravel the problem.
SEI Open Supply Functions for Cybersecurity Problem Competitions
Builders can use a number of open supply purposes to develop challenges and to orchestrate cybersecurity competitions. The SEI has developed the next two purposes for working cybersecurity competitions:
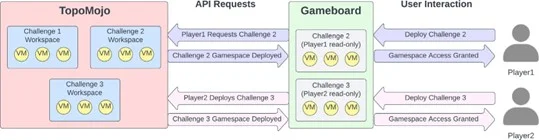
- TopoMojo is an open supply lab builder and participant utility that builders can use to develop cybersecurity challenges. It supplies digital workspaces during which problem improvement can happen. The workspaces permit builders so as to add VMs, digital networks, and some other assets which can be required for growing or fixing a single problem.
- Gameboard is an open supply utility that organizers can use for orchestrating cybersecurity competitions. It allows organizers to create competitions that may both be crew or particular person based mostly and that encompass both single or a number of rounds. Challenges are organized into rounds and opponents try to unravel as many challenges as they will to maximise their rating. Gameboard makes use of the TopoMojo API to deploy the opponents’ recreation area for every problem.
Gameboard additionally serves because the authoritative location for opponents to submit solutions or tokens. Furthermore, as a part of dealing with reply and token submissions, Gameboard has logging, brute power protections, and different options to make sure the integrity of the competitors.
Determine 1 exhibits how the TopoMojo and Gameboard purposes work together. Builders use TopoMojo workspaces to develop challenges. Opponents then use Gameboard to deploy and in- teract with challenges. When a participant deploys a problem, Gameboard will work together with the To- poMojo API to request a brand new recreation area for the competitor. TopoMojo creates and returns the participant’s problem recreation area.
Finest Practices Assist Higher Cybersecurity Competitions
The event practices we have now highlighted on this put up are the results of the SEI’s expertise growing cybersecurity challenges for the President’s Cup Cybersecurity Competitors. Cybersecurity competitions present a enjoyable and fascinating option to train technical expertise, establish and acknowledge cybersecurity expertise, and interact college students and professionals within the discipline. They will additionally function training and coaching alternatives. With america authorities, and the nation as a complete, going through a big scarcity within the cybersecurity workforce, cybersecurity competitions play an necessary position in growing and increasing the workforce pipeline.
There isn’t any single option to run a contest, and there’s no one option to develop cybersecurity challenges. Nevertheless, these greatest practices may also help builders make sure the challenges they create are efficient and fascinating. Problem improvement is the one most necessary and time-consuming side of working a cybersecurity competitors. It requires meticulous planning, technical improvement, and a rigorous quality-assurance course of. In our expertise, these practices guarantee efficiently executed competitions and enduring, hands-on cybersecurity belongings that competitors organizers and others can reuse many occasions over.
If you need to be taught extra concerning the work we do to strengthen the cybersecurity workforce and the instruments we have now developed to help this mission, contact us at information@sei.cmu.edu.