Inexperienced hydrogen will be produced by means of water electrolysis know-how, which makes use of renewable vitality to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen with out emitting carbon dioxide. Nevertheless, the manufacturing value of inexperienced hydrogen is presently round $5 per kilogram, which is 2 to 3 instances greater than grey hydrogen obtained from pure fuel.
For the sensible use of inexperienced hydrogen, innovation in water electrolysis know-how is required for the conclusion of hydrogen financial system, particularly for Korea the place the utilization of renewable vitality is restricted owing to geographical causes.
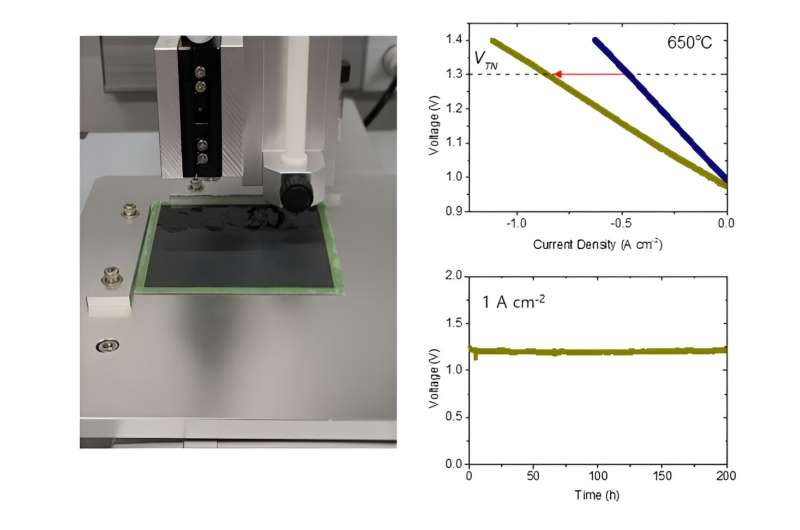
Dr. Kyung Joong Yoon’s analysis staff on the Power Supplies Analysis Heart of the Korea Institute of Science and Expertise (KIST) has developed a nanocatalyst for high-temperature water electrolysis that may retain a excessive present density of greater than 1A/cm2 for a protracted time period at temperatures above 600°. The work is printed within the Chemical Engineering Journal.
Whereas the degradation mechanisms of nanomaterials at excessive temperatures have been elusive so far, the staff recognized the basic causes of irregular habits of nanomateirals and efficiently resolved points, ultimately bettering efficiency and stability in practical water electrolysis cells.
The electrolysis know-how will be labeled into low- and high-temperature electrolysis. Whereas low-temperature electrolysis working at temperatures beneath 100° Celsius has lengthy been developed and is technologically extra mature, high-temperature electrolysis working above 600° Celsius presents greater effectivity and is taken into account as a next-generation know-how with a powerful potential for additional cost-down.
Nevertheless, its commercialization has been hindered by the dearth of thermal stability and inadequate lifetime owing to high-temperature degradation, equivalent to corrosion and structural deformation. Specifically, nanocatalysts, that are broadly used to enhance the efficiency of low-temperature water electrolyzers, shortly deteriorate at excessive working temperatures, making it tough to successfully use them for high-temperature water electrolysis.
To beat this limitation, the staff developed a brand new nanocatalyst artificial approach that suppresses the formation of dangerous compounds inflicting excessive temperature degradation.
By systematically analyzing the nanoscale phenomena utilizing transmission electron microscopy, the researchers recognized particular substances inflicting extreme structural alterations, equivalent to strontium carbonate and cobalt oxide and efficiently eliminated them to realize extremely steady nanocatalysts, when it comes to chemical and bodily properties.
When the staff utilized the nanocatalyst to a high-temperature water electrolysis cell, it greater than doubled hydrogen manufacturing charge and operated for greater than 400 hours at 650° with out degradation. This method was additionally efficiently utilized to a sensible large-area water electrolysis cell, confirming its sturdy potential for scale-up and business use.
“Our newly-developed nanomaterials achieved each excessive efficiency and stability for high-temperature water electrolysis know-how, and it may possibly contribute to decrease the manufacturing value of inexperienced hydrogen, making it economically aggressive with grey hydrogen sooner or later,” mentioned Dr. Kyungjoong Yoon of KIST.
“For commercialization, we plan to develop automated processing strategies for mass manufacturing in cooperation with business cell producers.”
Extra data:
Mi Younger Park et al, In situ synthesis of extraordinarily small, thermally steady perovskite nanocatalysts for high-temperature electrochemical vitality units, Chemical Engineering Journal (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.146924
Quotation:
Creating nanocatalysts to beat limitations of water electrolysis know-how (2023, December 28)
retrieved 28 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-nanocatalysts-limitations-electrolysis-technology.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


