On this submit I’m going to point out you ways I tracked the situation of my Tesla Mannequin 3 in actual time and plotted it on a map. I stroll via an finish to finish integration of requesting knowledge from the automobile, streaming it right into a Kafka Subject and utilizing Rockset to reveal the info through its API to create actual time visualisations in D3.

Getting began with Kafka
When beginning with any new software I discover it greatest to go searching and see the artwork of the potential. Inside the Rockset console there’s a catalog of out of the field integrations that will let you connect Rockset to any variety of present functions you might have. The one which instantly caught my eye was the Apache Kafka integration.
This integration lets you take knowledge that’s being streamed right into a Kafka matter and make it instantly obtainable for analytics. Rockset does this by consuming the info from Kafka and storing it inside its analytics platform nearly immediately, so you may start querying this knowledge immediately.
There are a selection of nice posts that define intimately how the Rockset and Kafka integration works and learn how to set it up however I’ll give a fast overview of the steps I took to get this up and operating.
Establishing a Kafka Producer
To get began we’ll want a Kafka producer so as to add our actual time knowledge onto a subject. The dataset I’ll be utilizing is an actual time location tracker for my Tesla Mannequin 3. In Python I wrote a easy Kafka producer that each 5 seconds requests the actual time location from my Tesla and sends it to a Kafka matter. Right here’s the way it works.
Firstly we have to setup the connection to the Tesla. To do that I used the Good Automotive API and adopted their getting began information. You may attempt it totally free and make as much as 20 requests a month. If you happen to want to make extra calls than this there’s a paid choice.
As soon as authorised and you’ve got all of your entry tokens, we will use the Good Automotive API to fetch our car data.
vehicle_ids = smartcar.get_vehicle_ids(entry['access_token'])['vehicles']
# instantiate the primary car within the car id record
car = smartcar.Car(vehicle_ids[0], entry['access_token'])
# Get car data to check the connection
data = car.data()
print(data)
For me, this returns a JSON object with the next properties.
{
"id": "XXXX",
"make": "TESLA",
"mannequin": "Mannequin 3",
"yr": 2019
}
Now we’ve efficiently linked to the automobile, we have to write some code to request the automobile’s location each 5 seconds and ship that to our Kafka matter.
from kafka import KafkaProducer
# initialise a kafka producer
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['localhost:1234'])
whereas True:
# get the automobiles location utilizing SmartCar API
location = car.location()
# ship the situation as a byte string to the tesla-location matter
producer.ship('tesla-location', location.encode())
time.sleep(5)
As soon as that is operating we will double examine it’s working through the use of the Kafka console client to show the messages as they’re being despatched in actual time. The output ought to look just like Fig 1. As soon as confirmed it’s now time to hook this into Rockset.
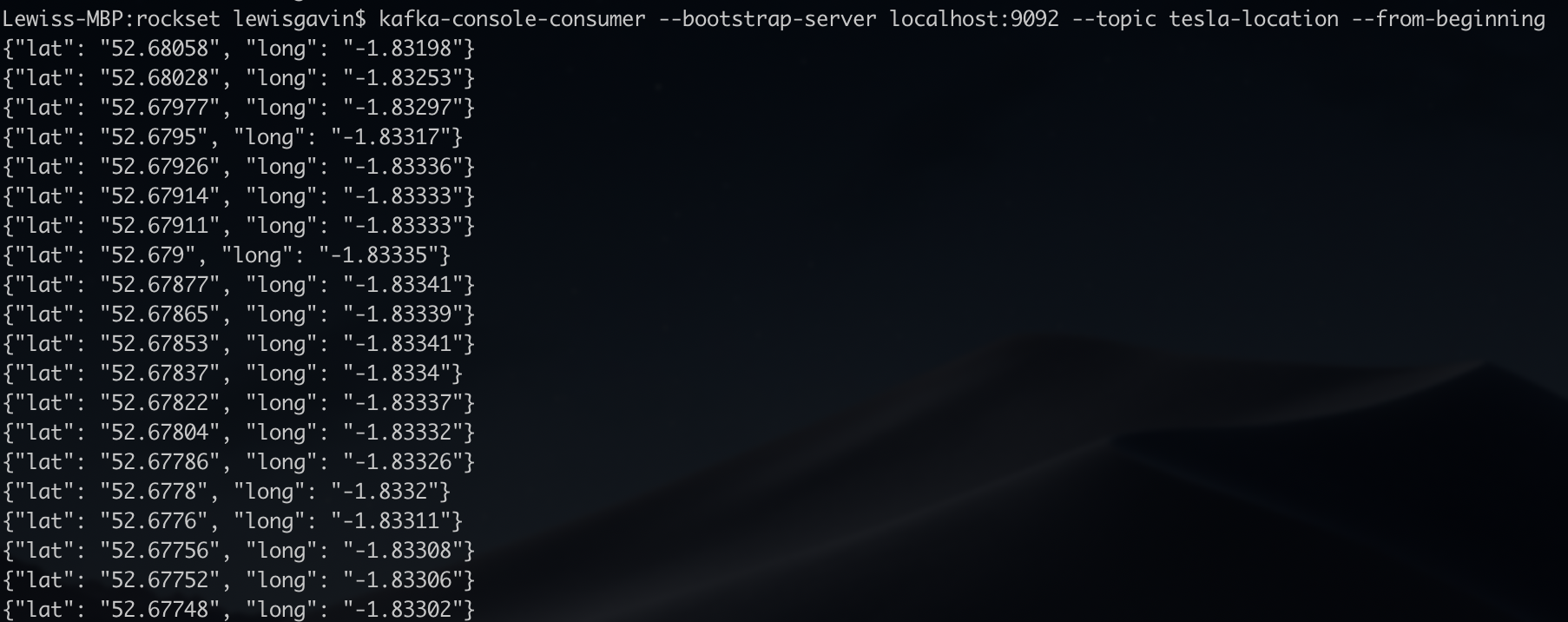
Fig 1. Kafka console client output
Streaming a Kafka Subject into Rockset
The workforce at Rockset have made connecting to an present Kafka matter fast and straightforward through the Rockset console.
- Create Assortment
- Then choose Apache Kafka
- Create Integration – Give it a reputation, select a format (JSON for this instance) and enter the subject identify (tesla-location)
- Observe the 4 step course of supplied by Rockset to put in Kafka Join and get your Rockset Sink operating
It’s actually so simple as that. To confirm knowledge is being despatched to Rockset you may merely question your new assortment. The gathering identify would be the identify you gave in step 3 above. So throughout the Rockset console simply head to the Question tab and do a easy choose out of your assortment.
choose * from commons."tesla-integration"
You’ll discover within the outcomes that not solely will you see the lat and lengthy you despatched to the Kafka matter however some metadata that Rockset has added too together with an ID, a timestamp and a few Kafka metadata, this may be seen in Fig 2. These will likely be helpful for understanding the order of the info when plotting the situation of the car over time.
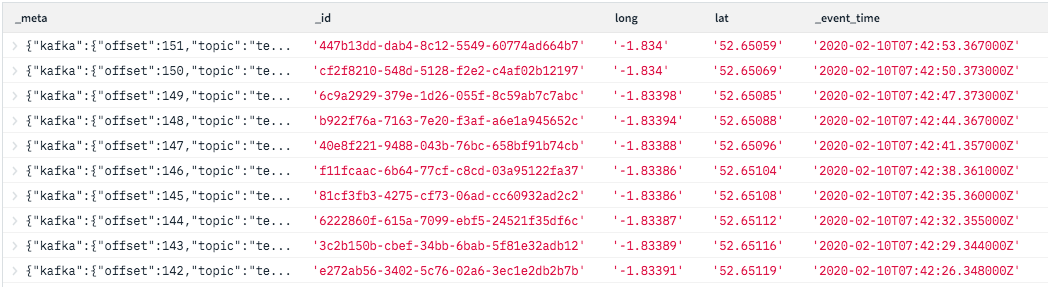
Fig 2. Rockset console outcomes output
Connecting to the REST API
From right here, my subsequent pure thought was learn how to expose the info that I’ve in Rockset to a entrance finish internet utility. Whether or not it’s the actual time location knowledge from my automobile, weblogs or some other knowledge, having this knowledge in Rockset now offers me the facility to analyse it in actual time. Slightly than utilizing the in-built SQL question editor, I used to be searching for a option to enable an internet utility to request the info. This was once I got here throughout the REST API connector within the Rockset Catalog.
Fig 3. Relaxation API Integration
From right here I discovered hyperlinks to the API docs with all the data required to authorise and ship requests to the in-built API (API Keys may be generated throughout the Handle menu, underneath API Keys).
Utilizing Postman to Check the API
After you have your API key generated, it’s time to check the API. For testing I used an utility known as Postman. Postman gives a pleasant GUI for API testing permitting us to shortly stand up and operating with the Rockset API.
Open a brand new tab in Postman and also you’ll see it’s going to create a window for us to generate a request. The very first thing we have to do is locate the URL we need to ship our request to. The Rockset API docs state that the bottom deal with is https://api.rs2.usw2.rockset.com and to question a set you could append /v1/orgs/self/queries – so add this into the request URL field. The docs additionally say the request sort must be POST, so change that within the drop down too as proven in Fig 4.
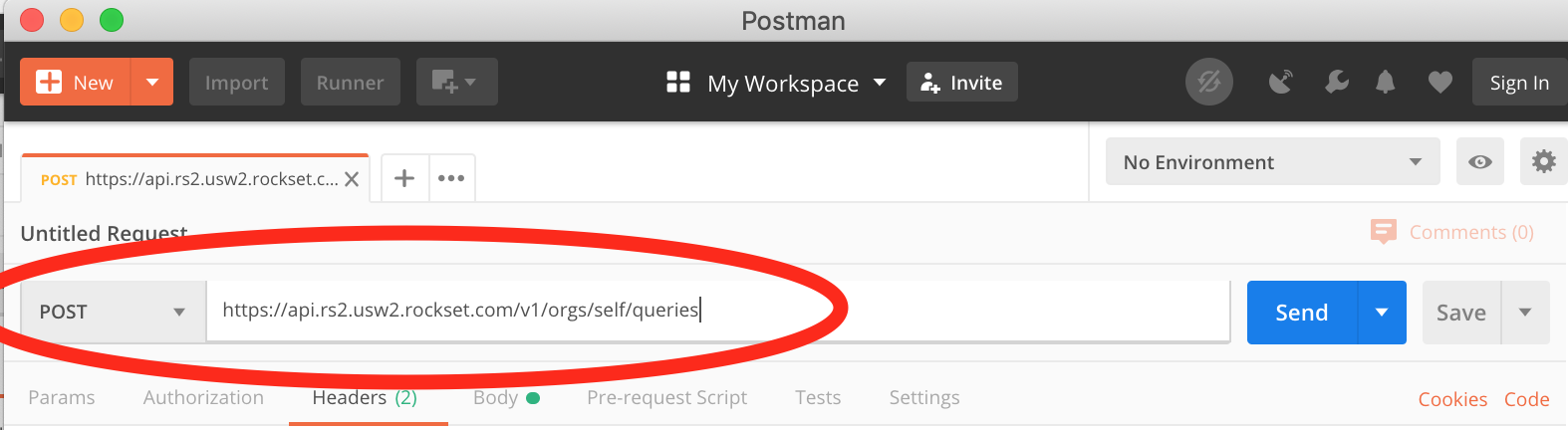
Fig 4. Postman setup
We are able to hit ship now and check the URL now we have supplied works. If that’s the case you need to get a 401 response from the Rockset API saying that authorization is required within the header as proven in Fig 5.
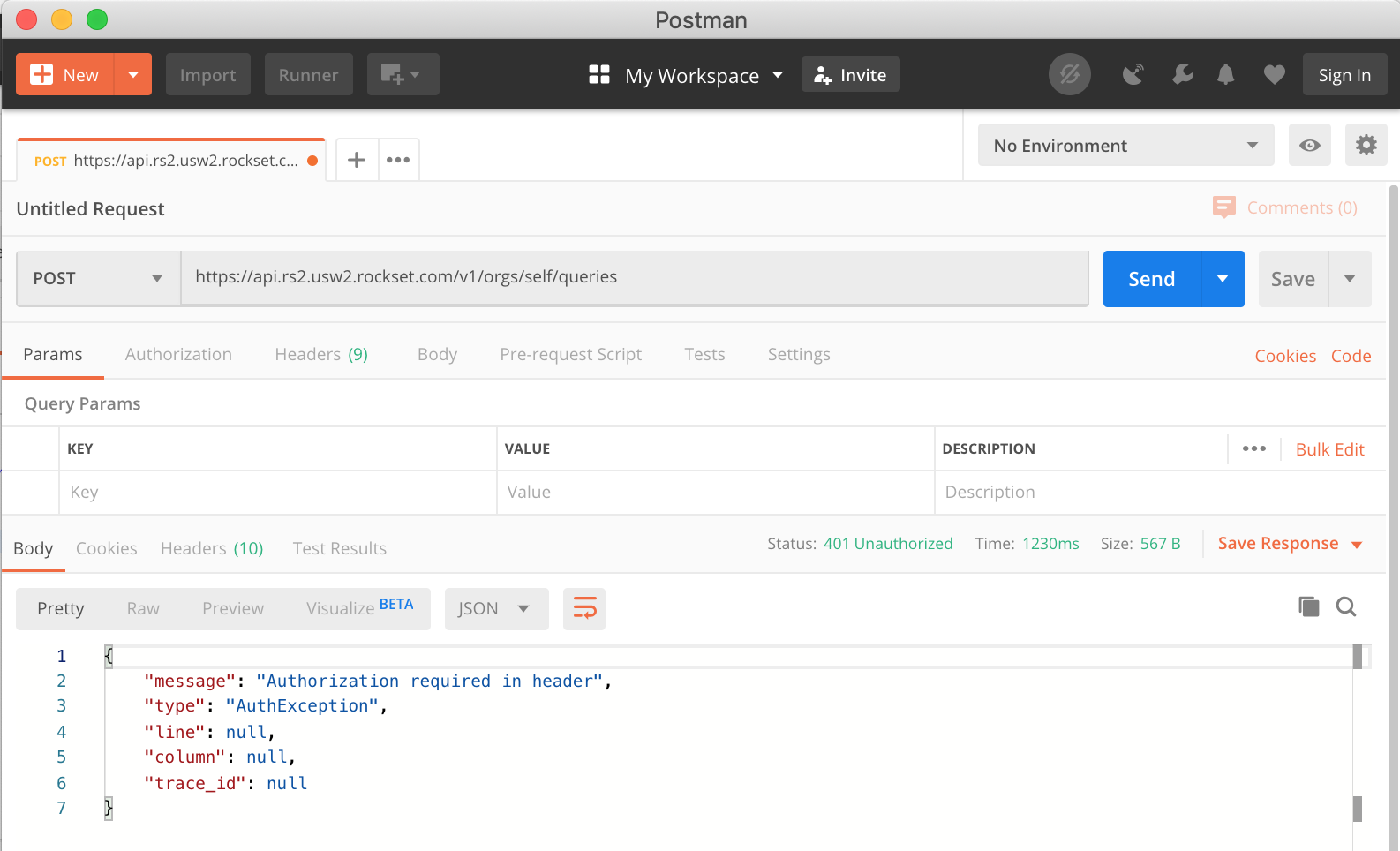
Fig 5. Auth error
To resolve this, we’d like the API Key generated earlier. If you happen to’ve misplaced it, don’t fear because it’s obtainable within the Rockset Console underneath Handle > API Keys. Copy the important thing after which again in Postman underneath the “Headers” tab we have to add our key as proven in Fig 6. We’re basically including a key worth pair to the Header of the request. It’s essential so as to add ApiKey to the worth field earlier than pasting in your key (mine has been obfuscated in Fig 6.) While there, we will additionally add the Content material-Kind and set it to utility/json.
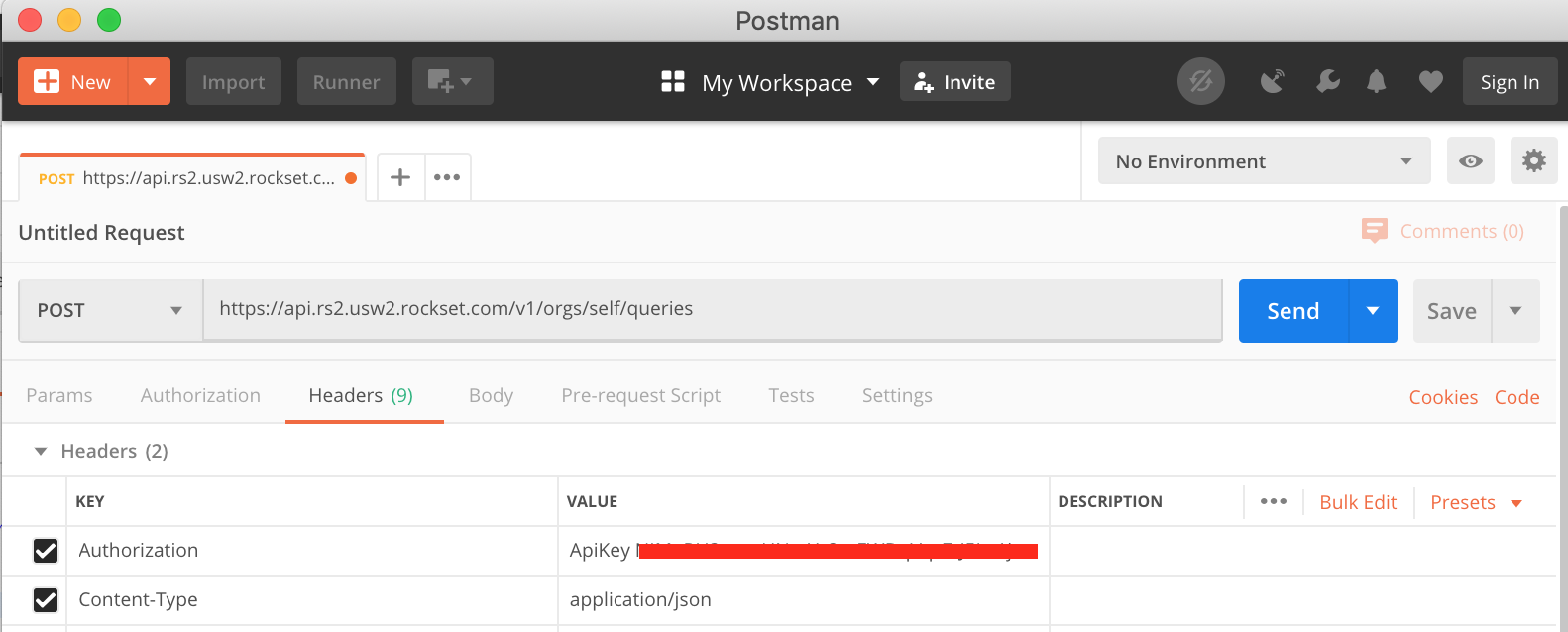
Fig 6. Postman authorization
Once more, at this level we will hit Ship and we must always get a unique response asking us to offer a SQL question within the request. That is the place we will begin to see the advantages of utilizing Rockset as on the fly, we will ship SQL requests to our assortment that may quickly return our outcomes to allow them to be utilized by a entrance finish utility.
So as to add a SQL question to the request, use the Physique tab inside Postman. Click on the Physique tab, be sure that ‘uncooked’ is chosen and make sure the sort is about to JSON, see Fig 7 for an instance. Inside the physique area we now want to offer a JSON object within the format required by the API, that gives the API with our SQL assertion.
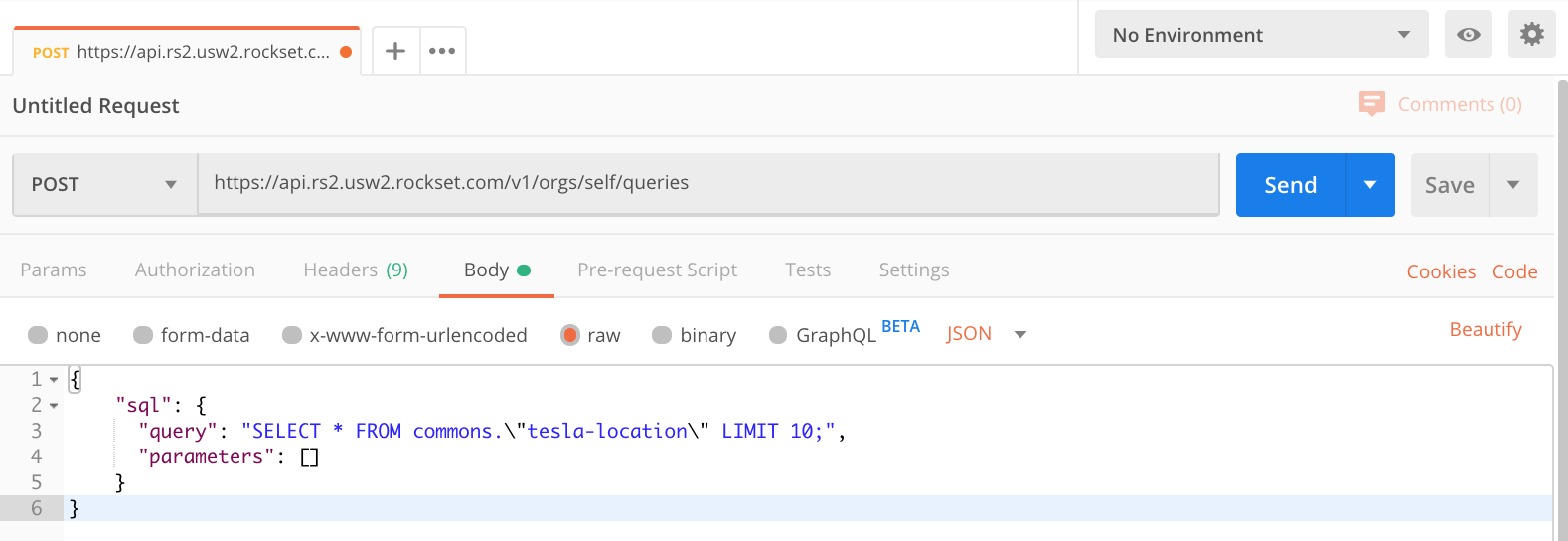
Fig 7. Postman uncooked physique
As you may see in Fig 7 I’ve began with a easy SELECT assertion to simply seize 10 rows of knowledge.
{
"sql": {
"question": "choose * from commons."tesla-location" LIMIT 10",
"parameters": []
}
}
It’s essential you employ the gathering identify that you simply created earlier and if it comprises particular characters, like mine does, that you simply put it in quotes and escape the quote characters.
Now we actually are able to hit ship and see how shortly Rockset can return our knowledge.
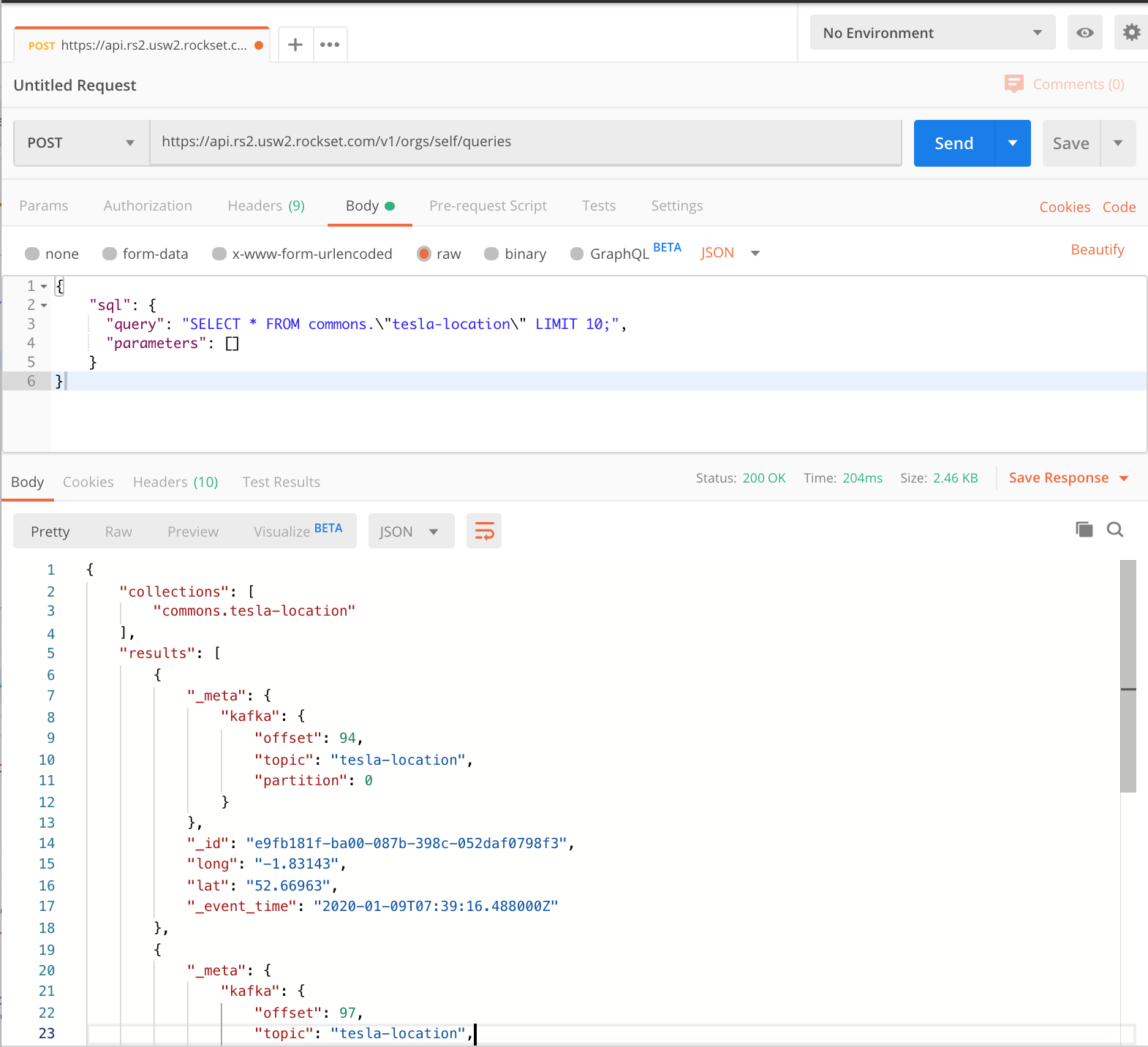
Fig 8. Rockset outcomes
Fig 8 exhibits the outcomes returned by the Rockset API. It gives a collections object so we all know which collections have been queried after which an array of outcomes, every containing some Kafka metadata, an occasion ID and timestamp, and the lat lengthy coordinates that our producer was capturing from the Tesla in actual time. In line with Postman that returned in 0.2 seconds which is completely acceptable for any entrance finish system.
After all, the chances don’t cease right here, you’ll typically need to carry out extra complicated SQL queries and check them to view the response. Now we’re all arrange in Postman this turns into a trivial activity. We are able to simply change the SQL and maintain hitting ship till we get it proper.
Visualising Information utilizing D3.js
Now we’re in a position to efficiently name the API to return knowledge, we need to utilise this API to serve knowledge to a entrance finish. I’m going to make use of D3.js to visualise our location knowledge and plot it in actual time because the automobile is being pushed.
The move will likely be as follows. Our Kafka producer will likely be fetching location knowledge from the Tesla each 3 seconds and including it to the subject. Rockset will likely be consuming this knowledge right into a Rockset assortment and exposing it through the API. Our D3.js visualisation will likely be polling the Rockset API for brand new knowledge each 3 seconds and plotting the most recent coordinates on a map of the UK.
Step one is to get D3 to render a UK map. I used a pre-existing instance to construct the HTML file. Save the html file in a folder and identify the file index.html. To create an internet server for this so it may be considered within the browser I used Python. When you’ve got python put in in your machine you may merely run the next to begin an internet server within the present listing.
python -m SimpleHTTPServer
By default it’s going to run the server on port 8000. You may then go to 127.0.0.1:8000 in your browser and in case your index.html file is setup accurately you need to now see a map of the UK as proven in Fig 9. This map would be the base for us to plot our factors.
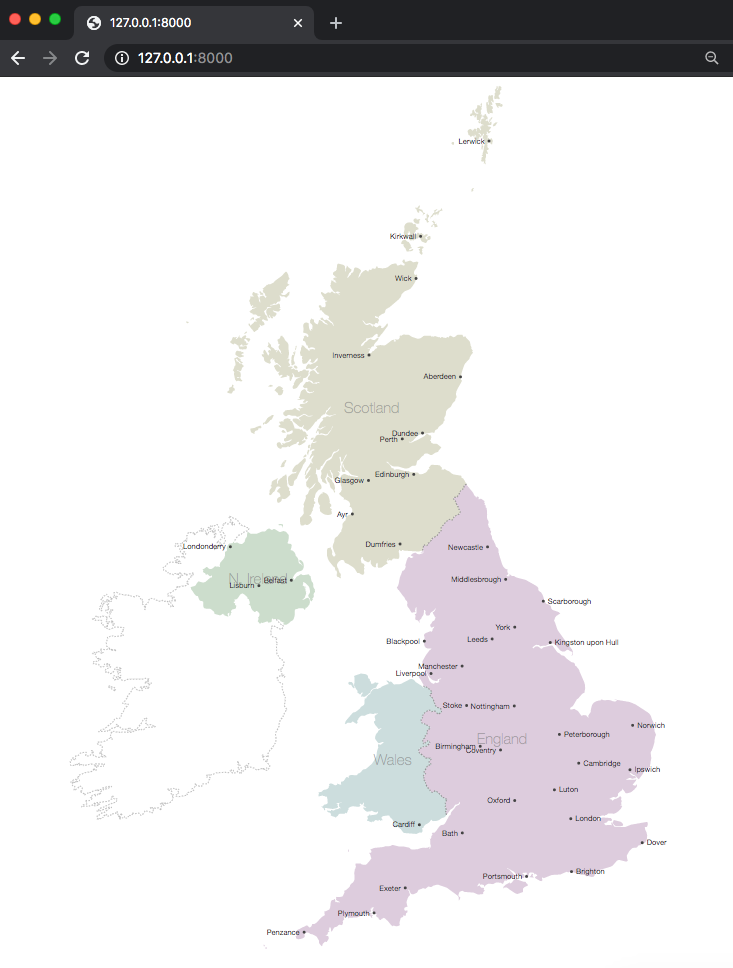
Fig 9. UK Map drawn by D3.js
Now now we have a map rendering, we’d like some code to fetch our factors from Rockset. To do that we’re going to put in writing a perform that may fetch the final 10 rows from our Rockset assortment by calling the Rockset API.
perform fetchPoints(){
// initialise SQL request physique utilizing postman instance
var sql="{ "sql": { "question": "choose * from commons."tesla-location" order by _event_time LIMIT 10","parameters": [] }}"
// ask D3 to parse JSON from a request.
d3.json('https://api.rs2.usw2.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self/queries')
// setting headers the identical means we did in Postman
.header('Authorization','ApiKey AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGG1234567')
.header('Content material-Kind','utility/json')
// Making our request a POST request and passing the SQL assertion
.submit(sql)
.response(perform(d){
// now now we have the response from Rockset, lets print and examine it
var response = JSON.parse(d.response)
console.log(response);
// parse out the record of outcomes (rows from our rockset assortment) and print
var newPoints = response.outcomes
console.log(newPoints)
})
}
When calling this perform and operating our HTTP server we will view the console to take a look at the logs. Load the webpage after which in your browser discover the console. In Chrome this implies opening the developer settings and clicking the console tab.
You must see a printout of the response from Rockset displaying the entire response object just like that in Fig 10.
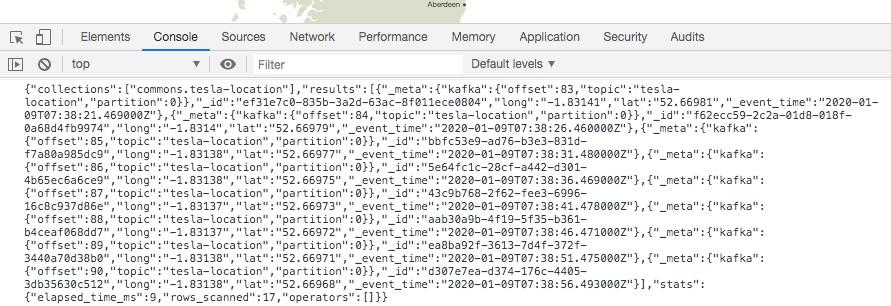
Fig 10. Rockset response output
Beneath this ought to be our different log displaying the outcomes set as proven in Fig 11. The console tells us that it is an Array of objects. Every of the objects ought to characterize a row of knowledge from our assortment as seen within the Rockset console. Every row consists of our Kafka meta, rockset ID and timestamp and our lat lengthy pair.
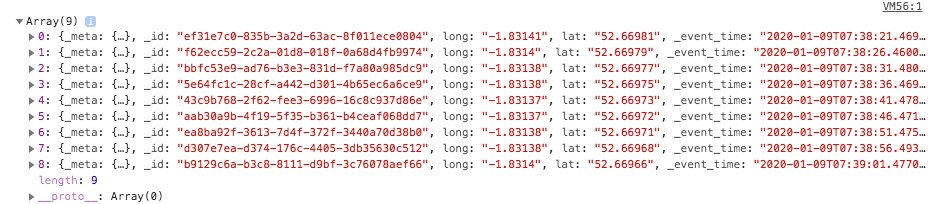
Fig 11. Rockset outcomes log
It’s all coming collectively properly. We now simply must parse the lat lengthy pair from the outcomes and get them drawn on the map. To do that in D3 we have to retailer every lat lengthy inside their array with the longitude in array index 0 and the latitude in array index 1. Every array of pairs ought to be contained inside one other array.
[ [long,lat], [long,lat], [long,lat]... ]
D3 can then use this as the info and venture these factors onto the map. If you happen to adopted the instance earlier within the article to attract the UK map then you need to have all of the boilerplate code required to plot these factors. We simply must create a perform to name it ourselves.
I’ve initialised a javascript object for use as a dictionary to retailer my lat lengthy pairs. The important thing for every coordinate pair would be the row ID given to every outcome by Rockset. This can imply that once I’m polling Rockset for brand new coordinates, if I obtain the identical set of factors once more, it received’t be duplicated in my array.
{
_id : [long,lat],
_id : [long,lat],
…
}
With this in thoughts, I created a perform known as updateData that may take this object and all of the factors and draw them on the map, every time asking D3 to solely draw the factors it hasn’t seen earlier than.
perform updateData(coords){
// seize solely the values (our arrays of factors) and cross to D3
var mapPoints = svg.selectAll("circle").knowledge(Object.values(coords))
// inform D3 to attract the factors and the place to venture them on the map
mapPoints.enter().append("circle")
.transition().period(400).delay(200)
.attr("cx", perform (d) { return projection(d)[0]; })
.attr("cy", perform (d) { return projection(d)[1]; })
.attr("r", "2px")
.attr("fill", "crimson")
}
All that’s left is to vary how we deal with the response from Rockset in order that we will repeatedly add new factors to our dictionary. We are able to then maintain passing this dictionary to our updateData perform in order that the brand new factors get drawn on the map.
//initialise dictionary
var factors = {}
perform fetchPoints(){
// initialise SQL request physique utilizing postman instance
var sql="{ "sql": { "question": "choose * from commons."tesla-location" order by _event_time LIMIT 10","parameters": [] }}"
// ask D3 to parse JSON from a request.
d3.json('https://api.rs2.usw2.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self/queries')
// setting headers the identical means we did in Postman
.header('Authorization','ApiKey AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGG1234567')
.header('Content material-Kind','utility/json')
// Making our request a POST request and passing the SQL assertion
.submit(sql)
.response(perform(d){
// now now we have the response from Rockset, lets print and examine it
var response = JSON.parse(d.response)
// parse out the record of outcomes (rows from our rockset assortment) and print
var newPoints = response.outcomes
for (var coords of newPoints){
// add lat lengthy pair to dictionary utilizing ID as key
factors[coords._id] = [coords.long,coords.lat]
console.log('updating factors on map ' + factors)
// name our replace perform to attract factors on th
updateData(factors)
}
})
}
That’s the bottom of the applying accomplished. We merely must loop and repeatedly name the fetchPoints perform each 5 seconds to seize the most recent 10 data from Rockset to allow them to be added to the map.
The completed utility ought to then carry out as seen in Fig 12. (sped up so you may see the entire journey being plotted)
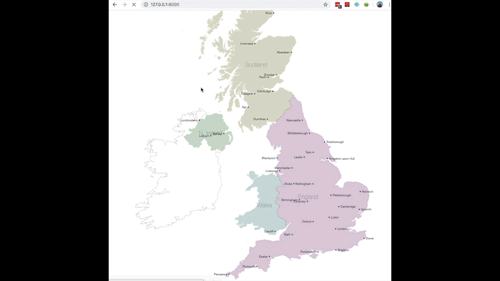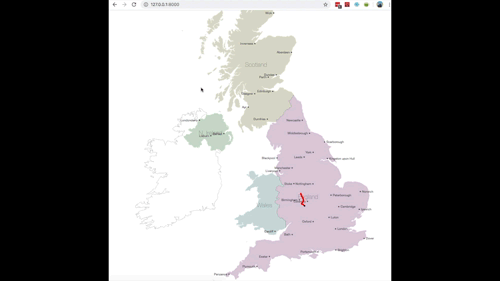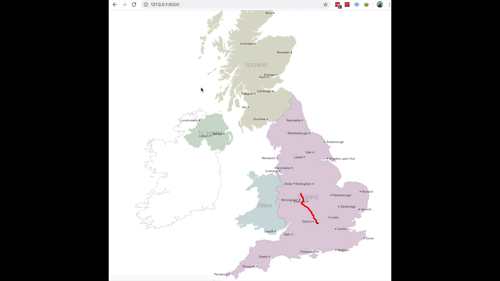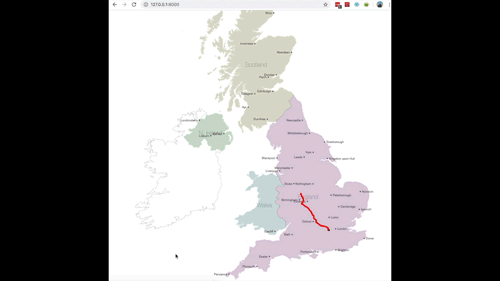
Fig 12. GIF of factors being plotted in actual time
Wrap up
By means of this submit we’ve learnt learn how to efficiently request actual time location knowledge from a Tesla Mannequin 3 and add it to a Kafka matter. We’ve then used Rockset to devour this knowledge so we will expose it through the in-built Rockset API in actual time. Lastly, we known as this API to plot the situation knowledge in actual time on a map utilizing D3.js.
This provides you an concept of the entire again finish to entrance finish journey required to have the ability to visualise knowledge in actual time. The benefit of utilizing Rockset for that is that we couldn’t solely use the situation knowledge to plot on a map but in addition carry out analytics for a dashboard that might for instance present journey size or avg time spent not transferring. You may see examples of extra complicated queries on linked automobile knowledge from Kafka on this weblog, and you may attempt Rockset with your individual knowledge right here.
Lewis Gavin has been an information engineer for 5 years and has additionally been running a blog about expertise throughout the Information group for 4 years on a private weblog and Medium. Throughout his pc science diploma, he labored for the Airbus Helicopter workforce in Munich enhancing simulator software program for navy helicopters. He then went on to work for Capgemini the place he helped the UK authorities transfer into the world of Large Information. He’s at the moment utilizing this expertise to assist remodel the info panorama at easyfundraising.org.uk, a web based charity cashback website, the place he’s serving to to form their knowledge warehousing and reporting functionality from the bottom up.


