How do you stability safety and velocity in giant groups? This query surfaced throughout my latest work with a buyer that had greater than 10 groups utilizing a Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), which is an agile software program improvement methodology. In aiming for correctness and safety of product, in addition to for improvement pace, groups confronted pressure of their aims. One such occasion concerned the event of a continuous-integration (CI) pipeline. Builders needed to develop options and deploy to manufacturing, deferring non-critical bugs as technical debt, whereas cyber engineers needed compliant software program by having the pipeline fail on any safety requirement that was not met. On this weblog submit, I discover how our workforce managed—and ultimately resolved—the 2 competing forces of developer velocity and cybersecurity enforcement by implementing DevSecOps practices .
Originally of the venture, I noticed that the pace of growing new options was of highest priority: every unit of labor was assigned factors primarily based on the variety of days it took to complete, and factors have been tracked weekly by product homeowners. To perform the unit of labor by the deadline, builders made tradeoffs in deferring sure software-design choices as backlog points or technical debt to push options into manufacturing. Cyber operators, nevertheless, sought full compliance of the software program with the venture’s safety insurance policies earlier than it was pushed to manufacturing. These operators, as a earlier submit defined, sought to implement a DevSecOps precept of alerting “somebody to an issue as early within the automated-delivery course of as attainable in order that that particular person [could] intervene and resolve the problems with the automated processes.” These conflicting aims have been typically resolved by both sacrificing developer velocity in favor of security-policy enforcement or bypassing safety insurance policies to allow sooner improvement.
Along with sustaining velocity and safety, there have been different minor hurdles that contributed to the issue of balancing developer velocity with cybersecurity enforcement. The client had builders with various levels of expertise in secure-coding practices. Numerous safety instruments have been out there however not steadily used since they have been behind separate portals with completely different passwords and insurance policies. Workers turnover was such that staff who left didn’t share the information with new hires, which induced gaps within the understanding of sure software program techniques, thereby elevated the danger in deploying new software program. I labored with the client to develop two methods to treatment these issues: adoption of DevSecOps practices and instruments that carried out cyber insurance policies in an automatic method.
Adopting DevSecOps
A steady integration pipeline had been partly carried out earlier than I joined the venture. It included a pipeline with some automated assessments in place. Deployment was a handbook course of, initiatives had various implementations of assessments, and assessment of safety practices was deferred as a activity merchandise simply earlier than a serious launch. Till lately, the workforce relied on builders to have secure-coding experience, however there was no approach to implement this on the codebase aside from by means of peer assessment. Some automated instruments have been out there for developer use, however they required logging in to an exterior portal and operating assessments manually there, so these instruments have been used sometimes. Automating the enforcement mechanism for safety insurance policies (following the DevSecOps mannequin) shortened the suggestions loop that builders obtained after operating their builds, which allowed for extra fast, iterative improvement. Our workforce created a typical template that could possibly be simply shared amongst all groups so it could possibly be included as a part of their automated builds.
The usual template prescribed the assessments that carried out this system’s cyber coverage. Every coverage corresponded to a person check, which ran each time a code contributor pushed to the codebase. These assessments included the next:
- Container scanning—Since containers have been used to package deal and deploy purposes, it was crucial to find out whether or not any layers of the imported picture had present safety vulnerabilities.
- Static software testing—This sort of testing helped stop pushing code with excessive cyclomatic complexity and was susceptible to buffer-overflow assaults, or different widespread programming errors that introduce vulnerabilities.
- Dependency scanning— After the Photo voltaic Winds assault, better emphasis has been placed on securing the software program provide chain. Dependency scanning seems to be at imported libraires to detect any present vulnerabilities in them.
- Secret detection—A check that alerts builders of any token, credentials, or passwords they may have launched into the codebase, thereby compromising the safety of the venture.
There are a number of benefits to having a person coverage run on separate levels, which return to historic finest practices in software program engineering, e.g., expressed within the Unix philosophy, agile software program methodologies, and many seminal works. These embrace modularity, chaining, and customary interfaces:
- Particular person levels on a pipeline executing a singular coverage present modularity so that every coverage might be developed, modified, and expanded on with out affecting different levels (the time period “orthogonality” is usually used). This modularity is a key attribute in enabling refactoring.
- Particular person levels additionally enable for chaining workflows, whereby a stage that produces an artifact can absorb that artifact as its enter and produce a brand new output. This sample is clearly seen in Unix applications primarily based on pipes and filters, the place a program takes the output of one other program as its enter and create new workflows thereafter.
- Making every coverage into its personal stage additionally permits for clear distinction of software program layers by means of customary interfaces, the place a safety operator may have a look at a stage, see if it handed, and maybe change a configuration file with out having to delve into the internals of the software program implementing the stage.
These three key attributes resolved the problem of getting a number of workforce members coding and refactoring safety insurance policies with no lengthy onboarding course of. It meant safety scans have been at all times run as a part of the construct course of and builders didn’t have to recollect to go to completely different portals and execute on-demand scans. The strategy additionally opened up the chance for chaining levels for the reason that artifact of 1 job could possibly be handed on to the subsequent.
In a single occasion, a construct job created a picture tag that modified relying on the sort of department on which it was being deployed. The tag was saved as an artifact and handed alongside to the subsequent stage: container scanning. This stage required the right picture tag to carry out the scanning. If the mistaken tag was supplied, the job would fail. For the reason that tag title may change relying on the construct job, it couldn’t work as a worldwide variable. By passing the tag alongside as an artifact, nevertheless, the container-scanning stage was assured to make use of the best tag. You’ll be able to see a diagram of this circulation under:
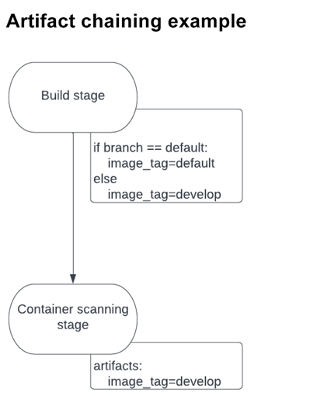
Declarative Safety Insurance policies
In sure conditions, there are a number of benefits to utilizing declarative reasonably than crucial coding practices. As an alternative of understanding how one thing is carried out, declarative expressions present the what. By utilizing business instruments we will specify a configuration file with the favored YAML language. The pipeline takes care of operating the builds whereas the configuration file signifies what check to run (with what parameters). On this method, builders don’t have to fret in regards to the specifics of how the pipeline works however solely in regards to the assessments they want to run, which corresponds with the modularity, chaining, and interface attributes described beforehand. An instance stage is proven under:
container_scanning:
docker_img: example-registry.com/my-project:newest
embrace:
- container_scanning.yaml
The file defines a container_scanning stage, which scans a Docker picture and determines whether or not there are any recognized vulnerabilities for it (by means of using open-source vulnerability trackers). The Docker picture is outlined within the stage, which might be a picture in a neighborhood or distant repository. The precise particulars of how the container_scanning stage works is within the container_scanning.yaml file. By abstracting the performance of this stage away from the primary configuration file, we make the configuration modular, chainable, and simpler to grasp—conforming to the rules beforehand mentioned.
Rollout and Learnings
We examined our DevSecOps implementation by having two groups use the template of their initiatives and check whether or not safety artifacts have been being generated as anticipated. From this preliminary batch, we discovered that (1) this customary template strategy labored and (2) groups may independently take the template and make minor changes to their initiatives as crucial. We subsequent rolled out the template for the remainder of the groups to implement of their initiatives.
After we rolled out the template to all groups, I spotted that any adjustments to the template meant that each workforce must implement the adjustments themselves, which incurred inefficient and pointless work (on high of the options that groups have been working to develop). To keep away from this additional work, the usual safety template could possibly be included as a dependency on their very own venture template (like code libraries are imported on information) utilizing Yaml’s embrace command. This strategy allowed builders to cross down project-specific configurations as variables, which might be dealt with by the template. It additionally allowed these growing the usual template to make crucial adjustments in an orthogonal method, as under:
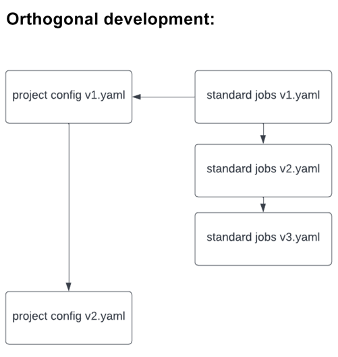
Consequence: A Higher Understanding of Safety Vulnerabilities
The implementation of DevSecOps rules into the pipeline enabled groups to have a greater understanding of their safety vulnerabilities, with guards in place to robotically implement cyber coverage. The automation of coverage enabled a fast suggestions loop for builders, which maintained their velocity and elevated the compliance of written code. New members of the workforce rapidly picked up on creating safe code by reusing the usual template, with out having to know the internals of how these jobs work, because of the interface that abstracts away pointless implementation particulars. Velocity and safety have been due to this fact utilized in an efficient method to a DevSecOps pipeline in a method that scales to a number of groups.


