You’re about to begin a enterprise within the US. You’ve got an ideal thought and a successful workforce. You’ve thought by way of your marketing strategy. You’re able to make it official—however earlier than you possibly can start, you need to resolve what sort of enterprise entity makes essentially the most sense on your new firm.
There are a number of varieties of enterprise entities and the one you select determines how your online business is regulated and taxed. Your alternative of entity basically boils down to some key issues:
- How income are taxed
- The complexity and price of organising the enterprise, in addition to ongoing governance and administration
- Legal responsibility safety, significantly of an proprietor’s private belongings
Whereas in some circumstances the selection will be apparent, it isn’t at all times. Every entity sort provides a singular mix of authorized and tax implications, and determining what’s proper for a particular enterprise will be difficult.
With greater than 20 years of expertise in accounting—together with greater than 14 years of offering CFO providers to firms throughout a number of industries—I’ve suggested quite a few C companies, S companies, LLCs, and partnerships on tax and entity-choice issues. On this article, I’ll current the essential factors to bear in mind when you must make this choice.
Observe: It is a top-level information and sure particulars might not apply to your particular enterprise. Any remaining choices needs to be made with the assistance of a tax or authorized advisor.
Understanding the Completely different Forms of Enterprise Entities
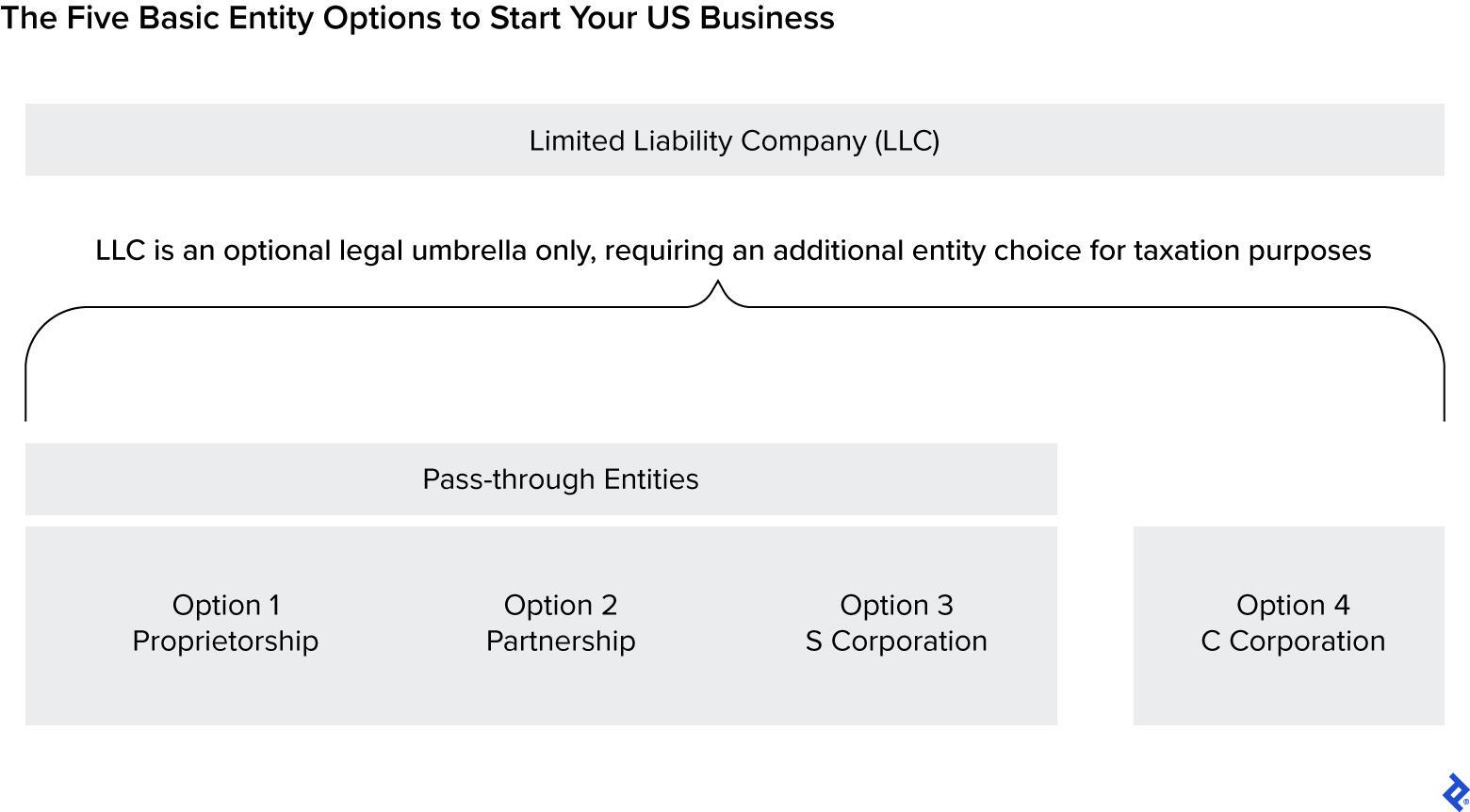
The IRS acknowledges 4 most important varieties of enterprise entities: proprietorship, partnership, S company, and C company. These sorts have main variations in terms of taxes, setup prices, administrative prices, and authorized protections, however any of them will be fashioned as an LLC for legal responsibility assurance, then taxed as in the event that they have been one of many entity sorts acknowledged by the IRS.
Earlier than we dive into the enterprise entity sorts or focus on LLCs, nonetheless, it’s essential to grasp pass-through entities.
What Are Move-through Entities?
Proprietorships, partnerships, and S companies are all pass-through entities. They’re referred to as that as a result of their taxable earnings “passes by way of” to the non-public tax returns of the house owners and is taxed there.
S companies and partnerships do file firm tax returns, however these returns merely show the corporate’s taxable earnings and allocate that earnings to the house owners on a Schedule Okay-1 (Kind 1065). Every proprietor’s Schedule Okay-1 quantity is then reported and taxed on their private tax return—Kind 1040—in addition to on any state and native returns that will apply.
In distinction, sole proprietorships don’t file a enterprise tax return in any respect. The enterprise earnings is calculated straight on Schedule C, Schedule E, or Schedule F of the proprietor’s private Kind 1040.
Move-through standing is important as a result of the house owners of a pass-through entity pay private earnings tax on the income of the corporate, however they will then withdraw these income as tax-free dividends from the corporate. This isn’t true of C companies, which not solely pay their very own earnings tax but additionally maintain taxable dividends. Primarily, the C company pays tax on its earnings first, and the remaining cash is distributed to the stockholders, who pay private earnings tax on it. That is known as double taxation.
|
Instance: Taxation of S Company vs. C Company Earnings |
||
|---|---|---|
|
S Company |
C Company |
|
|
Taxable earnings |
$1,000,000 |
$1,000,000 |
|
Company tax fee |
N/A |
21.0% |
|
Prime particular person tax fee |
37.0% |
N/A |
|
Tax owed by company |
$0 |
$210,000 |
|
Tax owed by proprietor |
$370,000 |
$0 |
|
After-tax money remaining |
$630,000 |
$790,000 |
|
Tax fee on distribution to proprietor |
0.0% |
23.8% |
|
Further tax owed on dividend distribution |
$0 |
$188,020 |
|
Web after-tax money remaining |
$630,000 |
$601,980 |
At a big firm, the double taxation drawback {that a} C company faces is mitigated by this entity’s different advantages, such because the low tax fee on company income and limitless shareholder allowance. For many small to midsize companies, although, the cons of a C company will typically outweigh the professionals.
Now that we’ve established that key distinction between S and C companies, let’s have a look at the totally different entities in higher depth.
What Are Sole Proprietorships?
Essentially, sole proprietorships are supposed for easy companies owned by one individual or a married couple. Such companies are usually freelance companies, consultancies, small service companies, meals stands, and many others. Sole proprietorships don’t have shares or possession items, that means that the one exit choice is to promote the belongings of the corporate.
Sole proprietorships are by far the best enterprise construction. A bona fide enterprise that begins with out formally incorporating is, by default, a sole proprietorship or partnership (relying on the variety of house owners). Sole proprietors with no workers don’t even have to register with the Inner Income Service (IRS). The proprietor can merely use their Social Safety quantity because the enterprise tax ID. Some factors to pay attention to:
- Enterprise bills are deductible. Opposite to in style perception, there’s typically no have to “incorporate” to deduct enterprise bills. Even an unincorporated sole proprietorship is eligible to deduct its enterprise bills.
- Proprietors pay private earnings tax on income. Proprietors can not pay themselves wages. They merely withdraw firm income as wanted. Every year they owe private earnings tax on your complete taxable income of the enterprise, no matter whether or not they have withdrawn the income or not.
- Earnings are topic to FICA tax and federal earnings tax. As of 2023, FICA tax (which pays for Social Safety and Medicare) is 15.3% of earnings as much as the Social Safety restrict of $160,200 and a pair of.9% of earnings earned past that. There’s additionally the further Medicare tax of 0.9% that applies after self-employment earnings exceed $200,000 for single taxpayers. In my expertise, many small sole proprietors find yourself owing extra FICA tax than federal earnings tax, however this depends upon particular person circumstances.
|
Execs and Cons of Sole Proprietorships |
|
|---|---|
|
Execs |
Cons |
|
Very straightforward to arrange |
All income topic to FICA tax |
|
Simple for many house owners to grasp |
Proprietor’s private belongings usually are not protected, except firm is fashioned as an LLC |
|
Separate enterprise tax return not required |
|
|
No payroll to run if there aren’t any workers |
|
What Are Partnerships?
A partnership is basically the multi-owner model of a sole proprietorship. Most states require little or no (if any) paperwork to type and preserve a partnership. This circumstance alone is the rationale many comparatively easy, early-stage companies which have but to realize vital profitability are organized as partnerships, quite than formal companies.
The association will be particularly enticing for small firms with out workers, wherein the house owners do a lot of the work. Partnerships are additionally generally used for actual property holding firms (as a result of rental earnings isn’t topic to FICA tax no matter entity sort) and sure skilled service companies, equivalent to accounting companies.
Regardless that paperwork necessities for a partnership are minimal, multi-owner firms are by nature extra difficult than sole proprietorships, so this can be very essential to have a partnership working settlement that controls the operations and possession of the corporate. Listed below are the main monetary issues you will want to plan for as effectively:
- Earnings don’t must be divided equally. Distinctive to partnerships, the enterprise earnings doesn’t have to be allotted proportionate to possession. This flexibility will be useful when there’s a silent associate who contributes a lot of the preliminary capital however isn’t anticipating a commensurate share of the income. Any such association have to be clearly specified by a partnership settlement.
- Partnership earnings is usually topic to FICA tax. As with sole proprietorships, a serious draw back of partnerships is that your complete taxable earnings of a partnership is usually topic to FICA tax. It is a key purpose most bigger, extremely worthwhile firms aren’t partnerships—the tax burden merely turns into too excessive.
- Funds to companions usually are not wages. A part of the simplicity of a partnership is that companions don’t obtain wages, however quite assured funds for his or her providers.
- The partnership doesn’t have to run payroll or file payroll studies if there aren’t any non-owner workers. This may save the partnership the numerous value and problem of payroll providers and related charges. Relying on the dimensions of the corporate, the financial savings right here might assist to offset the elevated FICA tax burden and make the partnership association extra engaging.
|
Execs and Cons of Partnerships |
|
|---|---|
|
Execs |
Cons |
|
Simple to arrange and administer |
Earnings typically topic to FICA tax |
|
Simple for many house owners to grasp |
House owners’ private belongings usually are not protected, except firm is fashioned as a restricted partnership or LLC |
|
Versatile revenue allocation allowed |
|
|
Nopayroll to run if there aren’t any workers aside from companions |
|
What Are S Companies?
As firms grow to be extra worthwhile, proprietorships and partnerships are typically much less appropriate attributable to how they’re taxed. Enter S companies, a well-liked entity alternative for small and midsize privately held firms.
Though each partnerships and S companies are pass-through entities, the latter are usually favored by bigger companies due to FICA tax. S company house owners are required to pay themselves an inexpensive wage (topic to FICA tax), however the remaining enterprise income are topic solely to earnings tax, not FICA tax.
Think about a enterprise that makes $1,000,000 per 12 months. Let’s say the proprietor receives compensation of $100,000 and the remaining $900,000 is enterprise revenue. The chart beneath exhibits how shifting from partnership to S company standing would save the proprietor roughly $31,000 per 12 months in FICA tax, all else being equal.
|
FICA Tax on Complete Earnings/Proprietor Compensation |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Partnership |
S Company |
|
|
Taxable earnings earlier than proprietor compensation |
$1,000,000 |
$1,000,000 |
|
Proprietor wages |
N/A |
$100,000 |
|
Proprietor’s assured funds |
$100,000 |
N/A |
|
Remaining business-taxable earnings |
$900,000 |
$900,000 |
|
FICA tax on proprietor wages |
$0 |
$15,300 |
|
FICA tax on proprietor’s assured funds |
$15,300 |
$0 |
|
FICA tax on remaining taxable earnings |
$31,346 |
$0 |
|
Complete FICA tax owed |
$46,646 |
$15,300 |
Observe 2: Calculations are based mostly on 2023 FICA tax thresholds.
Whereas this profit appears placing, for a really small firm it might not be worthwhile. The requirement to pay an inexpensive wage means even a “solopreneur” with no workers should run payroll and file payroll tax studies with the IRS (and the state, if relevant). The added administrative burden and price of dealing with this and managing different necessities make this a drawback in comparison with partnerships and sole proprietorships.
S companies are additionally typically topic to stricter guidelines than the opposite entity sorts. For instance:
- Usually, solely particular person US residents and residents can personal an curiosity in an S company. Some exceptions exist for sure trusts and estates to be allowed as stockholders.
- Earnings and distributions have to be allotted in accordance with possession.
- Loss utilization will be restricted. In some circumstances, an proprietor of an S company that has losses might not have the ability to deduct that loss on their private tax return. The loss must be carried ahead to a future 12 months.
- Just one class of inventory is allowed. There can solely be voting and nonvoting shares—no others.
- There’s a most of 100 stockholders for S companies.
The authorized situations for organising and sustaining S companies normally require the assistance of a lawyer and/or accountant, which will increase the related prices. Regardless of these potential drawbacks, the FICA tax financial savings are onerous to beat, accounting for the recognition of S companies. S companies additionally protect the house owners’ belongings from legal responsibility within the occasion of authorized claims—one thing proprietorships and partnerships don’t do. Additionally, by forming an LLC that elects to be taxed as an S company, you possibly can keep away from among the inflexible authorized necessities.
In some circumstances, a partnership will be extra tax-efficient than an S company, even after factoring in FICA tax. On this state of affairs, the companions forgo paying themselves assured funds and as a substitute deal with all payouts as distributions. There are vital caveats to adopting this method—you must work with a tax skilled to see if it’s best for you—however it’s widespread sufficient that I might be remiss if I didn’t point out it.
|
Execs and Cons of S Companies |
|
|---|---|
|
Execs |
Cons |
|
Earnings past wages not topic to FICA tax |
Full authorized setup required |
|
Company authorized protect operate |
Typically tough for house owners to grasp |
|
Inflexible revenue allocation and distribution guidelines |
|
|
Restricted deductibility of losses |
|
|
Solely an individual (not an entity) can personal shares |
|
|
Most of 100 stockholders |
|
|
Usually have to be owned by a US citizen |
|
|
Payroll have to be run even when there aren’t any non-owner workers |
|
|
Just one class of inventory allowed |
|
What Are C Companies?
As companies proceed to get greater and extra complicated, they could outgrow the S company construction. If the variety of traders exceeds the 100 stockholder restrict (as with a publicly held firm), or if totally different share class constructions are required, then it’s time to think about the C company.
All massive American publicly traded companies are C companies. Privately held C companies are uncommon and usually make the most of the construction for causes aside from earnings tax considerations.
Excessive-growth startups in search of collection funding usually make the most of the C company construction. These non-public firms are compelled to go this route as a result of their goal traders could also be entities or overseas people, neither of that are allowed to put money into an S company.
Whereas US firms might register in any state or territory, it’s widespread for C companies to decide on Delaware as its well-defined and court-tested company rules have made it the state of alternative for incorporation. In keeping with the State of Delaware, greater than 68% of Fortune 500 firms are domiciled there.
One vital downside of the C company construction is the double taxation problem we checked out in our dialogue of pass-through entities—the corporate pays tax on the earnings, after which stockholders pay tax on their dividends.
Moreover, C company losses can’t be deducted in opposition to stockholders’ different private earnings. The mixture of those pitfalls discourages many non-public companies from adopting this construction.
In brief, the thought of utilizing the C company construction for tax optimization has benefit in particular conditions. For many small to midsize companies, although, the cons will typically outweigh the professionals.
|
Execs and Cons of C Companies |
|
|---|---|
|
Execs |
Cons |
|
Low tax fee on company income |
Full authorized setup required |
|
Company authorized protect operate |
Double taxation of company income |
|
Limitless stockholders allowed |
Restricted deductibility of losses |
|
Stockholders might embody such entities as trusts and funds |
|
|
Potential for tax-free sale of inventory upon exit |
|
Now that you’ve got a way of the traits of the 4 most important enterprise entity sorts acknowledged for tax functions, let’s have a look at whether or not turning into an LLC is smart on your firm.
What Are Restricted Legal responsibility Corporations (LLCs)?
Because the title suggests, a restricted legal responsibility firm is a enterprise construction that gives “restricted legal responsibility” to house owners of the corporate and informs the world that the proprietor isn’t personally responsible for claims.
An LLC is a authorized entity solely and isn’t acknowledged by the IRS as a taxpaying enterprise construction. For tax functions, if the proprietor decides to type the corporate as an LLC they need to additionally resolve whether or not it’s going to be a C company, S company, partnership, or proprietorship.
It’s utterly acceptable to arrange as any of the 4 enterprise entity sorts we’ve mentioned with out being an LLC. Why, then, does it seem to be virtually all new firms are fashioned as LLCs?
- The LLC construction helps protect the proprietor’s private belongings from a lawsuit in opposition to the enterprise. In different phrases, with out an LLC, a sole proprietor or associate could also be personally responsible for a lawsuit or judgment that exceeds the enterprise belongings. That occasion would topic the proprietor’s private belongings to potential claims.
- In comparison with conventional S or C companies, an LLC construction is usually easier to manage. Companies are sometimes required to carry annual conferences and hold information of assembly minutes; an LLC is usually not topic to those rules, even when it’s taxed as a company.
- Beginning out as an LLC provides an organization flexibility for a later entity change. Whereas an organization can change its entity sort with out being an LLC, the simplified rules and administration of an LLC create much less friction for conversion. For instance, a standard path is to type an LLC taxed as a partnership, then elect S company standing after the corporate turns into worthwhile.
LLCs and enterprise entities are fashioned on the state degree. Accordingly, the precise course of for organising a brand new firm varies by state, and will entail varied charges. Company governance and reporting necessities can range barely by state as effectively.
What doesn’t range is federal tax regulation. Every entity sort is topic to particular federal tax legal guidelines that apply to all US firms of that sort, whatever the state it’s registered in.
Partnership, Proprietorship, C Corp, S Corp: In Evaluation
Once more, the three most important issues when selecting a enterprise entity are how income are taxed, administrative value and complexity, and legal responsibility.
From a tax standpoint, the S company could also be optimum, because it provides a single layer of taxation (in contrast to C companies) and earnings usually are not topic to FICA tax (in contrast to partnerships and proprietorships).
Sole proprietorships are splendid while you’re contemplating the associated fee and complexity of setup and upkeep. They’re by far the least difficult and have the bottom value of setup and ongoing governance and administration. However for a multi-owner firm fashioned as an LLC, a partnership is usually preferable for flexibility.
Lastly, from a legal responsibility standpoint, the LLC construction is tough to beat. It provides legal responsibility safety together with any of the 4 entity constructions. A non-LLC S corp or C corp can even supply strong protections from a legal responsibility perspective.
|
Comparability of Enterprise Entity Choices |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Proprietorship |
Partnership |
S Company |
C Company |
|
|
Federal tax fee on income (2023) |
10%-37% |
10%-37% |
10%-37% |
21% |
|
Topic to double taxation |
No |
No |
No |
Sure |
|
FICA tax on income |
Sure |
Sure |
No |
No |
|
Price of Setup/Ongoing Administration |
Low |
Reasonable |
Excessive |
Excessive |
|
Legal responsibility safety |
No |
Usually no |
Sure |
Sure |
|
Benefit of LLC umbrella |
Legal responsibility safety |
Legal responsibility safety |
Easier governance |
Easier governance |
Which Entity Kind Ought to You Select for Your Enterprise?
That can assist you perceive the thought course of behind selecting an entity sort, I’m going to make use of 4 fictional firms to discover how totally different entity sorts will be helpful relying on how a enterprise is constructed and what the stakeholders need.
1. A Summer season Facet Hustle
Joe’s Mowing
- Joe is a 21-year-old school scholar on the lookout for further earnings. He has determined to begin a small garden care enterprise.
- Joe is planning to buy tools price $5,000 and is hoping to show a revenue of $15,000 for the summer season.
- Joe’s Mowing may have no workers aside from Joe.
Which Entity Kind Is Proper for Joe’s Mowing?
As a younger entrepreneur with a short-term marketing strategy, Joe is an ideal candidate for a sole proprietorship. An S company would require vital value to arrange, and he must pay himself an inexpensive wage (topic to FICA tax). His wage would probably wipe out his $15,000 revenue, which might negate any FICA financial savings. Plus the trouble of operating payroll wouldn’t be price it. An LLC umbrella would add legal responsibility safety if Joe felt he wanted that.
2. A Household-owned Condominium Complicated
LBD Group
- Lucia, Ben, and Dorcas are siblings who personal equal percentages of an house complicated.
- Lucia is a silent investor; Ben and Dorcas handle and preserve the property.
- Lucia has agreed that she doesn’t have to obtain an equal share of the income, as a result of she is contributing nothing however capital to the mission.
Which Entity Kind Is Proper for LBD Group?
An LLC taxed as a partnership would clearly be the most suitable choice for LBD Group. Since rental earnings isn’t topic to FICA tax, the S company benefit doesn’t apply. Partnerships enable income to be distributed unequally to house owners, which is a aim of this group. There aren’t any non-owner workers, which implies no payroll could be required if the entity have been a partnership. And given the legal responsibility points in the actual property enterprise, an LLC would give protection to the house owners within the case of a lawsuit.
3. A Married Couple’s Fledgling Household Enterprise
Good Concepts
- Good Concepts is a brand new copywriting enterprise based by Invoice and Malia.
- Its first quick tax 12 months, together with solely the months because the firm’s founding in June, goes to finish with a internet lack of $10,000.
- Nevertheless, the couple believes subsequent 12 months shall be worthwhile to the tune of $250,000.
Which Entity Kind Is Proper for Good Concepts?
With losses this 12 months, and an anticipated $250,000 in revenue subsequent 12 months, Invoice and Malia seem like good candidates for forming an LLC and electing to be taxed as a proprietorship or spousal partnership this 12 months, then electing S company standing subsequent 12 months. That approach they will use this 12 months’s enterprise losses to offset wages or different earnings. Subsequent 12 months they’ll draw wages from the S company, and the remaining income won’t be topic to FICA tax.
4. A Fintech Startup Run by A number of Entrepreneurs
FreeBooks
- Led by a small workforce of entrepreneurs, FreeBooks is an early-stage fintech startup.
- The founders are in search of non-public fairness traders.
- The aim is to be in the marketplace inside a 12 months and be a related participant inside three years, with a number of capital infusions alongside the best way.
Which Entity Kind Is Proper for FreeBooks?
As a basic expertise startup hoping to obtain enterprise capital or non-public fairness funding, it has little choice aside from to be a C company. The opposite varieties of entities wouldn’t enable the complicated share class and possession constructions a lot of these firms require. The one different construction to think about could be to type first as an LLC taxed as a partnership or S company, then swap to C corp standing when the company traders grow to be a actuality. On this state of affairs, structuring the corporate as an LLC could be vastly helpful as it will enable extra flexibility for these entity adjustments, hold issues easy early on, and permit early traders to deduct losses on their private tax returns.
Altering Your Entity Kind to Match Future Wants
Beginning your organization is thrilling, however it’s additionally a time to be cautious and ensure you’re doing issues proper. Earlier than you select an entity sort, attain out to your tax advisor for course in your particular scenario.
Whereas tough, it’s attainable to alter your organization’s authorized construction and enterprise entity sort additional down the road as your wants and profitability change. For instance, when you’re beginning a conventional enterprise (service, manufacturing, retail, and many others.) with co-owners and workers, contemplate an LLC taxed as a partnership to begin, then elect S company standing when it will get comparatively worthwhile. That gives the pliability of a partnership upfront and avoids FICA tax on income as soon as income begins flowing. Simply understand that switching can have tax implications and lead to a large administrative burden.
Make sure that you do sufficient due diligence to accurately weigh all the professionals and cons of the totally different choices on your firm. Getting your entity sort proper from the beginning will put your organization on a sound footing to realize its potential.
This text has lately undergone a complete replace to include the most recent and most correct info. Feedback beneath might predate these adjustments.