Synthetic nanostructures created particularly to switch the properties of sunshine are often called metamaterials. Nevertheless, an environment friendly manufacturing that might allow mass commercialization of those nanostructures has but to be realized.
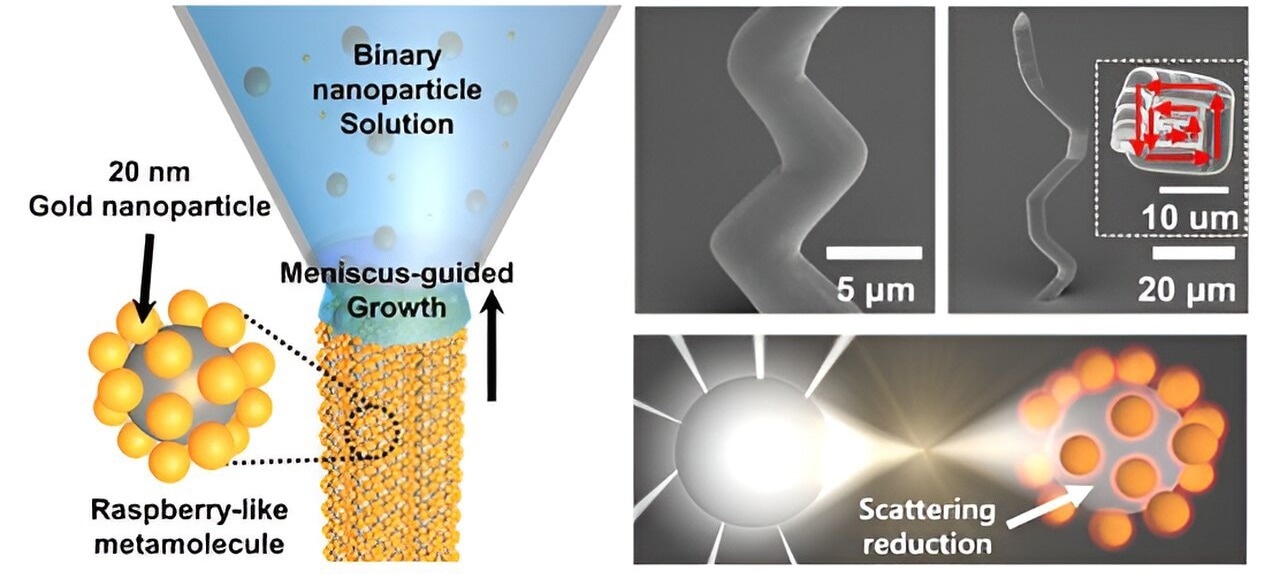
A analysis group at Pohang College of Science and Know-how (POSTECH) headed by Ph.D. candidate Hongyoon Kim from the Division of Mechanical Engineering, researcher Received-Geun Kim, and Professor Junsuk Rho from the Division of Chemical Engineering and Mechanical Engineering has developed a way to deal with this commercialization drawback.
Utilizing co-assembly expertise and three-dimensional nano printing, their method strikes metamaterials one step nearer to being made commercially obtainable. Their findings had been revealed in Small.
Historically, metamaterials are created by layering bodily and chemical layers onto supplies like silicon and resin (plastic), then lithography. Regrettably, this course of is pricey and limiting when it comes to supplies that can be utilized. Because of this, the tutorial neighborhood has not too long ago turned its emphasis towards manufacturing metamaterials by particle meeting moderately than the pricey process of floor shaving.
The analysis group used a mix of three-dimensional nano printing and co-assembly approaches of their research. Initially, they used silica (glass) and gold nanoparticles of various sizes to create raspberry-like metamolecules. These raspberry-like buildings had been then piled on high of each other, culminating within the profitable fabrication of millimeter-sized metamaterials.
Basically, as an alternative of utilizing costlier and conventional methods, the analysis group has developed a course of expertise that enables the cost-effective synthesis of metamaterials in particular shapes.
The experiments performed showcased the light-controlling capabilities of metamaterials generated by way of the group’s course of. Notably, there was a big discount in scattered gentle inside the seen area. This analysis marks the primary occasion of verifying the optical properties of metamolecules in answer utilizing millimeter-sized buildings.
This technique doesn’t require specialised tools for verification as a result of the outcomes might be seen with the unaided eye or beneath a fundamental microscope setup. The scientists additionally adjusted the proportion of silica to gold nanoparticles within the metamaterial to acquire exact management over the optical traits.
This breakthrough allows the design and implementation of free-form nanophotons, surpassing the constraints of current metamaterial fabrication processes. The flexibility of this expertise affords a variety of fabric decisions together with quantum dots, catalyst particles, and polymers, making it relevant to various fields from sensors to shows along with metamaterial analysis.
Junsuk Rho, Professor, Division of Mechanical Engineering and Chemical Engineering, Pohang College of Science and Know-how
Journal Reference:
Kim, W.-G., et al. (2023) Freestanding, Freeform Metamolecule Fibers Tailoring Synthetic Optical Magnetism. Small. doi:10.1002/smll.202303749
Supply: https://worldwide.postech.ac.kr/


