Persistent lung infections, persistent wounds, and well being care-associated infections are sometimes rather more troublesome to deal with than different kinds of bacterial infections. It is because they’re typically attributable to biofilms, that’s, colonies of microbes—primarily micro organism— that develop collectively in a self-produced matrix that protects and isolate them from the exterior surroundings.
Now, a brand new triple-acting antibiotic agent has managed to interrupt by the biofilm extracellular matrix and remove greater than 50% of the pathogens in a single shot, based on a examine printed within the journal npj Biofilms and Microbiomes. The examine was led by Eduard Torrents, lecturer on the Division of Genetics, Microbiology and Statistics of the College of Biology and head of the group on Bacterial Infections: Antimicrobial Remedy of the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC).
This extracellular matrix exacerbates antibiotic resistance, one of many greatest threats to international well being, based on the World Well being Group (WHO), since killing the micro organism contained in the movie is as much as a thousand occasions more durable. Biofilm infections are subsequently an important nonspecific mechanism of antimicrobial resistance.
Attacking these microbes utilizing solely antibiotics isn’t sufficient. There’s a want for instruments that break down the extracellular matrix to entry and kill the micro organism inside. The primary writer of this examine, which has achieved this milestone, is Núria Blanco-Cabra, postdoctoral researcher of the group led by Eduard Torrents on the UB and IBEC. The examine was carried out along with scientists from CIDETEC (Basque Nation).
A triple-acting drug mixture
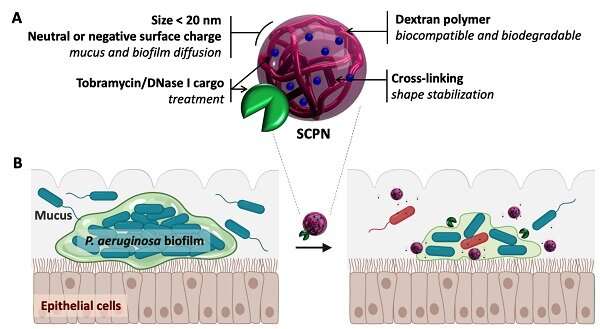
The examine centered on the micro organism Pseudomonas areuginosa, a pathogen that always grows in biofilms within the lungs of these sufferers with cystic fibrosis or persistent obstructive pulmonary illness (COPD), inflicting persistent infections. “We grew biofilm cultures in vitro, utilizing a way that resembles to the best way wherein they exist and develop in nature,” added Torrents.
In medical follow, these infections are often handled with an antibiotic known as tobramycin. Nevertheless, its effectiveness is restricted by its incapacity to penetrate the movie. This occurs as a result of tobramycin, which is positively charged, is neutralized by the extracellular matrix (with a detrimental cost).
The researchers loaded the antibiotic into negatively charged nanoparticle carriers. This might neutralize the constructive cost earlier than the drug reached the biofilm, which enabled it to interrupt the extracellular matrix and kill the micro organism inside. What’s extra essential, these carriers—constructed by dextran-based single chain nanoparticles—have been in a position to transport as much as 40% of the load of the antibiotic.
“Most of the beforehand studied nanotransporters have solely been in a position to maintain a small load of the goal compound, which has prevented their medical use. We managed to beat this impediment,” says Torrents.
The antibiotic-loaded nanocarriers have been additionally coated in an enzyme known as DNase I. One of many compounds that holds micro organism biofilms collectively is structural DNA discovered all through the extracellular matrix. DNase I can break down this “glue,” inflicting the matrix to loosen, and permitting the antibiotic to penetrate the biofilm even additional.
“By combining an antibiotic with a few brokers that break the biofilm up, we now have created a drug that’s extra highly effective than the antibiotic alone which kills the micro organism that lives contained in the movie,” notes Eduard Torrents, principal researcher of the examine.
Utilizing microscopy photos, the researchers discovered that the brand new agent had not solely dissolved the structural DNA within the extracellular matrix, but additionally that it was appearing on and killing the micro organism inside. With only a single utility, they lowered the bacterial biomass by greater than half.
“Having achieved such important biofilm clearance with a single dose of our agent, we predicted {that a} full course of antibiotics may considerably scale back the burden of those infections, that are extraordinarily troublesome to deal with.”
In future medical makes use of, this agent might be administered in a number of doses, as is normal follow with antibiotics. The subsequent step is to work on the medical validation of this method. Its commercialization would signify a decisive advance within the remedy of biofilm infections, the worldwide financial value of which at present quantities to 4 billion {dollars} a yr.
Núria Blanco-Cabra et al, Neutralization of ionic interactions by dextran-based single-chain nanoparticles improves tobramycin diffusion right into a mature biofilm, npj Biofilms and Microbiomes (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41522-022-00317-9
Quotation:
Breaking down micro organism’s protecting armor to beat antibiotic resistance (2022, October 7)
retrieved 10 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-bacteria-armor-antibiotic-resistance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


