Each startup’s journey is exclusive, and the street to success isn’t
linear, however value is a story in each enterprise at each time limit,
particularly throughout financial downturns. In a startup, the dialog round
value shifts when transferring from the experimental and gaining traction
phases to excessive development and optimizing phases. Within the first two phases, a
startup must function lean and quick to come back to a product-market match, however
within the later phases the significance of operational effectivity ultimately
grows.
Shifting the corporate’s mindset into attaining and sustaining value
effectivity is absolutely troublesome. For startup engineers that thrive
on constructing one thing new, value optimization is usually not an thrilling
subject. For these causes, value effectivity usually turns into a bottleneck for
startups sooner or later of their journey, similar to accumulation of technical
debt.
How did you get into the bottleneck?
Within the early experimental section of startups, when funding is proscribed,
whether or not bootstrapped by founders or supported by seed funding, startups
typically concentrate on getting market traction earlier than they run out of their
monetary runway. Groups will choose options that get the product to market
shortly so the corporate can generate income, preserve customers completely happy, and
outperform opponents.
In these phases, value inefficiency is a suitable trade-off.
Engineers might select to go along with fast customized code as an alternative of coping with
the effort of organising a contract with a SaaS supplier. They might
deprioritize cleanups of infrastructure parts which are not
wanted, or not tag assets because the group is 20-people sturdy and
everybody is aware of every little thing. Attending to market shortly is paramount – after
all, the startup won’t be there tomorrow if product-market match stays
elusive.
After seeing some success with the product and reaching a fast development
section, these earlier selections can come again to harm the corporate. With
site visitors spiking, cloud prices surge past anticipated ranges. Managers
know the corporate’s cloud prices are excessive, however they could have hassle
pinpointing the trigger and guiding their groups to get out of the
state of affairs.
At this level, prices are beginning to be a bottleneck for the enterprise.
The CFO is noticing, and the engineering group is getting a whole lot of
scrutiny. On the identical time, in preparation for an additional funding spherical, the
firm would want to indicate affordable COGS (Price of Items Offered).
Not one of the early selections had been incorrect. Creating a wonderfully scalable
and price environment friendly product will not be the correct precedence when market traction
for the product is unknown. The query at this level, when value begins
changing into an issue, is easy methods to begin to cut back prices and change the
firm tradition to maintain the improved operational value effectivity. These
adjustments will make sure the continued development of the startup.
Indicators you might be approaching a scaling bottleneck
Lack of value visibility and attribution
When an organization makes use of a number of service suppliers (cloud, SaaS,
growth instruments, and so forth.), the utilization and price knowledge of those providers
lives in disparate programs. Making sense of the whole know-how value
for a service, product, or group requires pulling this knowledge from numerous
sources and linking the fee to their product or characteristic set.
These value stories (similar to cloud billing stories) might be
overwhelming. Consolidating and making them simply comprehensible is
fairly an effort. With out correct cloud infrastructure tagging
conventions, it’s unattainable to correctly attribute prices to particular
aggregates on the service or group stage. Nonetheless, until this stage of
accounting readability is enabled, groups shall be compelled to function with out
absolutely understanding the fee implications of their selections.
Price not a consideration in engineering options
Engineers take into account numerous components when making engineering selections
– practical and non-functional necessities (efficiency, scalability
and safety and so forth). Price, nonetheless, will not be all the time thought-about. A part of the
motive, as coated above, is that growth groups usually lack
visibility on value. In some circumstances, whereas they’ve an inexpensive stage of
visibility on the price of their a part of the tech panorama, value might not
be perceived as a key consideration, or could also be seen as one other group’s
concern.
Indicators of this downside is perhaps the shortage of value concerns
talked about in design paperwork / RFCs / ADRs, or whether or not an engineering
supervisor can present how the price of their merchandise will change with scale.
Homegrown non-differentiating capabilities
Corporations typically keep customized instruments which have main overlaps in
capabilities with third-party instruments, whether or not open-source or business.
This may occasionally have occurred as a result of the customized instruments predate these
third-party options – for instance, customized container orchestration
instruments earlier than Kubernetes got here alongside. It may even have grown from an
early preliminary shortcut to implement a subset of functionality supplied by
mature exterior instruments. Over time, particular person selections to incrementally
construct on that early shortcut lead the group previous the tipping level that
might need led to using an exterior instrument.
Over the long run, the whole value of possession of such homegrown
programs can turn into prohibitive. Homegrown programs are sometimes very
simple to begin and fairly troublesome to grasp.
Overlapping capabilities in a number of instruments / instrument explosion
Having a number of instruments with the identical function – or at the least overlapping
functions, e.g. a number of CI/CD pipeline instruments or API observability instruments,
can naturally create value inefficiencies. This usually comes about when
there isn’t a paved
street,
and every group is autonomously selecting their technical stack, reasonably than
selecting instruments which are already licensed or most popular by the corporate.
Inefficient contract construction for managed providers
Selecting managed providers for non-differentiating capabilities, such
as SMS/e mail, observability, funds, or authorization can enormously
help a startup’s pursuit to get their product to market shortly and
preserve operational complexity in verify.
Managed service suppliers usually present compelling – low cost or free –
starter plans for his or her providers. These pricing fashions, nonetheless, can get
costly extra shortly than anticipated. Low cost starter plans apart, the
pricing mannequin negotiated initially might not swimsuit the startup’s present or
projected utilization. One thing that labored for a small group with few
prospects and engineers may turn into too costly when it grows to 5x
or 10x these numbers. An escalating pattern in the price of a managed
service per consumer (be it staff or prospects) as the corporate achieves
scaling milestones is an indication of a rising inefficiency.
Unable to achieve economies of scale
In any structure, the fee is correlated to the variety of
requests, transactions, customers utilizing the product, or a mix of
them. Because the product beneficial properties market traction and matures, firms hope
to achieve economies of scale, lowering the typical value to serve every consumer
or request (unit
value)
as its consumer base and site visitors grows. If an organization is having hassle
attaining economies of scale, its unit value would as an alternative enhance.
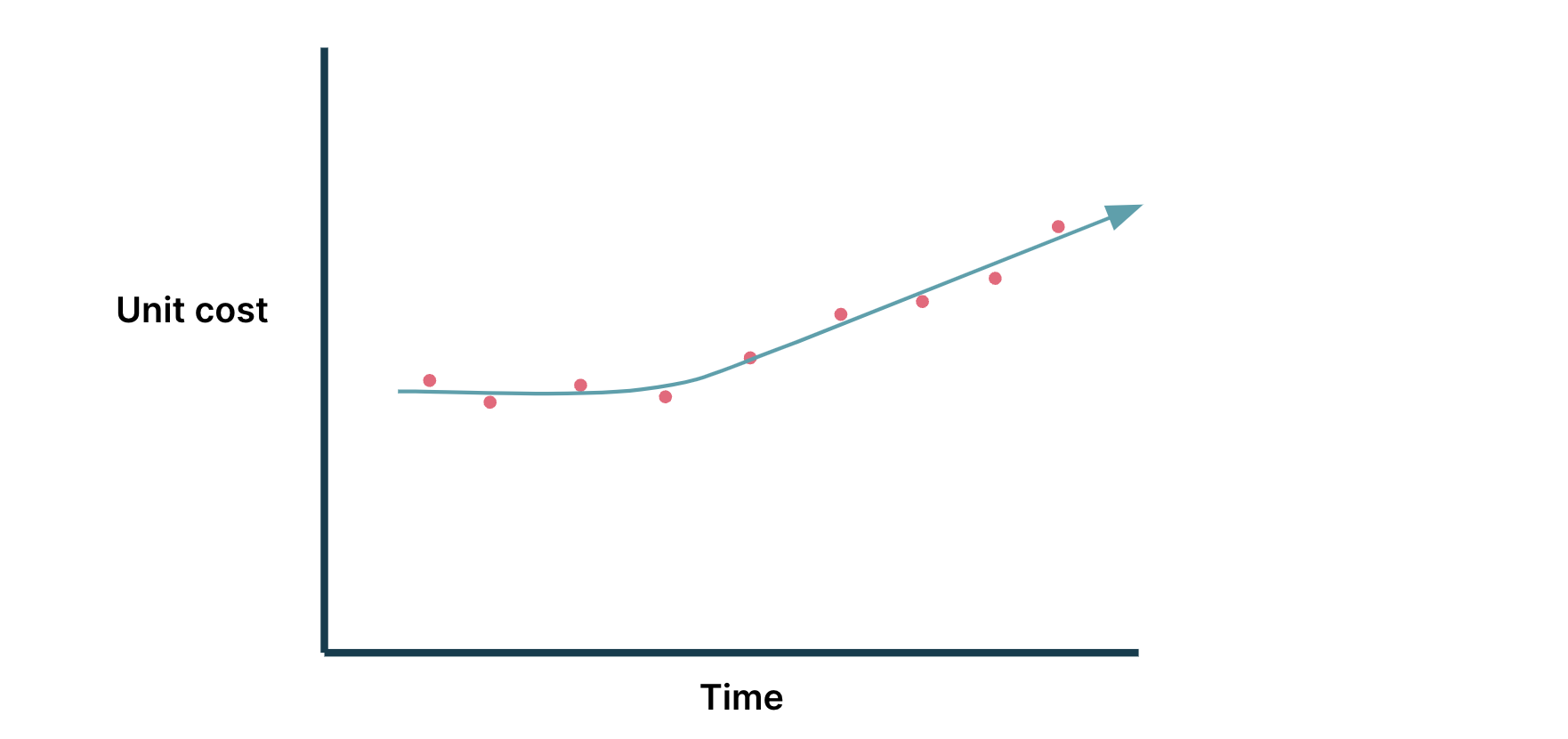
Determine 1: Not reaching economies of scale: rising unit value
Observe: on this instance diagram, it’s implied that there are extra
models (requests, transactions, customers as time progresses)
How do you get out of the bottleneck?
A traditional situation for our group once we optimize a scaleup, is that
the corporate has seen the bottleneck both by monitoring the indicators
talked about above, or it’s simply plain apparent (the deliberate funds was
fully blown). This triggers an initiative to enhance value
effectivity. Our group likes to arrange the initiative round two phases,
a cut back and a maintain section.
The cut back section is concentrated on quick time period wins – “stopping the
bleeding”. To do that, we have to create a multi-disciplined value
optimization group. There could also be some concept of what’s doable to
optimize, however it’s essential to dig deeper to essentially perceive. After
the preliminary alternative evaluation, the group defines the method,
prioritizes based mostly on the impression and energy, after which optimizes.
After the short-term beneficial properties within the cut back section, a correctly executed
maintain section is essential to keep up optimized value ranges in order that
the startup doesn’t have this downside once more sooner or later. To help
this, the corporate’s working mannequin and practices are tailored to enhance
accountability and possession round value, in order that product and platform
groups have the mandatory instruments and data to proceed
optimizing.
As an instance the cut back and maintain phased method, we are going to
describe a current value optimization enterprise.
Case examine: Databricks value optimization
A consumer of ours reached out as their prices had been rising
greater than they anticipated. They’d already recognized Databricks prices as
a prime value driver for them and requested that we assist optimize the fee
of their knowledge infrastructure. Urgency was excessive – the rising value was
beginning to eat into their different funds classes and rising
nonetheless.
After preliminary evaluation, we shortly shaped our value optimization group
and charged them with a purpose of lowering value by ~25% relative to the
chosen baseline.
The “Cut back” section
With Databricks as the main target space, we enumerated all of the methods we
may impression and handle prices. At a excessive stage, Databricks value
consists of digital machine value paid to the cloud supplier for the
underlying compute functionality and price paid to Databricks (Databricks
Unit value / DBU).
Every of those value classes has its personal levers – for instance, DBU
value can change relying on cluster sort (ephemeral job clusters are
cheaper), buy commitments (Databricks Commit Models / DBCUs), or
optimizing the runtime of the workload that runs on it.
As we had been tasked to “save value yesterday”, we went in quest of
fast wins. We prioritized these levers in opposition to their potential impression
on value and their effort stage. Because the transformation logic within the
knowledge pipelines are owned by respective product groups and our working
group didn’t have a great deal with on them, infrastructure-level adjustments
similar to cluster rightsizing, utilizing ephemeral clusters the place
applicable, and experimenting with Photon
runtime
had decrease effort estimates in comparison with optimization of the
transformation logic.
We began executing on the low-hanging fruits, collaborating with
the respective product groups. As we progressed, we monitored the fee
impression of our actions each 2 weeks to see if our value impression
projections had been holding up, or if we would have liked to regulate our priorities.
The financial savings added up. Just a few months in, we exceeded our purpose of ~25%
value financial savings month-to-month in opposition to the chosen baseline.
The “Maintain” section
Nonetheless, we didn’t need value financial savings in areas we had optimized to
creep again up once we turned our consideration to different areas nonetheless to be
optimized. The tactical steps we took had lowered value, however sustaining
the decrease spending required continued consideration as a result of an actual danger –
each engineer was a Databricks workspace administrator able to
creating clusters with any configuration they select, and groups had been
not monitoring how a lot their workspaces value. They weren’t held
accountable for these prices both.
To deal with this, we got down to do two issues: tighten entry
management and enhance value consciousness and accountability.
To tighten entry management, we restricted administrative entry to only
the individuals who wanted it. We additionally used Databricks cluster insurance policies to
restrict the cluster configuration choices engineers can choose – we needed
to attain a stability between permitting engineers to make adjustments to
their clusters and limiting their decisions to a smart set of
choices. This allowed us to reduce overprovisioning and management
prices.
To enhance value consciousness and accountability, we configured funds
alerts to be despatched out to the homeowners of respective workspaces if a
specific month’s value exceeds the predetermined threshold for that
workspace.
Each phases had been key to reaching and sustaining our targets. The
financial savings we achieved within the lowered section stayed steady for a variety of
months, save for fully new workloads.

