Cells in organisms have a particularly excessive capability for info processing and communication by transporting molecules or ions via small channels that cross the cell membrane. Marco Rolandi’s laboratory at UC Santa Cruz and companions at MIT have developed a gadget that replicates this organic thought to establish illness.
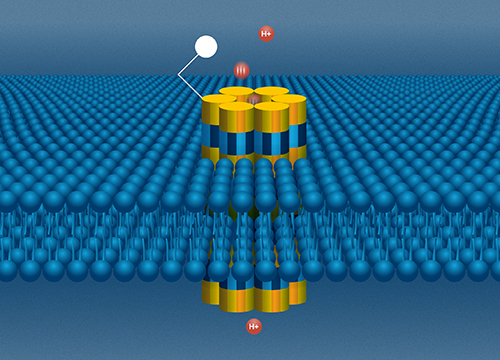
The bioprotonic system. A DNA nanopore sits in a lipid bilayer as an electrode sends a stream of protons via the channel. Picture Credit score: Molly Positive
The researchers can establish biomolecules that sign the presence of human illness utilizing their bioprotonic system, a tool that merges digital elements with organic elements and employs electrical currents of protons, amongst different purposes. The system’s specs had been simply revealed within the journal Nature Communications.
Cells are typically interconnected—they discuss to one another, or they discuss to the exterior surroundings, utilizing these intermembrane channels. What we got down to do with our collaborators at MIT was create a synthetic ion channel in a approach that we might tune the properties of the ion channel and its performance as we need.
Marco Rolandi, Affiliate Professor, Electrical Engineering, College of California, Santa Cruz
The researchers at MIT can bioengineer a strand of DNA, which naturally takes the form of a double helix, into no matter form they select utilizing a course of generally known as DNA origami. For this analysis, they developed a miniature tunnel exactly designed for a stream of protons (H-plus) to undergo greatest. This small channel is named a nanopore, and it was first proposed at UCSC.
Rolandi’s bioprotonic system, which is supposed to simulate the watery, ion-conducting world of the mobile surroundings, homes the DNA nanopore. A double layer of lipids, analogous to a cell membrane, divides water, which represents the surroundings exterior of the cell, from an electrode, which represents the within of the cell, and the implanted nanopore works as a conduit between the 2 sides.
The electrode creates a stream of protons that go down the nanopore channel to the other aspect of the nanopore, the place a molecule binding website may be tailor-made to draw sure biomolecules of curiosity. If a type of molecules is within the water, it should cling to the nanopore’s one finish and hinder the stream of protons via the channel.
The know-how converts the proton sign into {an electrical} sign that may be learn by the researchers. The researchers know {that a} biomolecule is current when the tools doesn’t detect protons touring via the channel.
The system additionally has two handles composed of ldl cholesterol which might be positioned throughout the lipid bilayer to advertise proton conductivity throughout the nanopore channel.
Rolandi added, “The individuality of the strategy is the mix of those proton-conducting gadgets with supportive lipid bilayers, and I imagine we’re the one teams which might be engaged on these, with this dock design for the DNA nanopores. The novelty is each the combination of the system and the flexibility to sense utilizing these DNA nanopores.”
The researchers show of their examine that they’ll make the most of the bioprotonic system to detect the biomolecule B-type natriuretic peptide, which is an indication of coronary heart illness. This demonstrates the system’s potential for biomolecule identification in an in-vitro or scientific context.
The system might in the future embody many nanopores, every of which might be set as much as detect a unique sort of biomolecule, in accordance with the researchers’ predictions for the longer term.
Rolandi concluded, “It’s positively a part of the attractiveness of the system—within the close to future we might multiplex, so we might have a full suite of biosensors.”
Le (Dante) Luo, Yunjeong Park, and Jesse Sanchez, all from UCSC, labored on this examine. Moreover concerned on this effort had been researchers from the College of Washington and the TOBB College of Economics and Know-how in Ankara, Turkey. The Nationwide Science Basis funded the analysis.
Journal Reference
Luo, L., et al. (2023) DNA nanopores as synthetic membrane channels for bioprotonics. Nature Communications. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40870-1
Supply: https://www.ucsc.edu/index.html

