Oct 10, 2023
(Nanowerk Information) In an effort to develop simpler shielding from electromagnetic (EM) radiation, researchers have turned to nature for inspiration. A brand new research particulars how proteins can improve the properties of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) to soak up microwave radiation. Revealed within the journal Small (“Hierarchical-Bioinspired MOFs Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption”), the findings display the promise of bioinspired supplies to advance EM shielding applied sciences.
Key Takeaways
Researchers have found that proteins, particularly bovine serum albumin (BSA), can enhance the microwave absorption capabilities of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
The optimized composite, 2-BSA@Mil-100, achieved vital reflection loss at essential frequencies for radar and satellite tv for pc communications.
The combination of proteins with MOFs might supply light-weight and versatile shielding towards a broad vary of microwave frequencies.
Potential functions lengthen to biomedical gadgets, protection merchandise, and extra.
Regardless of promising outcomes, additional analysis is required to evaluate stability, recyclability, and security earlier than widespread industrial use.
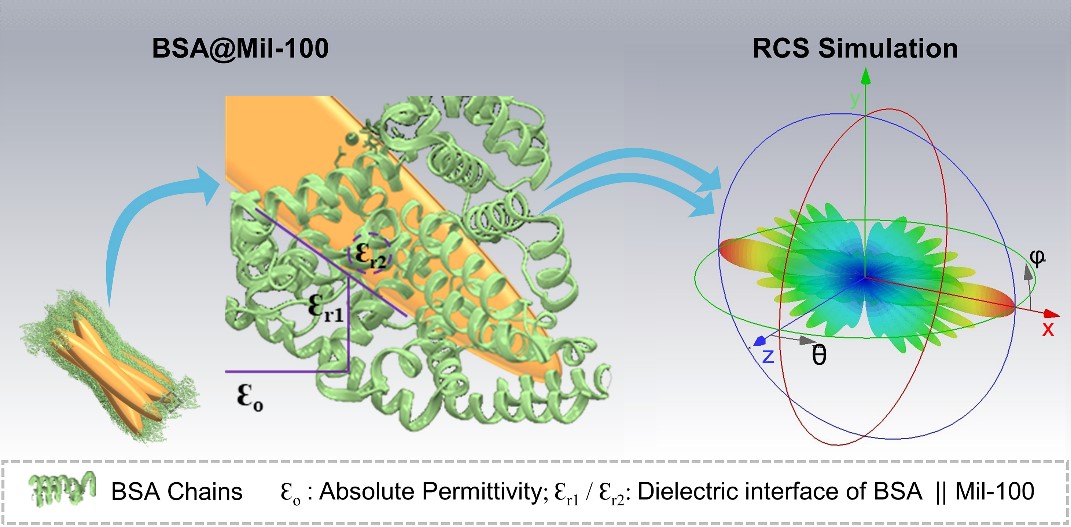
The outcomes uncover intricate structural parameters, notably protein cage thickness, and their influence on electromagnetic properties. The current exploration dissects their function in shaping dielectric properties and attaining optimum impedance matching, shedding mild on structural mechanisms that contribute to the fabric’s radar cross part (RCS) absorption efficiency. (Picture: Sajid)
The Analysis
Publicity to EM radiation from sources like radar, cell telephones, and wifi has dramatically elevated. On the identical time, the necessity for light-weight and versatile radiation shielding continues to develop, particularly for electronics and protection functions. Supplies like carbon and MOFs have proven potential, however attaining broad, high-performance microwave absorption stays difficult.
In accordance with the researchers from the Excessive Magnetic Subject Laboratory in China, proteins supply an answer to boost MOFs. The complicated molecular construction and useful teams of proteins can information the formation of intricate MOF networks. Lead creator Dr. Kun Ma defined, “Proteins exhibit complicated and numerous multi-dimensional buildings together with a variety of useful teams able to binding metallic ions.” By leveraging these traits, the synthesis and ensuing morphology of MOFs will be refined.
To check their speculation, the scientists centered on a protein known as bovine serum albumin (BSA). Plentiful in cows’ blood, BSA comprises a collection of amino acids and teams ripe for coordinating with metals. The crew mixed BSA with an iron-based MOF known as Mil-100 in numerous ratios utilizing hydrothermal synthesis.
Analyses revealed {that a} BSA focus of 40% optimally formed the MOF into uniform, extremely interconnected nanoflowers. This 2-BSA@Mil-100 composite displayed distinctive microwave absorption capabilities. At a mere 2.8 mm thickness, it achieved a mirrored image lack of -58 dB at 8.85 GHz frequency. This span encompasses your complete Ku band (12-18 GHz) essential for radar and satellite tv for pc communications.
Dr. Ma attributes the improved efficiency to synergistic results between the BSA and MOF. The amino acid teams seemingly work together with iron atoms to effectively convert EM power into warmth. BSA additionally introduces further nitrogen-based defects that increase conductivity. Importantly, the biotemplating preserves the excessive floor space essential for absorption whereas regularizing the construction.
Co-author Dr. Junfeng Wang added, “Our analysis sheds new mild on the importance of proteins, particularly biomineralized BSA, in directing the synthesis of MOFs with enhanced construction and microwave absorption efficiency.”
In comparison with different latest EM shielding supplies, the BSA-MOF composite shows distinctive bandwidth in a remarkably skinny configuration. With additional improvement, the bioinspired method might allow light-weight, versatile shielding towards a large spectrum of microwave frequencies.
Past electronics and telecommunications, the supplies present promise for biomedical and protection merchandise. Implanted medical gadgets want safety from EM interference, whereas radar-absorbing navy plane and coatings depend on broad bandwidth supplies. The research’s lead authors, Dr. Sajid and Xu, famous the BSA@Mil-100’s excessive absorption capability makes it nicely fitted to these real-world functions.
Nevertheless, the steadiness and recyclability of proteins built-in with MOFs require additional evaluation earlier than commercialization. Security is one other key consideration when incorporating organic elements into useful supplies.
Nonetheless, specialists see the early outcomes as an thrilling proof of idea. Harnessing the traditional ingenuity of proteins might be the lacking hyperlink to boost next-gen instruments reliant on EM shielding. Dr. Wang summarized, “This method affords a promising new avenue for the design and improvement of high-performance microwave absorption supplies.”
The synergistic mixture of biology and superior supplies might maintain options to fill essential gaps in rising applied sciences. Because the researchers now concentrate on optimization and scaling, their bio-inspired MOFs transfer nearer to enabling lighter, extra versatile EM shielding throughout numerous functions.
 The outcomes uncover intricate structural parameters, notably protein cage thickness, and their influence on electromagnetic properties. The current exploration dissects their function in shaping dielectric properties and attaining optimum impedance matching, shedding mild on structural mechanisms that contribute to the fabric’s radar cross part (RCS) absorption efficiency. (Picture: Sajid)
The outcomes uncover intricate structural parameters, notably protein cage thickness, and their influence on electromagnetic properties. The current exploration dissects their function in shaping dielectric properties and attaining optimum impedance matching, shedding mild on structural mechanisms that contribute to the fabric’s radar cross part (RCS) absorption efficiency. (Picture: Sajid)
 The outcomes uncover intricate structural parameters, notably protein cage thickness, and their influence on electromagnetic properties. The current exploration dissects their function in shaping dielectric properties and attaining optimum impedance matching, shedding mild on structural mechanisms that contribute to the fabric’s radar cross part (RCS) absorption efficiency. (Picture: Sajid)
The outcomes uncover intricate structural parameters, notably protein cage thickness, and their influence on electromagnetic properties. The current exploration dissects their function in shaping dielectric properties and attaining optimum impedance matching, shedding mild on structural mechanisms that contribute to the fabric’s radar cross part (RCS) absorption efficiency. (Picture: Sajid)