As power and utilities firms try to make use of the sting to innovate new options for delivering extra environment friendly and resilient companies, cybersecurity dangers to finishing up these enterprise missions loom massive. Ransomware attackers and different cybercriminals have more and more discovered power and utilities organizations a worthwhile goal, lobbying high-profile assaults in the previous few years which have threatened security and uptime within the course of.
Operational and safety specialists at these firms are effectively conscious of the balancing act they have to obtain underneath these situations, based on a brand new {industry} breakout of the AT&T Cybersecurity Insights Report. Launched this week, the AT&T Cybersecurity Insights Report: Give attention to Vitality and Utilities exhibits that technologists in these organizations are known as upon by the enterprise to roll out edge use circumstances similar to remote-control operations, self-healing belongings, and clever grid administration. On the similar time, they have to guarantee these deployments are accomplished with cybersecurity as a central element, because the influence of assaults towards this vertical’s edge-connected belongings might have drastic penalties for firms tasked with delivering probably the most very important sources for contemporary residing.
Speedy charge of power and utility innovation
One of many key areas examined by the AT&T Cybersecurity Insights Report is the speed of adoption of edge computing, the use circumstances in play, and their stage of maturity. This was tracked throughout six main sectors. This newest {industry} report dives into the developments for firms that present companies and sources similar to electrical energy, oil and gasoline, water, and sewer. The research exhibits that some 77% of power and utilities respondents worldwide are planning to implement, have partially carried out, or have absolutely carried out an edge use case. The research dug into 9 industry-specific use circumstances and examined their stage of adoption throughout the power and utilities sector.
Combining the mid-stage and mature stage adoption charges reveals that using edge computing in infrastructure leak detection has the very best mixed adoption maturity (82%) amongst survey respondents. Some examples of how this seems in motion consists of utilizing sensors to gauge the movement of water in a municipal water system and utilizing the low latency of edge connections to watch that knowledge in actual time for drops or spikes in stress that might point out the necessity for preventive upkeep or rapid servicing of kit. That is in fact a single instance in a broad vary of use circumstances at present underneath exploration on this sector.
Edge computing has opened up great alternatives for power and utilities firms to resolve powerful issues throughout your entire worth chain, together with the secure acquisition of power provides on the entrance finish of the availability chain, the right monitoring of consumption of power and sources on the again finish, and the environment friendly use of services and tools to run the capabilities between the 2 phases. Some extra examples mostly cited had been:
- Distant management operations
- Geographic infrastructure exploration, discovery, and administration
- Related subject companies
- Clever grid administration
Curiously, regardless of many power firms engaged in proof-of-concept and insulated initiatives, total the sector’s charge of mature adoption was the least prevalent in comparison with all different sectors, sitting at about 40%. Survey evaluation signifies this is not from a scarcity of curiosity, however as an alternative a product of the justifiably cautious nature of this {industry}, which retains security and availability high of thoughts. The truth that this market phase had the very best degree of adoption in mid-stage in comparison with different industries gives a clue that these firms are all-in on edge deployments however taking their time contemplating and accounting for the dangers—together with these on the cybersecurity entrance.
Compromise worries develop
The research exhibits that 79% of power and utilities respondents consider there’s a excessive or very excessive chance of a compromise in one of many use circumstances supposed for manufacturing throughout the subsequent three years. When respondents had been requested in regards to the influence {that a} profitable compromise would have, power and utilities {industry} respondents had been probably the most involved of all {industry} respondents. That is hardly stunning given the grave real-world, bodily penalties that may stem from a lack of management or security over operational know-how (OT) belongings that run the ability crops and pipelines inside this {industry}.
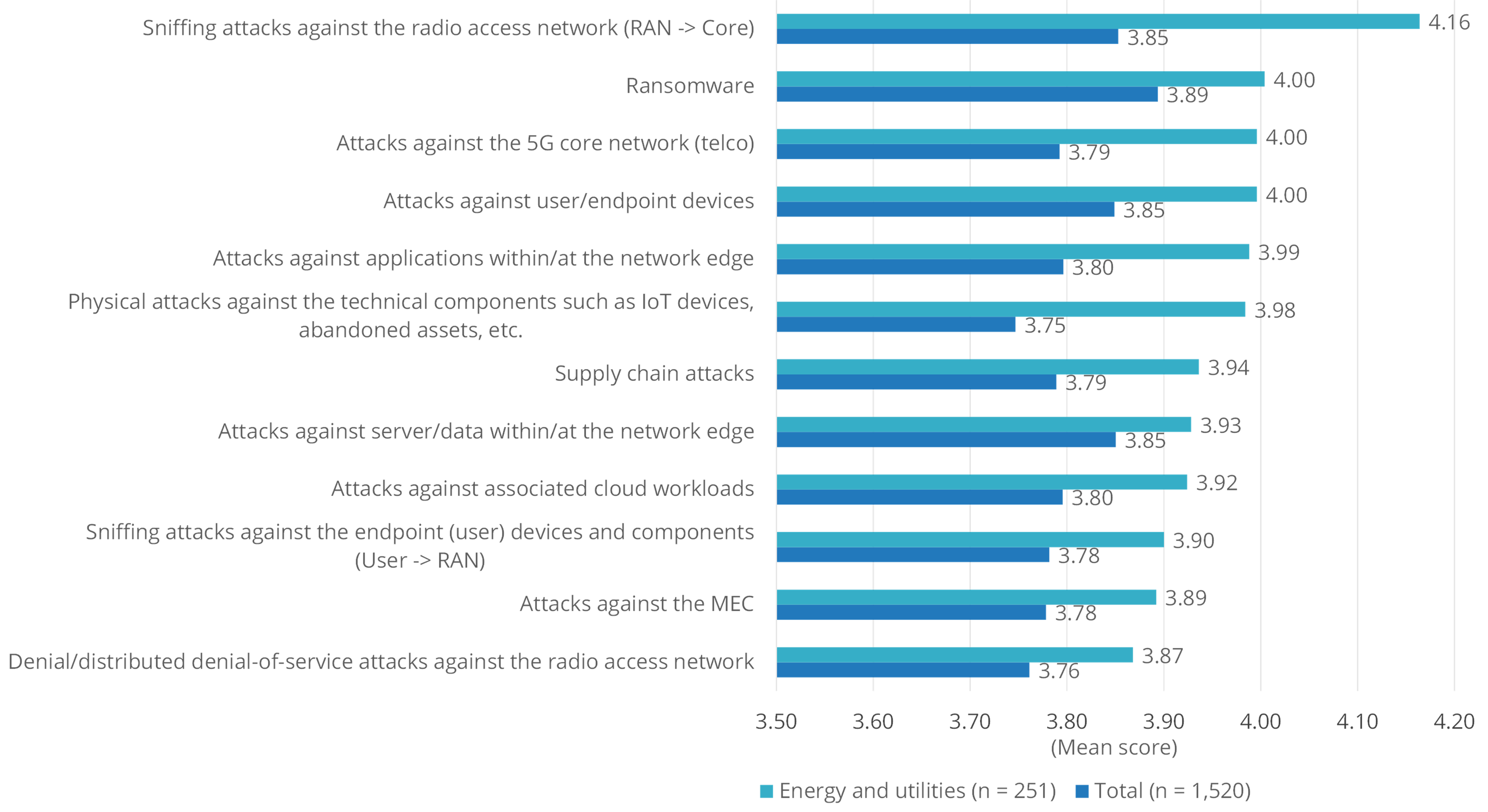
Given the media consideration surrounding very public ransomware assaults on this sector lately, it is no shock that ransomware is likely one of the high cybersecurity considerations for know-how leaders on this house. Nonetheless, it’s however not the primary cybersecurity concern for know-how leaders within the power and utilities house, sitting as an alternative as quantity two behind the extra urgent challenge of potential sniffing assaults towards radio entry networks (RAN). Additionally tied for second alongside ransomware had been assaults towards 5G core networks, and assaults towards consumer/endpoint units.
An attention-grabbing level to notice about this {industry} is its heightened degree of concern over bodily assaults towards technical elements similar to IoT units. The {industry} rated this concern a lot larger than the common respondent. That is probably a operate of the {industry}’s rising reliance on distant sensors, units, and endpoints in low-latency (and sometimes far-flung) environments.
The distinctive cyber issues in power OT environs
Defending the power of a company to securely present dependable electrical energy, correct payments, and secure pipelines will more and more require cyber controls be utilized to the exterior belongings that ship the advantages of edge computing use circumstances. Happily, power and utilities leaders are investing accordingly in cybersecurity controls across the edge.
The research exhibits that the power and utilities sector has the second-highest dedication to main safety investments baked into edge use circumstances in comparison with the others, lagging solely barely behind the US public sector. Roughly 65% of power and utilities corporations are allocating 11% or extra of their edge funding straight for safety.
One of many challenges in making use of that funding is the so-called IT-OT safety hole that face industrial sectors like this one. Vitality and utilities corporations cannot depend on many traditional cybersecurity controls like different industries, because of the limitations in know-how and operational elements not discovered elsewhere. For instance, many OT methods cannot be patched in a well timed vogue because of the operational dangers posed by a failed replace and the truth that many OT units could run months and even years between scheduled upkeep home windows. Operators on this sector have a particularly low tolerance safety actions that doubtlessly danger bringing down a complete oil refinery or wastewater remedy facility. For this reason when the report examined the effectiveness score of safety controls on this {industry}, patching ranked lifeless final, as in comparison with a comparatively excessive score in all different industries.
Additional, it might be difficult to gather and normalize knowledge for monitoring functions given the rise in knowledge throughout merged IT/OT networks. OT networks can’t be monitored in the identical method that IT networks are, attributable to distinctive protocols and in addition comparable danger issues that the safety ‘treatment’ could also be worse than the illness. For instance, lively scanning strategies can usually disrupt or take down OT networks. That is probably why intrusion detection options had been rated to have the very best complete value of possession (TCO) inside this specific sector.
As power and utilities firms try for the precise steadiness of innovation and safety on the edge, we suggest a cautious method that accounts for the truth that conventional endpoint-centric controls like patching cannot all the time be the go-to answer. Proactive controls similar to micro segmentation, passive vulnerability scans, and risk looking needs to be thought of for these harder use circumstances. These organizations ought to contemplate getting skilled steerage from service suppliers on the entrance finish to guage highway maps for present and proposed use circumstances. The specialists at these suppliers have already tread this floor and may finest advise on the potential hazards that a company could face alongside the way in which.