Posted by Pedro Barbosa, Safety Engineer, and Daniel Bleichenbacher, Software program Engineer
Paranoid is a undertaking to detect well-known weaknesses in massive quantities of crypto artifacts, like public keys and digital signatures. On August third 2022 we open sourced the library containing the checks that we applied to date (https://github.com/google/paranoid_crypto). The library is developed and maintained by members of the Google Safety Group, however it isn’t an formally supported Google product.
Why the Venture?
Crypto artifacts could also be generated by techniques with implementations unknown to us; we check with them as “black containers.” An artifact could also be generated by a black-box if, for instance, it was not generated by one among our personal instruments (corresponding to Tink), or by a library that we will examine and take a look at utilizing Wycheproof. Sadly, generally we find yourself counting on black-box generated artifacts (e.g. generated by proprietary HSMs).
After the disclosure of the ROCA vulnerability, we questioned what different weaknesses could exist in crypto artifacts generated by black containers, and what we might do to detect and mitigate them. We then began engaged on this undertaking in 2019 and created a library to carry out checks in opposition to massive quantities of crypto artifacts.
The library incorporates implementations and optimizations of current work discovered within the literature. The literature exhibits that the era of artifacts is flawed in some instances – under are examples of publications the library relies on.
As a current instance, CVE-2022-26320 discovered by Hanno Böck, confirmed the significance of checking for identified weaknesses. Paranoid has already discovered related weak keys independently (by way of the CheckFermat take a look at). We additionally consider the undertaking has potential to detect new vulnerabilities since we usually try and generalize detections as a lot as we will.
Name for Contributions
The objective of open sourcing the library is to extend transparency, permit different ecosystems to make use of it (corresponding to Certificates Authorities – CAs that must run related checks to fulfill compliance), and obtain contributions from exterior researchers. By doing so, we’re making a name for contributions, in hopes that after researchers discover and report crypto vulnerabilities, the checks are added into the library. This fashion, Google and the remainder of the world can reply rapidly to new threats.
Word, the undertaking is meant to be mild in its use of computational assets. The checks have to be quick sufficient to run in opposition to massive numbers of artifacts and should make sense in actual world manufacturing context. Initiatives with much less restrictions, corresponding to RsaCtfTool, could also be extra acceptable for various use instances.
Along with contributions of recent checks, enhancements to those who exist already are additionally welcome. By analyzing the launched supply one can see some issues which are nonetheless open. For instance, for ECDSA signatures through which the secrets and techniques are generated utilizing java.util.random, we now have a precomputed mannequin that is ready to detect this vulnerability given two signatures over secp256r1 typically. Nevertheless, for bigger curves corresponding to secp384r1, we now have not been capable of precompute a mannequin with vital success.
Along with ECDSA signatures, we additionally applied checks for RSA and EC public keys, and common (pseudo) random bit streams. For the latter, we have been capable of construct some enhancements on the NIST SP 800-22 take a look at suite and to incorporate extra checks utilizing lattice discount strategies.
Preliminary outcomes
Much like different printed works, we now have been analyzing the crypto artifacts from Certificates Transparency (CT), which logs issued web site certificates since 2013 with the objective of constructing them clear and verifiable. Its database incorporates greater than 7 billion certificates.
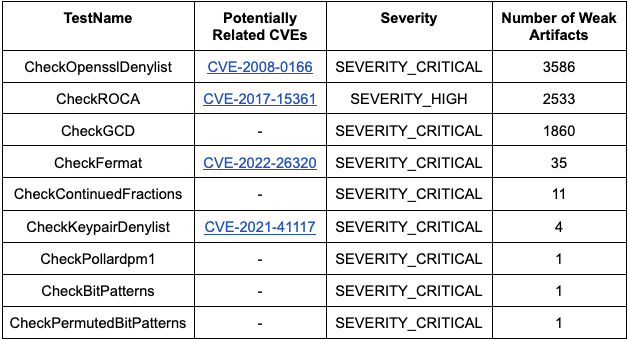
For the checks of EC public keys and ECDSA signatures, to date, we now have not discovered any weak artifacts in CT. For the RSA public key checks with severities excessive or vital, we now have the next outcomes:
A few of these certificates have been already expired or revoked. For those that have been nonetheless lively (many of the CheckGCD ones), we instantly reported them to the CAs to be revoked. Reporting weak certificates is necessary to maintain the web safe, as said by the insurance policies of the CAs. The Let’s Encrypt coverage, for instance, is outlined right here. In one other instance, Digicert states:
Certificates revocation and certificates drawback reporting are an necessary a part of on-line belief. Certificates revocation is used to stop using certificates with compromised non-public keys, scale back the specter of malicious web sites, and deal with system-wide assaults and vulnerabilities. As a member of the web neighborhood, you play an necessary position in serving to preserve on-line belief by requesting certificates revocations when wanted.
What’s subsequent?
We plan to proceed analyzing Certificates Transparency, and now with the assistance of exterior contributions, we’ll proceed the implementation of recent checks and optimization of these current.
We’re additionally carefully watching the NIST Publish-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Course of for brand new algorithms that make sense to implement checks. New crypto implementations carry the opportunity of new bugs, and it’s important that Paranoid is ready to detect them.