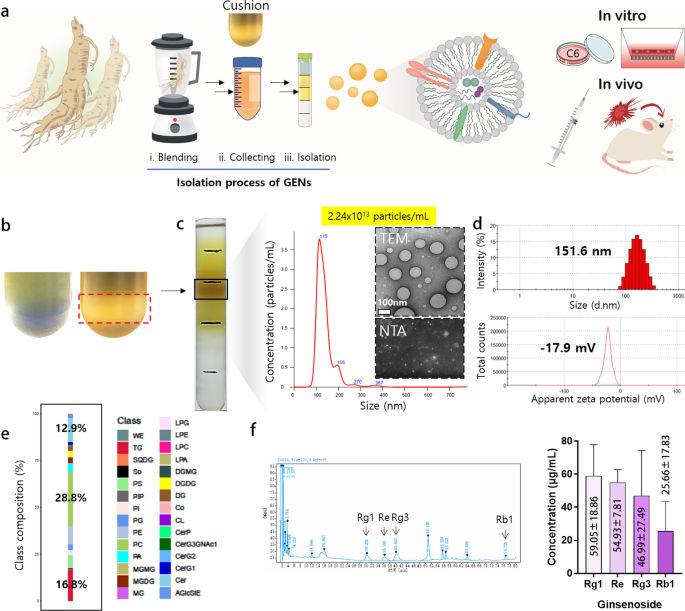
Isolation, characterization, and stability of GENs
To isolate exosome-like nanoparticles from Panax ginseng, uncooked contemporary ginseng was completely floor in 1X PBS. After sequential low-velocity centrifugation steps, giant particles and impurities have been faraway from the ginseng juice. The sucrose cushion technique was utilized to stop the aggregation and degradation of the exosomes, achieved by growing centrifugal drive (Fig. 1a, b). GENs have been noticed by sucrose gradient fractionation at 1.13–1.19 g/mL (Fig. 1c) and recognized based mostly on the common measurement of 151.6 nm with a low polydispersity index (PDI) ranges. The zeta potential of GENs indicated that GENs held a detrimental cost of –17.9 mV (Fig. 1d). The dimensions distribution and particle focus have been measured by nanoparticle monitoring evaluation (NTA). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) evaluation indicated that the GENs have been principally spherical and uniform in form, with out aggregation or degradation. The quantification of GENs was carried out by measuring the protein focus utilizing a Bradford assay package, which indicated that GENs from ginseng have been produced abundantly (roughly 1.68 mg per 10 g of ginseng tissue, based mostly on the protein focus). These outcomes recommend that homogenous GENs could be obtained on a big scale utilizing a easy and eco-friendly technique (Extra file 1: Fig. S1e).
Isolation and characterization of ginseng-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (GENs). a A schematic illustration of the isolation technique of GENs from contemporary ginseng. Ginseng juice was sequentially centrifuged at high and low velocity of pace to isolate GENs. The sucrose cushion technique was employed by layering sucrose at concentrations of 68% and 27%. GENs have been purified by a buoyant density from 1.13 to 1.19 g/mL utilizing a density gradient technique. After the purification of GENs, the mobile toxicity and therapeutic effectivity of GENs have been evaluated by in vitro and in vivo analyses. b The sucrose cushion technique to stop disruption of the extracellular vesicles (EVs) and contaminants attributable to extreme aggregates of EVs throughout centrifugation (proper). c The precise layer between 8 and 30% of sucrose was achieved and the focus of two.24 × 10.13 particles/mL and measurement distribution have been decided with a serial dilution of GENs by nanoparticle monitoring evaluation (NTA). The round-shaped morphology of GENs was noticed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM; inset). d The dimensions and zeta potential of GENs have been measured at 37 ℃ by dynamic mild scattering (DLS). e A graph of lipidomic evaluation was reported as the proportion of the parts of lipids of GENs. f The focus of ginsenosides of GENs was decided by excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC). wax esters (WE), triglycerides (TG), sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol (SQDG), sphingosine (So), phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP), phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylgylcerols (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidic acid (PA), monogalactosylmonoacylglycerol (MGMG), monogalactosylacylglycerols (MGDG), monoacylglycerol (MG), lysophosphatidylglycerol (LPG), lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE), lysophophatidylcholine (LPC), lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), digalactosylmonoacylglycerol (dgmg), digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), diacylglycerol (DG), coenzyme (Co), cardiolipin (CL), ceramide 1-phosphates (CerP), CerG3GNAc1, diglycosylceramide (CerG2), glucosylceramide (CerG1), ceramides (Cer), acylglucosyl-sitosterol esters (AGlcSiE)
To characterize the profile of GENs, we extracted whole RNA, encapsulated lipids, and protein and carried out RNA sequencing evaluation, whole lipid profiling, and proteomic evaluation (Fig. 1e, Extra file 1: Desk S2, S3). The outcomes indicated that GENs primarily consisted of phospholipids enriched in phosphatidylcholine (PC; 28.8%), triglycerides (TG; 16.8%), and ceramides (Cer; 12.9%). A complete of 98 miRNAs focusing on numerous genes in C6 glioma cells and 86 proteins much like these present in Panax ginseng have been recognized. We hypothesized that the plentiful membrane lipids in GENs contribute to their stability and should facilitate preferential uptake by the BBB and mind tumor tissues.
As well as, the ginsenosides have been extracted from GENs and analyzed by excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC). The extraction of ginsenosides from GENs was carried out beneath optimized extraction circumstances. The primary energetic parts of ginsenosides, together with Rg1, Re, Rg3, and Rb1, have been detected in GENs at various concentrations, which doubtlessly contributes to its effectiveness within the therapy (Fig. 1f).
To evaluate the steadiness of GENs, their measurement and zeta potential have been measured for 30 days. GENs have been aliquoted and saved at –80 ℃. The dimensions and zeta potential of GENs have been measured to remain intact round 150 nm with a low PDI worth, whereas the zeta potential of GENs maintained a detrimental cost of roughly –20 mV (Extra file 1: Fig. S1a, b). Typical freeze-drying of GENs was additionally carried out to ensure long-term stability. The morphology of GENs remained in the identical uniform spherical form after the freeze-drying as noticed by TEM. The dimensions and zeta potential of freeze-dried GENs confirmed slight will increase in comparison with the contemporary GENs (Extra file 1: Fig. S2a, b). Therefore, the freeze-dried GENs have been used within the consecutive experiments. To additional analyze the steadiness and profile of GENs, the concentrations of whole RNA and protein have been measured. The integrity of whole RNA extracted from ginseng tissue and GENs was analyzed by 10% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. It was noticed that the entire RNA of GENs was enriched, and the integrity and size of RNA fragments in GENs have been barely distinct from these extracted from ginseng tissues. Consequently, the RNA fragments remoted from GENs consisted of varied RNA fragments ranging in measurement from 50 to 500 base pairs (bp), whereas the RNA fragments remoted from ginseng tissues have been 80–1000 bp in measurement.
As well as, the samples of whole protein extracted from ginseng tissue and GENs have been separated by 15% SDS-PAGE gel. The proteins remoted from ginseng tissues and people remoted from GENs revealed comparable protein bands, indicating the dependable consistency of the protein parts (Extra file 1: Fig. S2c–e).
Impact of GENs on glioma cell apoptosis in vitro
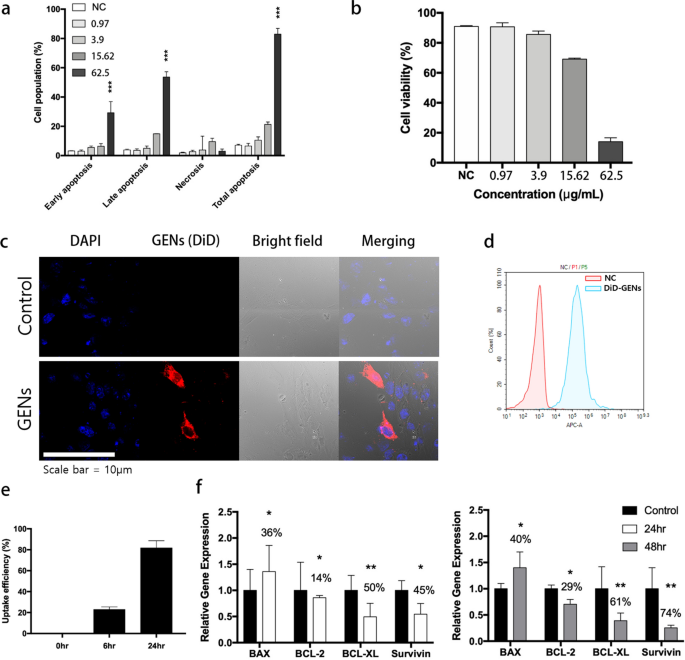
To quantify the ratio of C6 glioma apoptosis, apoptosis induced by GENs was analyzed by an Annexin V/PI assay. Because the focus of GENs elevated, the C6 glioma cells confirmed larger charges of early apoptosis (FITC + /PI−) and late apoptosis/necrosis (FITC + /PI +) in contrast with the detrimental management group (Fig. 2a, b). To check the impact of GENs on C6 glioma cell viability, the cells have been handled with GENs at concentrations starting from 1 to 62.5 μg/mL for twenty-four h. Consequently, C6 glioma apoptosis was initiated by therapy of GENs at a focus of 15.625 μg/mL and the entire apoptosis was considerably elevated at a focus of 62.5 μg/mL of GENs, exhibiting 81 ± 1.4% of apoptotic cell loss of life. Collectively, move cytometry evaluation indicated that GENs may primarily have an effect on C6 glioma cell apoptosis when administered on the highest focus.
Apoptosis in C6 glioma cells handled with ginseng-derived exosome like nanoparticles (GENs) and mobile uptake of GENs. a Cell apoptosis assay in C6 glioma cells by Annexin V/PI after therapy with GENs at concentrations starting from 0.975 to 62.5 μg/mL for twenty-four h (the concentrations have been decided by Bradford assay). b Cell viability after therapy with GENs on the indicated concentrations was expressed as a share of cells within the management group (three impartial experiments). c Confocal fluorescence imaging confirmed the internalization of typical liposomes comprised of egg yolk and GENs by C6 glioma cells. After incubating C6 glioma cells with DiD-labeled GENs for six h, the distribution of GENs was assessed. Nucleic acid and GENs have been stained with Hoechst (blue) and DiD staining dye (pink), respectively. d Mobile uptake of GENs after 6 h of incubation. e Measurement of uptake effectivity of GENs in cells for twenty-four h. f Quantitative PCR evaluation for the mRNA expression of apoptosis-associated genes in C6 glioma cells handled with GENs. 50 µg/mL of GENs was handled in C6 glioma cells for twenty-four h and 48 h. The mRNA expression ranges have been normalized to these of GAPDH (housekeeping gene) and expressed as a ratio of the management group (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001)
Mobile uptake and internalization of GENs and in vitro BBB penetration
C6 glioma cells have been handled with DiD-labeled GENs and analyzed by confocal microscopy to find out the internalization of GENs. As proven in Fig. 2c, after 6 h of incubation, the distribution of DiD-labeled GENs in cells considerably elevated in contrast with DiD-labeled liposomes, indicating the selective uptake of GENs by C6 glioma cells. Additionally, the uptake of GENs continued to extend over a 24 h interval (Fig. 2c–e). To stimulate the mind surroundings, an in vitro transwell BBB mannequin was used (Extra file 1: Fig. S3). By using a co-culture transwell membrane with a pore measurement of 0.4 μm, we aimed to evaluate the internalization of GENs by the BBB. Mind capillary endothelial cells (BCECs) have been seeded on the higher compartment and incubated for 16 days till the transepithelial/endothelial electrical resistance (TEER) degree reached above 200 Ω cm2 (Extra file 1: Fig. S3b). Previous to the 24 h incubation of GENs, C6 glioma cells have been seeded within the decrease compartment. Then, DiD-labeled GENs have been positioned within the higher compartment and additional incubated for 12 h. C6 glioma cells within the decrease compartment have been collected and the environment friendly mobile uptake of GENs was noticed. Consequently, the DiD-labeled GENs may go by and be taken up by C6 glioma cells (Extra file 1: Fig. S3c). Thus, GENs could be internalized into the tumor by penetrating by the mimicked BBB and have the potential for drug supply to mind endothelial cells.
To guage the uptake mechanism of GENs into C6 glioma cells by the BBB, BCECs seeded on a transwell membrane have been handled for six h with a collection of inhibitors together with chlorpromazine (an inhibitor of clathrin-mediated endocytosis), cytochalasin D (a phagocytosis inhibitor), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (lipid raft disruptor), colchicine (pinocytosis and phagocytosis inhibitor), and antibodies for occludin and claudin-5 (paracellular transport inhibitors) (Extra file 1: Fig. S4). Moreover, to judge the internalization of DiD-labeled GENs at low temperatures, BCECs on the transwell have been incubated at 4 ℃ for 1 h, after which C6 glioma cells incubated with DiD-labeled GENs for 12 h within the higher compartment have been collected, and the fluorescence depth was measured (Extra file 1: Fig. S4). In contrast with the management group, a big discount (60.1% and 60.2%) in mobile uptake was noticed at 4 ℃ and with colchicin, a microtubule-disrupting drug. In distinction, chlorpromazine, methyl-β-cyclodextrin, and cytochalasin-D both had no have an effect on or barely disturbed the endocytosis of GENs by C6 glioma cells. Samples handled with occludin and claudin-5 antibodies, which block the transmembrane protein of tight junctions concerned in paracellular transport, exhibited roughly 98.2% and 91.2% mobile uptake in comparison with the controls. The internalization of DiD-labeled GENs considerably decreased at low temperatures and upon the addition of colchicine. It may be concluded that low-temperature circumstances can hinder the internalization of GENs, and that the mobile uptake mechanism of GENs in BCEC is mediated by phagocytosis.
To guage the cytotoxicity of GENs, an MTT assay was carried out to evaluate the expansion of C6 glioma cells after therapy with numerous concentrations of GENs (starting from 0.97 to 31.25 μg/mL) (Extra file 1: Fig. S5). The proliferation of C6 cells was not decreased and remained at about 100% after therapy with 31.25 μg/mL GENs for twenty-four h, and the inhibitory focus 50 (IC50) was decided to be 53 μg/mL (information not proven). These outcomes indicated that GENs are secure and don’t compromise cell viability. Moreover, GENs may present a secure and efficient platform for anticancer remedy.
Expression of apoptosis-related genes induced by GENs
To guage the impact of GENs on apoptosis in tumor cells, the induction of apoptosis was measured utilizing western blotting and RT-qPCR. C6 glioma cells have been incubated within the presence of GENs starting from 0.24 to 62.5 μg/mL. Protein expression ranges of BAX household genes have been analyzed. Consequently, the degrees of the apoptosis-related gene BAX elevated, whereas these of the anti-apoptotic genes equivalent to BCL-2 and Survivin considerably decreased (Extra file 1: Fig. S6a). These observations point out that GENs can activate BAX and downregulate BCL-2 and Survivin in C6 glioma cells in a dose-dependent method (Extra file 1: Fig. S6b–g).
The outcomes of RT-qPCR evaluation confirmed constant outcomes with the western blotting findings. After 48 h of therapy with GENs, an upregulation of BAX mRNA was noticed, whereas mRNA ranges of BCL-2, BCL-xL, and Survivin have been decreased by 29%, 61%, and 74%, respectively, in contrast with the management group (Fig. 2f). General, GENs seem to induce apoptosis in mind tumor cells (Fig. 2f).
GENs suppress mobile progress in glioma cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells
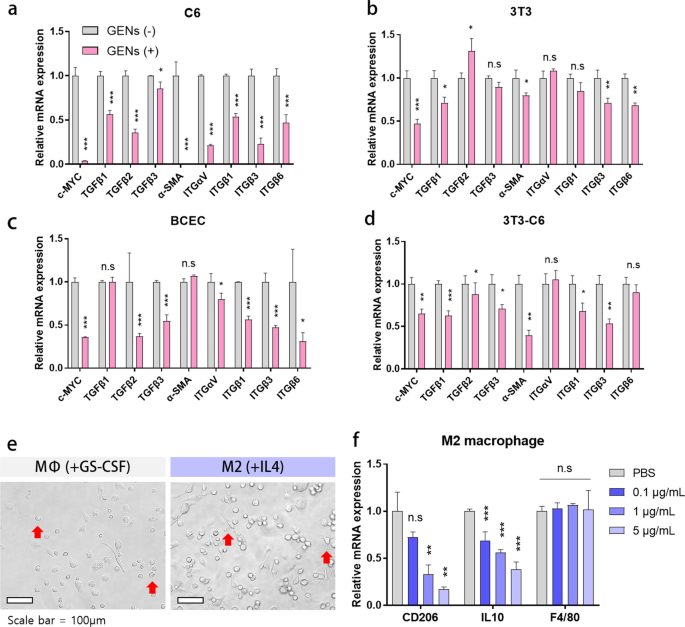
As proven in Fig. 3, we carried out multiplex cytokine evaluation to additional assess the regulation of CAFs by GENs. We evaluated the mRNA expression ranges of α-SMA, a marker of CAFs, and people of cell progress components together with c-MYC, TGF-β1/2/3, and integrin αVβ1/3/6 by RT-qPCR. After therapy with 10 μL of 1 mg/mL GENs for 48 h, we noticed a big lower within the mRNA ranges of c-MYC, TGF-β1/2/3, integrin αVβ1/3/6, and α-SMA. Comparable traits have been noticed in cell progress components in 3T3 cells and BCECs. Nevertheless, the expression ranges of some cytokines, equivalent to TGF-β3 and integrin αVβ1 in 3T3 cells and TGF-β1 and α-SMA (a marker of CAFs) in BCECs, didn’t differ considerably.
Inhibition of overexpressed c-MYC and activation of TGF-β and integrin in glioma cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells and the impact of therapy of M2 bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs). a–d Gene expression ranges of c-MYC proto-oncogene, TGFβ1, 2, 3, integrin αVβ1, 3, 6, and α-SMA in C6, 3T3, BCEC, and 3T3-C6 co-culture. e The morphology of BMMs, as noticed by microscopy. BMMs have been stimulated with GS-CSF for 7 days and with IL4 for 3 days. f The mRNA expression ranges in M2 macrophages after therapy with serially diluted GENs (*, P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001)
Furthermore, we co-cultured 3T3 and C6 at a 1:1 ratio to grasp the position of GENs in mimicking TMEs. After treating the co-cultured cells with GENs on the identical focus as within the earlier experiment, most cytokine genes, besides these encoding integrin αV and integrin β6, have been considerably downregulated (Fig. 3d). Collectively, GENs typically successfully suppressed cell progress components, CAFs, and a marker of CAFs in vitro.
GENs suppress M2 macrophage polarization
Macrophage phenotype transition is taken into account to be one of many main components in creating an efficient therapy choice for tumors. To know the impact of GENs on macrophages, we handled BMMs with GENs in vitro and assessed M2 macrophage polarization. Determine 3e exhibits the morphological variations in BMMs handled with numerous stimuli, together with GS-CSF and IL4. Unstimulated macrophages, MФs, confirmed a comparatively smaller and spherical morphology, whereas M2-treated macrophages confirmed a flat, elongated, and branching morphology. After treating the BMMs with serially diluted GENs starting from 0.1 to five μg/mL, we evaluated the gene expression ranges of CD206 and IL10, indicators of M2 macrophage polarization. As proven in Fig. 3f, in contrast with the management group, the mRNA expression ranges of CD206 and IL10 within the therapy teams decreased with growing concentrations of GENs. These outcomes point out that GENs successfully down-regulate M2 macrophage polarization and the expression of pro-tumoral cytokine with out inflicting cell harm.
Focusing on impact of GENs in vivo
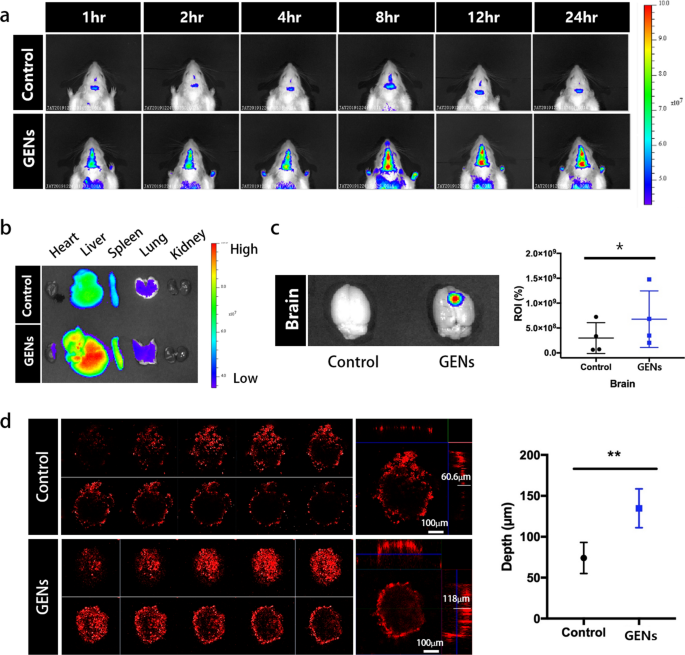
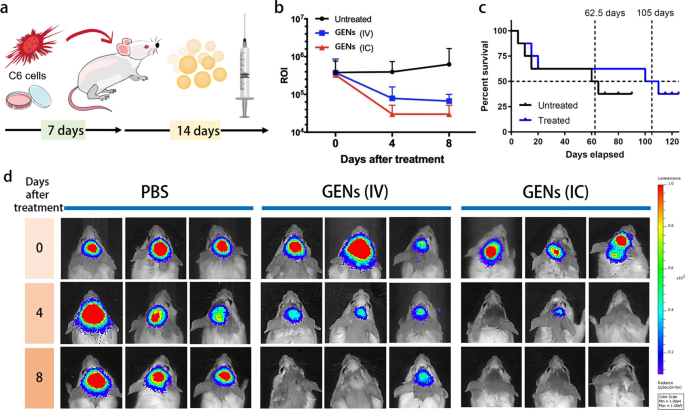
To guage the focusing on skill of GENs within the mind tumor, we ready 6–8-week-old Balb/C mice (18–20 g). DiD-labeled GENs have been intravenously injected, and the fluorescence depth of DiD-labeled GENs was measured utilizing an in vivo imaging system (IVIS) at completely different time factors over a time interval of 24 h (Fig. 4a). Prior to every pattern injection, we confirmed the comparable fluorescence depth of typical liposomes based mostly on egg-yolks and GENs to make sure constant experimental circumstances (not proven). In contrast with the standard liposomes, GENs confirmed a quickly growing accumulation within the mind in any respect timepoints. Particularly, GENs effectively crossed the BBB and reached the tumor inside 1 h after the administration. As well as, to find out the focusing on impact and bio-distribution of DiD-labeled GENs, we dissected and imaged a number of organs together with the guts, liver, pancreas, lung, kidney, and mind after 24 h of the injection of DiD-labeled typical liposomes and GENs (Fig. 4a–c). GENs demonstrated a preferential focusing on of mind tumors, exhibiting a better fluorescence depth than typical liposomes. By measuring the relative fluorescence intensities of the standard liposomes and GENs within the mind by area of curiosity (ROI), we discovered that GENs resulted in nearly 2.26-fold larger fluorescence depth in contrast with the management group (Fig. 4c). We additionally noticed a better accumulation of GENs within the liver, spleen, lung, and partly within the coronary heart in comparison with the standard liposomes. These findings could be attributed to the physiochemical properties of GENs.
The focusing on skill of GENs to glioma in vivo. a In vivo fluorescence imaging of DiD-labeled GENs. Typical liposomes based mostly on egg yolk have been used as a management. After intravenous (IV) administration of DiD-labeled GENs, fluorescence imaging was carried out at completely different time factors. b Ex vivo fluorescence imaging of the dissected organs 24 h after the IV injection of DiD-labeled GENs. Larger fluorescence depth within the mind was noticed in GENs in comparison with the management group. c Relative area of curiosity (ROI) of fluorescence depth within the mind samples. Utilizing ROI as a measure, the graph exhibits that GENs exhibited an nearly 2.26-fold larger fluorescence depth on common than the management group. d Penetration of GENs and traditional liposomes into 3D tumor spheroids (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01)
To additional consider the selective and particular penetration skill of GENs within the steric tumor surroundings, we generated a mimic tumor mannequin utilizing mobile aggregates by 3D non-scaffold-based cell cultures (Fig. 4d). 10 days after seeding C6 glioma cells, the diameter of the spheroids was measured to be roughly 400 μm. DiD-labeled GENs and traditional liposomes have been incubated with the tumor spheroids for 12 h. DiD-labeled GENs confirmed a a lot deeper penetration (118 ± 16.805 μm) in contrast with typical liposomes (60 ± 13.445 μm) (Fig. 4d). We hypothesize that GENs have a bonus in infiltrating tumors by macropinocytosis and because of the overexpression of glucose transporters 1 (GLUT-1) in C6 glioma cells [1, 16, 17]. In assist of this concept, when C6 glioma cells have been pre-treated with Nocodazole and a GLUT-1 inhibitor, the mobile uptake of GENs was considerably inhibited (Extra file 1: Fig. S7). This urged that macropinocytosis and the GLUT-1 pathway are the most important pathways concerned within the endocytosis of GENs in C6 glioma cells. Subsequently, GENs reveal appropriate physiological and chemical properties that allow enhanced intratumoral accumulation and quick penetration of the BBB.
Antitumor impact induced by GENs in vivo
To guage the anticancer impact of GENs, tumor-bearing Balb/C mice have been handled with 5 μL of two mg/mL GENs (based mostly on the protein focus) by intracranial (IC) injection and 200 μL of two mg/mL GENs (based mostly on the protein focus) by intravenous (IV) injection each different day for 14 days after orthotopic tumor implantation (Fig. 5a). The development of tumor progress was evaluated utilizing an IVIS from day 0 to eight, and the luminescence intensities of tumors within the experimental teams have been measured after the primary injection of GENs (Fig. 5b). Determine 5b displayed the luminescence depth of the tumor in a Balb/c mice, exhibiting a better luminescence depth within the management group, indicating tumor progress, in contrast with the GENs’ therapy group. In mice receiving each IV and IC injections of GENs, the luminescence intensities of C6-Luc decreased markedly because the therapy continued. Notably, a big lower within the luminescence depth of C6-Luc within the two experimental teams, particularly in mice receiving IC injection inside day 4 (Fig. 5b). The administration route appeared affect the efficacy of GENs, as they exhibited quicker tumor discount. The median survival time of the mice within the IV injection group was 105 days, considerably longer than that within the management group, with a median survival charge of 62.5 days (Fig. 5c).
In vivo anticancer impact induced by GENs and Kaplan–Meier survival evaluation. a Schematic illustration of the orthotopic mannequin utilizing a Balb/C mice. After the implantation of C6 glioma cells into the mind, GENs have been injected each different day for 14 days. b A area of curiosity (ROI) of luminescence depth in comparison with the management group after the indicated variety of days after the therapy (0 to eight days). c The survival charge of tumor-bearing mice handled with GENs in comparison with the management group (N = 8). d After orthotopic therapy, the luminescence depth of C6 cells (expressing luciferase) was measured by an in vivo imaging system. On day 8 after the therapy, a big discount within the luminescence depth of C6 glioma was noticed within the group handled with GENs in comparison with the management group (N = 8)
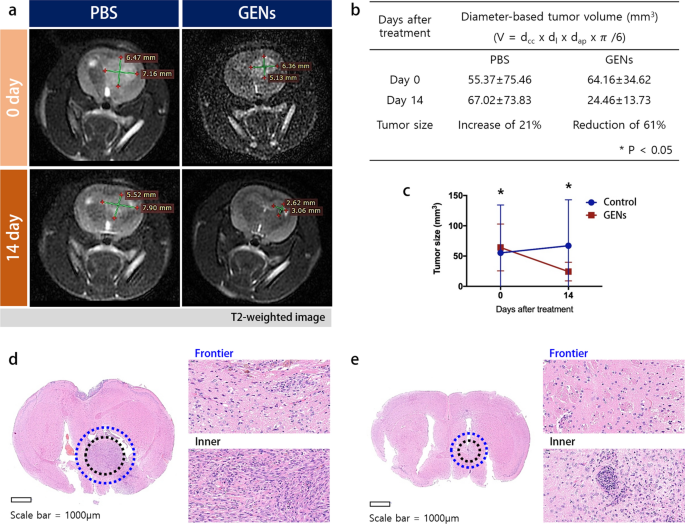
To visualise modifications within the tumor mass throughout the mind, we utilized the Wistar rat, and measured the tumor quantity of C6 glioma earlier than and after therapy with GENs. Orthotopic implantation of C6 glioma cells was carried out in 8-week-old Wistar rats (200–250 g). 14 days after the injection of GENs, tumor progress was monitored utilizing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with T2-weighted pictures 14 days after the injection of GENs (Fig. 6a). As proven in Fig. 6b, tumor quantity within the therapy group decreased considerably from 64.16 ± 34.62 mm3 to 24.46 ± 13.73 mm3, displaying a marked distinction with the management group the place tumor quantity elevated from 55.37 ± 75.46 mm3 to 67.02 ± 73.8 mm3.
Orthotopic-induced xenograft mind tumor tissue hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurement of the C6 glioma in Wistar rat. a After 14 days of therapy with GENs, the tumor quantity was measured by MRI imaging. b, c A desk and graph for the diameter-based tumor quantity. Tumors decreased in quantity by 61% at day 14 after therapy with GENs, whereas tumors elevated quantity by 21% within the management group. d–e H&E staining of the mind tissue of an management tumor and handled tumor, respectively (*P < 0.05)
As well as, three mice from every group (management, IV, and IC) have been sacrificed to gather mind tissues for evaluation. The mind tissues have been stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and reduce within the coronal aircraft. The outcomes revealed {that a} vital decreased in tumor measurement within the therapy teams, whereas a rise in tumor measurement was noticed within the management group (Fig. 6d, e). The H&E-stained mind tumor biopsy handled by GENs confirmed a decreased and small inhabitants of tumor cells, whereas the management group displayed vital histologic atypical modifications and a big inhabitants of tumor cell, as indicated by sturdy nuclear staining.
Analysis of liver toxicity of GENs in vivo
We additional analyzed the cytotoxicity of GENs in vivo. (Extra file 1: Fig. S8) After 7 instances of intravenous injections of GENs on the identical focus of therapy, the blood plasma was collected and the blood chemistry evaluation together with the blood aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), albumin (ALB), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), urea, creatine, and uric acid was carried out. Consequently, these indicators of liver operate weren’t elevated, indicating that the GENs weren’t dangerous and didn’t induce toxicity within the liver.
The regulation of CAFs results in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)
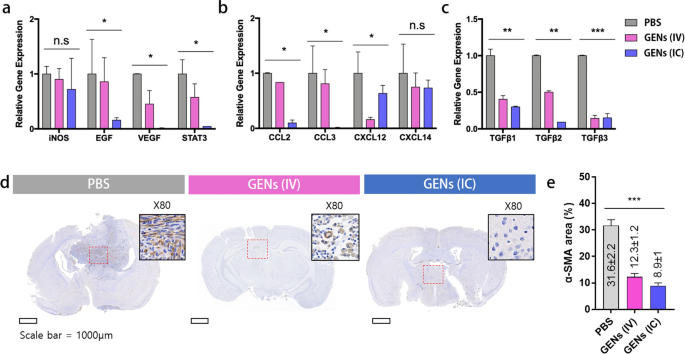
Regulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) is taken into account to be an necessary strategy for efficient remedy. The TME consists of a heterogeneous inhabitants of cells, together with infiltrating most cancers cells, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, mesenchymal macrophages, and fibroblasts. Cytokines and chemokines are excessively secreted from numerous cells, and uncontrolled cell signaling induces oncogenesis and ends in tumor development. Thus, when evaluating the therapeutic results towards tumors, it’s important to think about numerous points. To validate the immunomodulatory impact of GENs, we first examined the gene expression ranges of CAF within the TME within the mice. We assessed the mRNA expression ranges of progress components, angiogenic components, and chemokines. In contrast with the management group, we famous decreased mRNA ranges of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), epidermal progress issue (EGF), vascular endothelial progress issue (VEGF), sign transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT-3), and chemokines together with CCL2, CCL3, CXCL12, CXCL14, and the remodeling progress issue beta (TGF-β) household within the therapy teams (Fig. 7a–c). Decreased iNOS expression is accountable for decrease macrophage toxicity and may subsequently induce an immune response to deal with most cancers and suppress tumor progress [41]. Nevertheless, there was no vital distinction within the mRNA expression ranges of iNOS between the therapy teams. Apparently, the expression ranges of STAT3, which might doubtlessly management cell progress and act as an oncogenic driver by regulating a number of apoptosis-related pathways, have been considerably decreased within the therapy teams [6].
Gene expression of CAFs within the tumor microenvironment in tumor-bearing mice. a mRNA expression of CAF-related genes was decreased within the therapy group. b Decreased gene expression of chemokines. c Decreased gene expression of the TGFβ household within the therapy teams. Gray, PBS; pink, intravenous (IV) administration; blue, intracranial (IC) administration. d–e After therapy with GENs, α-SMA immunohistochemical staining within the mind tissue was decided (brown) (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001)
Moreover, the mRNA ranges of chemokines CCL2, CCL3, CXCL12, and CXCL14 have been additionally clearly decreased within the therapy teams. All issues thought of, GENs may not solely be a regulator of macrophage proliferation but in addition contribute to the downstream signaling pathway of apoptosis-related sign molecules in TAMs. Thus, GENs have the potential to develop into an important adjuvant therapeutic technique by lowering the expression of cytokines and selling tumor suppression.
To research the position of GENs in CAFs, the in vivo expression of α-SMA within the mind tissue was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining (Fig. 7d, e). Immunohistochemical staining of the mind tissue handled with GENs confirmed that the expression of α-SMA was considerably decreased in comparison with the mind tissue handled with PBS. The ratio of α-SMA-positive space was 31.6 ± 2.2% within the management group, whereas it was decreased to 12.3 ± 1.2%, and eight.9 ± 1%, within the GENs IV injection and GENs IC injection group, respectively. These outcomes confirmed that therapy with GENs successfully suppresses CAFs within the mind tumor-bearing mice, suggesting that GENs can function a promising therapeutic strategy to boost the effectiveness of most cancers therapy and enhance prognosis.
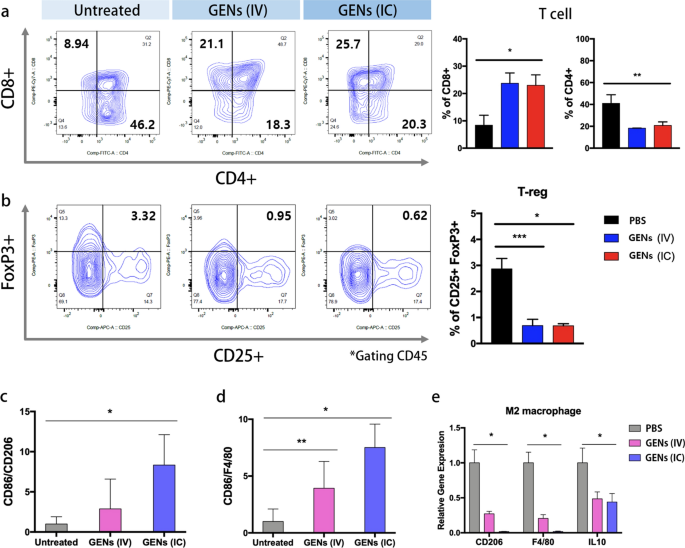
We had a selected curiosity in understanding the regulation of macrophages by GENs within the TME. To realize additional insights into immune regulation, we investigated the consequences of GENs on T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) (Fig. 8). T cells performs a vital position in defending towards infections and most cancers, whereas Tregs regulate the immune system. There’s a shut interplay between T cells and Tregs by a number of mechanisms. For instance, Tregs can inhibit T cell operate by secreting suppressive cytokines equivalent to TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-35. As well as, Tregs can suppress anticancer immunity and impede immune surveillance, thereby selling tumor progress and development [42]. Consequently, focusing on Tregs holds promise as an strategy for most cancers remedy. As proven in Fig. 8, therapy with GENs, led to a big enhance in CD8 + T cells, generally known as cytotoxic T cells, throughout the TME in contrast with the management group, whereas CD4 + T cells, generally known as helper T cells, have been decreased (Fig. 8a). The abundance of Tregs (FoxP3 + and CD25 +) was notably decreased within the therapy teams (Fig. 8b). These findings assist the beforehand described regulatory mechanism between Tregs and T cells. Molecular evaluation of macrophages displayed in Fig. 8c–e led us to anticipate better therapeutic results on T cells and Tregs in response to GENs therapy by IC injection. Nevertheless, the teams receiving GENs through IV and IC injections confirmed comparable abundances of T cells and Tregs. We speculated that, assessing the proliferation of T cells and Tregs would require, multiple week after the therapy to watch a discernible distinction in activation. The outcomes can also be attributed to the attenuation of exponential regulation of accumulation after therapy. Immune cells have been stimulated with appropriately concentrated GENs, and the immune cell evaluation outcomes have been per their maximal response to antigens. Earlier research have demonstrated that the expression of CD8 + and CD4 + in T cells just isn’t considerably altered by completely different administration routes when a excessive focus of vaccine is run [43, 44]. Subsequently, though completely different administration routes have been employed, GENs have been administered at a excessive focus to all tumor therapy teams, doubtless ensuing within the immune cells reaching a plateau by way of their ultimate expression. This speculation is supported by earlier studies [43, 45].
T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are induced by decreased cytokines within the tumor microenvironment (TME). a Evaluation of regulation of T cells. Fluorescently conjugated anti-CD8, CD4, and CD45 monoclonal antibodies have been used to research T cells. The abundance of CD8 of T cells, gated CD45, was elevated within the GENs therapy teams, whereas the abundance of CD4 was decreased in comparison with the PBS group. b Fluorescently conjugated anti-FoxP3, CD25, and CD45 monoclonal antibodies have been used to research Tregs. Tregs cell inhabitants was evaluated by FACS evaluation. The abundance of Tregs was decreased within the GENs therapy teams. c–e The ratio of the relative gene expressions of M1 and M2 (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001)
To evaluate the affect of GENs on TAMs and their cytokine launch, we carried out molecular evaluation utilizing M1 markers (together with CD86), M2 markers (together with CD206), and a pan macrophage marker (F4/80). M1-like macrophages are identified to advertise an antitumor response in TAMs by supporting a sort 1 T helper cell (Th1)-mediated anticancer response and facilitating the recruitment of cytotoxic T cells. Primarily based on the M1/M2 ratio, the therapy teams exhibited a normal enhance in M1-macrophages in contrast with the management teams, indicating an adjuvant antitumor impact on the glioma (Fig. 8c–e). The mRNA expression ranges of M2-macrophage markers, CD206 and IL10, have been considerably decreased within the therapy teams (Fig. 8e). M1 macrophages have been induced with RAW 264.7 cells by including 100 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide and 50 ng/mL interferon gamma (IFNγ). Subsequently these M1 macrophages have been handled with GENs in vitro. The outcomes confirmed a big enhance in CD86 expression, a marker of M1 macrophages, in any respect concentrations of GENs (Extra file 1: Fig. S9). General, within the GENs therapy teams, tumor suppression was noticed by the promotion of macrophage proliferation and modulation of the immune system, together with T cells and Tregs, that are concerned in angiogenesis regulation.
Gene silencing impact of ptc-miR396f on c-MYC
Earlier research reported [46, 47] the presence of bioactive compounds, together with nucleic acids, in greens, which have proven potential within the therapy. Consequently, PENs containing genes may function a therapeutic RNA supply brokers themselves, benefiting from their inherent abundance of genes and biocompatibility. Moreover, a number of particular genes together with siRNAs and miRNAs derived from crops or greens have been functionally validated and provide new prospects for nucleic acid-based therapeutics focusing on most cancers and irritation [46]. As well as, Teng et al. [47] reported that ginger-derived exosome-like nanoparticles which can be preferentially taken up by intestine biota, exerting regulatory actions on bacterial mRNA by their miRNAs. It’s confirmed that the miRNAs inside these nanoparticles can induce the manufacturing of IL-22, which is related to the advance of intestinal barrier operate. Nevertheless, it’s not clear whether or not the miRNAs in GENs play a task in suppressing tumor progress and inducing antitumor immunity in cells and the TMEs.
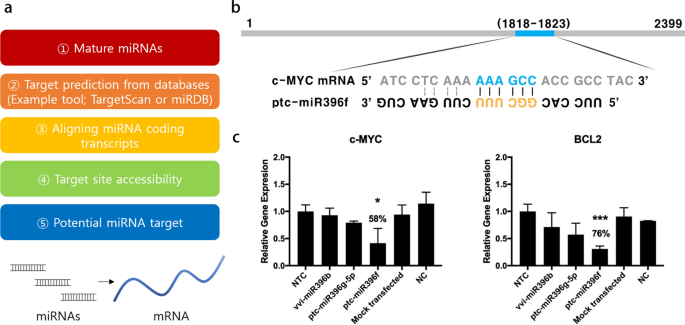
Hypothesizing that miRNA is likely to be a regulatory issue, we analyzed the miRNA profile of GENs. Subsequently, we utilized the miRNA databases (TargetScan and miRanda) to establish miRNAs in GENs and predicted their potential targets based mostly on sequence-based miRNA goal prediction (Fig. 9a). miRNA targets have been sorted by cumulative weighted context + + rating. Among the many miRNA targets, we chosen the goal gene and potential oncogene and additional examined the goal website accessibility of miRNAs within the coding transcripts [48, 49]. Then, a possible miRNA-target interplay was recognized. c-MYC is a predominant oncogene and the c-MYC signaling pathway is among the well-known pleiotropic gene-regulating sign pathways, together with BCL2 and TGF-β (Fig. 9b) [50, 51]. In C6 glioma cells, a parallel discount was noticed in gene expression ranges of c-MYC and BCL2 after transfection with the miRNAs named vvi-miR396b, ptc-miR396f, and ptc-miR396f, in comparison with non-targeting controls (Fig. 9c; Extra file 1: Tables S1–S5). The very best gene silencing impact was seen with ptc-miR396f in each goal genes, with 58% and 76% reductions in c-MYC and BCL2. As well as, to make the results of RNA sequencing information extra useful and clear, a pie chart of the miRNA abundance by miRNA household and the ten most plentiful miRNAs in GENs by the learn depend have been offered in Extra file 1: Fig. S10 and Fig. S11.
Prediction of miRNA targets and gene silencing impact of miRNAs mediated apoptosis of tumor cells by the regulation of apoptotic c-MYC signaling pathway. a miRNA targets have been predicted utilizing miRNA goal prediction software based mostly on sequence-based miRNA goal prediction. b The binding website of ptc-miR396f within the mRNA of c-MYC. c Relative gene expression ranges of c-MYC and BCL2 with miRNAs. There was a big gene silencing impact in comparison with mock-transfected and management teams, that are normalized to non-targeting management (NTC) (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001)
Provided that the lipid composition of GENs primarily consists of phospholipids (28.8% of PC), we anticipated that we may reveal the environment friendly supply of miRNAs utilizing the lipid element of GENs as a supply vector [47]. To look at whether or not the suppression of gene expression was induced as anticipated, the miRNAs have been delivered through GENs. We extracted lipids from GENs utilizing the Bligh and Dyer lipid extraction protocol and used the lipid content material of GENs as a transfection reagent at the side of the miRNAs (Extra file 1: Fig. S12a). The supply of ptc-miR396f through the extracted lipids exhibited the best gene silencing impact on each c-MYC and BCL2 (Extra file 1: Fig. S12b).
On this examine, we evaluated the anticancer exercise and the regulatory results of GENs on glioma. Numerous miRNAs concerned in various signaling pathways associated to apoptosis or cell proliferation have been examined. The findings of this examine confirmed that GENs are able to suppressing tumor progress by inducing apoptosis in tumors, regulating macrophages and TAMs, and exerting gene silencing results by exosomes. The outcomes spotlight the promising potential of GENs for the therapy of glioma.
Gene Ontology (GO) classification
A complete of seven,072,614 genes in GENs have been decided by GO enrichment evaluation. The outcomes indicated that these genes have been concerned in organic processes (BP), mobile parts (CC), and molecular features (MF) (Extra file 1: Fig. S14). Within the classes, essentially the most plentiful subcategories have been mobile element (5427 genes) and natural substance metabolic course of (5408 genes). The highest 5 most distinguished enrichment subcategories concerned within the BP class have been natural substance metabolic course of (5408 genes), major metabolic course of (5204 genes), mobile metabolic course of (5033 genes), DNA metabolic course of (1039 genes), and natural acid metabolic course of (803 genes).
Scatter plot of differential gene Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment
To additional perceive the mechanism of the differential expression of genes (DEGs) from the GENs described above, we carried out KEGG pathway enrichment testing. The diploma of KEGG enrichment was evaluated by the qvalue, the wealthy issue, and the variety of genes enriched within the pathway [52]. The enrichment represents the ratio of the proportion of DEGs concerned within the pathway to all genes. The upper wealthy issue is, the extra vital the enrichment degree of the DEGs within the pathway. The highest 20 pathways with essentially the most vital enrichment after screening are offered in Extra file 1: Fig. S15. These genes have been enriched within the porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, propanoate metabolism, ABC transporters, alanine, aspartate, glutamate metabolism, and pyrimidine metabolism pathways.