(Nanowerk Information) Two-dimensional (2D) transition steel dichalcogenides (TMDs), an rising class of supplies that can be utilized as semiconductors and insulators, have promising potential in varied purposes attributable to their distinctive properties. However the dependable manufacturing of those atomically skinny 2D supplies has been difficult. A analysis group led by a cloth scientist from Metropolis College of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed an environment friendly electrochemical exfoliation technique to attain high-yield manufacturing of TMD nanosheets. This new technique lays a brand new course for mass manufacturing of TMD nanosheets for large software in future. The analysis group was led by Dr Zeng Zhiyuan, Assistant Professor in CityU’s Division of Supplies Science and Engineering (MSE), in collaboration with scientists from the College of Montpellier and Ulsan Nationwide Institute of Science and Know-how (UNIST). Their findings have been printed within the educational journal Nature Protocols (“Excessive-yield manufacturing of mono- or few-layer transition steel dichalcogenide nanosheets by an electrochemical lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation technique”).
A easy technique that gives the next diploma of management
Beforehand, TMD nanosheets will be produced by a chemical technique referred to as lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation. Intercalation means the insertion of a molecule or ion into supplies which have layered buildings. If each layer is intercalated with lithium ions, then supplies with monolayers shall be produced after ultrasound sonication and exfoliation; if solely elements of the layers are intercalated with lithium ions, then the consequence shall be bi- or few-layer merchandise. Nevertheless, this conventional chemical technique must be carried out at a comparatively excessive temperature as much as 100 °C and for a very long time, some could take three days. Extra importantly, it’s troublesome to manage the quantity of lithium insertion.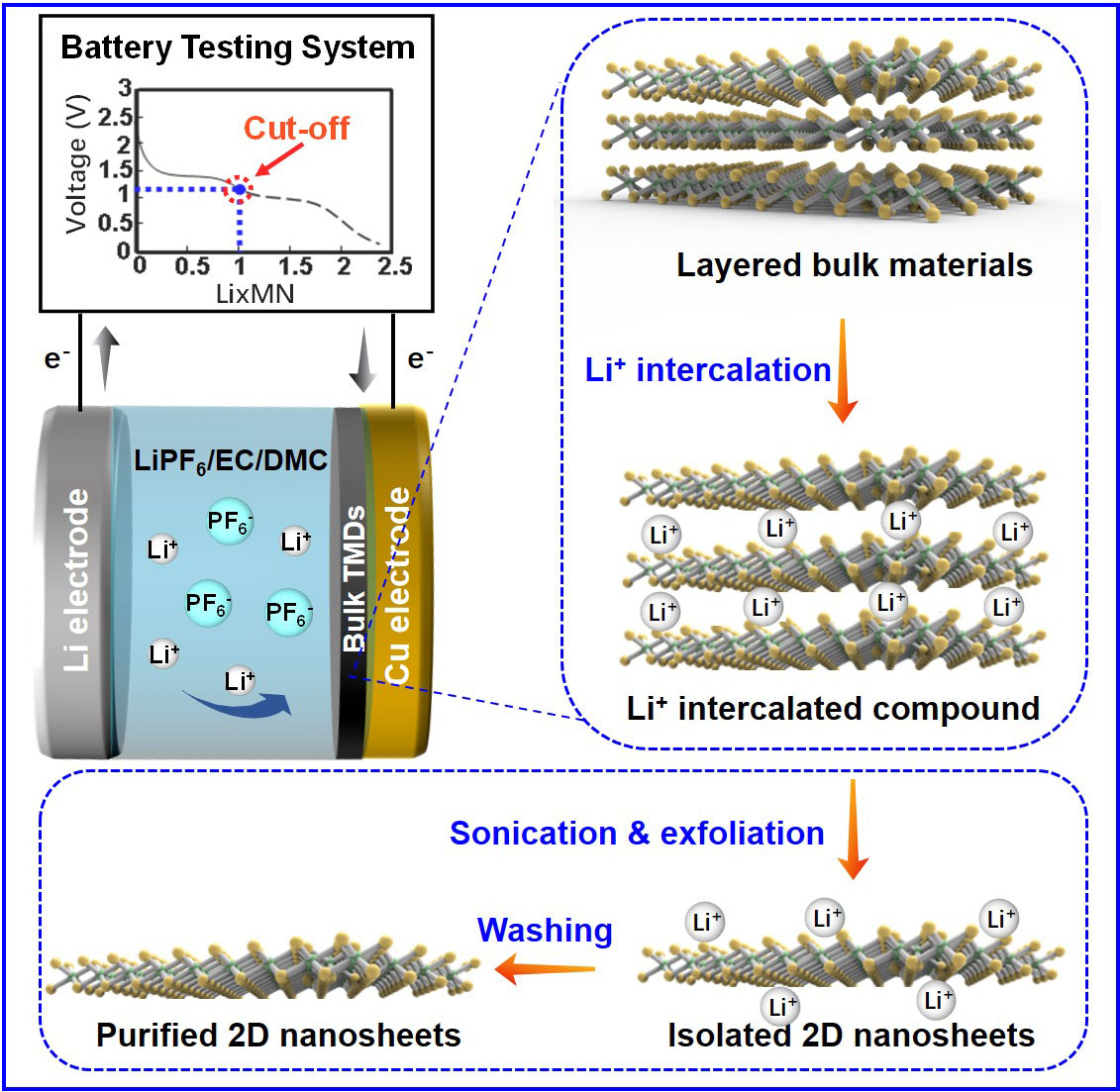 Schematic illustrations of the electrochemical lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation course of. (© Nature Protocols)
To beat the above challenges, Dr Zeng and his group adopted an electrochemical strategy to synthesise the mono- or few-layer inorganic nanosheets. “The tactic we developed is comparatively easy and simple, and it provides the next diploma of management beneath gentle circumstances. Utilizing our technique, high-yield preparation of monolayer TMD nanosheets will be simply performed at room temperature of about 25 °C inside 26 hours,” mentioned Dr Zeng.
Their electrochemical lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation technique includes three easy steps: electrochemical intercalation of lithium ion into layered bulk supplies, adopted by a light ultrasound sonication course of in deionised water or ethanol for five to 10 minutes, and lastly, exfoliate and centrifuged to get the purified 2D nanosheets.
Dr Zeng identified that utilizing their technique, the quantity of lithium intercalation will be managed successfully by tuning the cutoff voltage. “This superior characteristic could make the lithium intercalation course of cease at an applicable lithium quantity,” he added.
Schematic illustrations of the electrochemical lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation course of. (© Nature Protocols)
To beat the above challenges, Dr Zeng and his group adopted an electrochemical strategy to synthesise the mono- or few-layer inorganic nanosheets. “The tactic we developed is comparatively easy and simple, and it provides the next diploma of management beneath gentle circumstances. Utilizing our technique, high-yield preparation of monolayer TMD nanosheets will be simply performed at room temperature of about 25 °C inside 26 hours,” mentioned Dr Zeng.
Their electrochemical lithium ion intercalation-based exfoliation technique includes three easy steps: electrochemical intercalation of lithium ion into layered bulk supplies, adopted by a light ultrasound sonication course of in deionised water or ethanol for five to 10 minutes, and lastly, exfoliate and centrifuged to get the purified 2D nanosheets.
Dr Zeng identified that utilizing their technique, the quantity of lithium intercalation will be managed successfully by tuning the cutoff voltage. “This superior characteristic could make the lithium intercalation course of cease at an applicable lithium quantity,” he added.
Excessive-yield manufacturing of monolayer TMD nanosheets
Dr Zeng highlighted the 4 benefits of this electrochemical strategy. Firstly, a excessive yield of monolayer TMD is achieved. Taking MoS2 and TaS2, two sorts of TMDs they studied, as examples, among the many 2D nanosheets ready with this technique, over 90% of them (92% for MoS2 and 93% for TaS2) have been single layer, whereas the remainder of the 8% and seven% have been double layers, trilayers, and even multi-layers. Secondly, they might fabricate monolayer TMD nanosheets in a big lateral dimension. The lateral dimension of the MoS2 monolayer the group obtained by this preparation technique can attain 3 µm. Thirdly, their process is scalable. The group believes that additional scale-up of manufacturing of monolayer TMD nanosheets for business purposes will be realised by rising the majority TMD quantity from milligrams (mg) to grams (g), and even tons. And lastly, their TMD nanosheets are solution-processable and printable. They could possibly be broadly and evenly dispersed in aqueous answer with out including a surfactant, and could possibly be used as ink in printing know-how.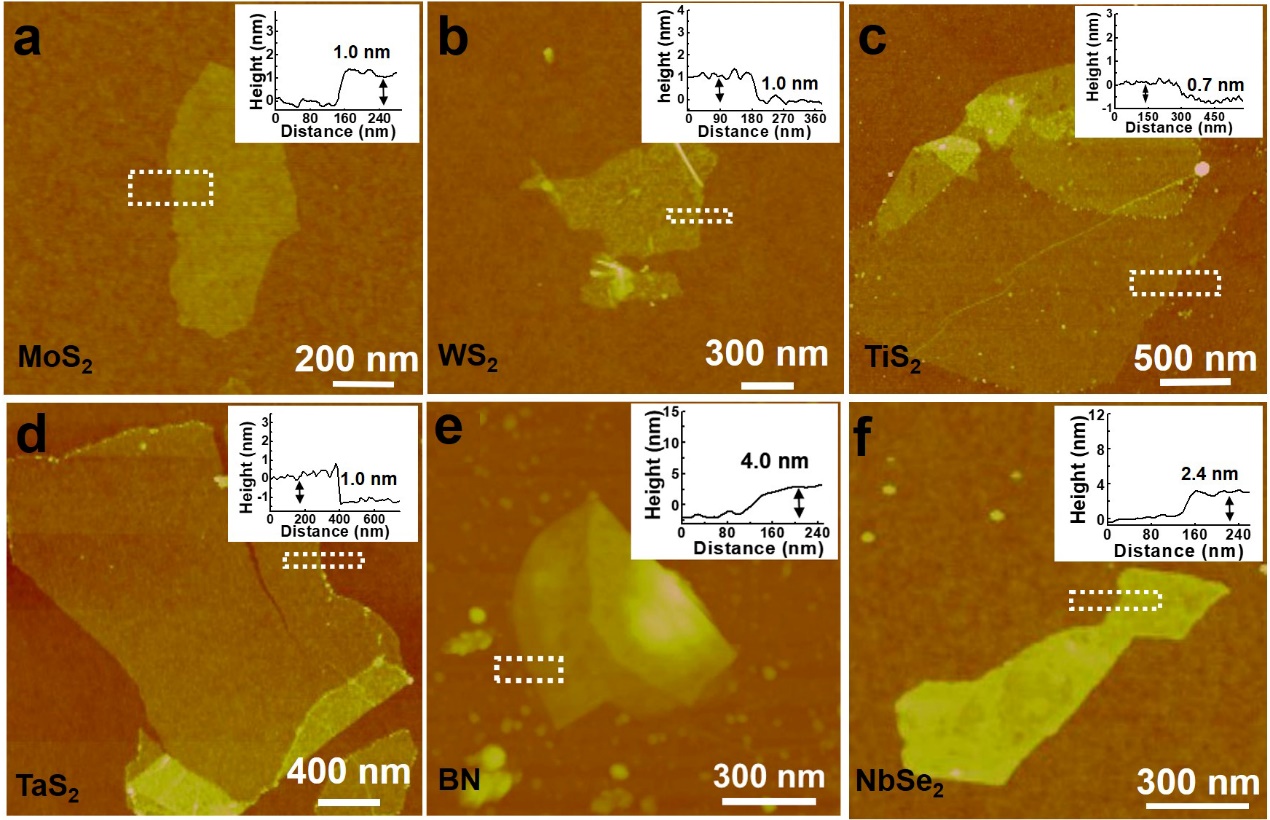 Pictures of the exfoliated nanosheets of a, MoS2. b, WS2. c, TiS2. d, TaS2. e, BN. f, NbSe2. Mono- and few-layer inorganic nanosheets have been efficiently produced by this technique. (© Nature Protocols)
Pictures of the exfoliated nanosheets of a, MoS2. b, WS2. c, TiS2. d, TaS2. e, BN. f, NbSe2. Mono- and few-layer inorganic nanosheets have been efficiently produced by this technique. (© Nature Protocols)