Northwestern College researchers have developed the primary selective remedy to forestall allergic reactions, which might vary in severity from itchy hives and watery eyes to hassle respiration and even loss of life.
To develop the brand new remedy, researchers adorned nanoparticles with antibodies able to shutting down particular immune cells (referred to as mast cells) liable for allergic responses. The nanoparticle additionally carries an allergen that corresponds to the affected person’s particular allergy. If an individual is allergic to peanuts, for instance, then the nanoparticle carries a peanut protein.
On this two-step strategy, the allergen engages the exact mast cells liable for the particular allergy, after which the antibodies shut down solely these cells. This extremely focused strategy allows the remedy to selectively forestall particular allergic reactions with out suppressing your complete immune system.
In a mouse research, the remedy demonstrated 100% success in stopping allergic responses with out inflicting noticeable unintended effects.
The analysis is revealed immediately (Jan. 16) within the journal Nature Nanotechnology. It marks the primary nanotherapy for inhibiting mast cells, thus stopping an allergic response to a particular allergen.
“At present, there are not any strategies out there to particularly goal mast cells,” mentioned Northwestern’s Evan A. Scott, who led the research. “All we have now are drugs like antihistamines to deal with signs, and people do not forestall allergic reactions. They counteract results of histamines after the mast cells have already got been activated.
“If we had a technique to inactivate the mast cells that reply to particular allergens, then we may cease harmful immune responses in extreme conditions like anaphylaxis in addition to much less critical responses like seasonal allergic reactions.”
“The largest unmet want is in anaphylaxis, which will be life-threatening,” mentioned Northwestern’s Dr. Bruce Bochner, an allergy skilled and research co-author. “Sure types of oral immunotherapy is likely to be useful in some circumstances, however we at the moment haven’t any FDA-approved remedy choices that persistently forestall such reactions aside from avoiding the offending meals or agent. In any other case, therapies like epinephrine are given to deal with extreme reactions—not forestall them.
“Would not or not it’s nice if there was a protected and efficient remedy for meals allergy that persistently made it attainable to reintroduce a meals into the eating regimen that you simply used to should strictly keep away from?”
Scott is the Kay Davis Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick Faculty of Engineering and a member of the Simpson Querrey Institute for BioNanotechnology and of the Worldwide Institute for Nanotechnology. Bochner is the Samuel M. Feinberg Emeritus Professor of Medication (allergy and immunology) at Northwestern College Feinberg Faculty of Medication.
The paper’s first writer is Fanfan Du, a postdoctoral fellow in Scott’s laboratory, who labored carefully with co-first authors Clayton Rische, a Ph.D. candidate co-mentored by each Bochner and Scott, and Yang Li, a Ph.D. candidate within the Scott lab.
Difficult goal
Positioned in practically all tissues all through the human physique, mast cells are finest identified for being primarily liable for allergic responses. However additionally they play a number of different necessary roles, together with regulation of blood move and preventing parasites. Subsequently, totally eliminating mast cells to forestall allergic reactions may very well be damaging to different helpful, wholesome responses.
“Though some medication are beneath growth, there are at the moment no FDA-approved medication that inhibit, or get rid of, mast cells,” Bochner mentioned. “This has been tough primarily as a result of medication that may have an effect on mast cell activation or survival additionally goal cells aside from mast cells, and thus are likely to have undesirable unintended effects as a consequence of influences on different cells.”
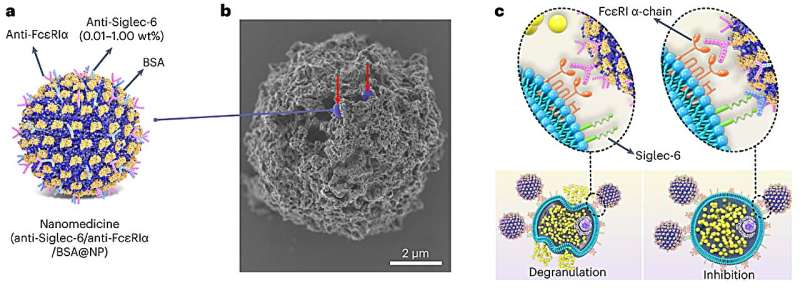
In earlier work, Bochner recognized Siglec-6, a novel inhibitory receptor that’s extremely and selectively discovered on mast cells. If researchers may goal that receptor with an antibody, then they might selectively inhibit mast cells to forestall allergy. However introducing this antibody by itself fell brief.
“It was tough to get a high-enough focus of the antibody to have an impact,” Scott mentioned. “We puzzled if we may improve this focus utilizing a nanoparticle. If we may pack a excessive density of antibodies onto a nanoparticle, then we may make it sensible to be used.”
Sticking antibodies onto a particle
To pack the antibodies onto a nanoparticle, Scott and his staff needed to overcome one other problem. For proteins (like antibodies) to stay to a nanoparticle, they sometimes should type a chemical bond that unfolds (or denatures) the protein, affecting its organic exercise. To bypass this problem, Scott turned to a nanoparticle beforehand developed in his laboratory.
Not like extra commonplace nanoparticles which have steady surfaces, Scott’s newly developed nanoparticle includes dynamic polymer chains, which might independently flip their orientation upon publicity to completely different solvents and proteins. When put into liquid options, the chains orient themselves to realize favorable electrostatic interactions with water molecules.
However when a protein touches the nanoparticle floor, the particular tiny polymer chains on the interface flip their orientations to stably maintain onto the protein with out covalently bonding to it. Scott’s staff additionally discovered that water-repelling pockets on protein surfaces have been key to the steady interplay.
When binding to surfaces, proteins sometimes denature, dropping their bioactivity. A singular facet of Scott’s nanoparticles is that they will stably bind enzymes and antibodies whereas sustaining their 3D construction and organic capabilities. This implies the anti-Siglec-6 antibodies maintained their sturdy affinity for the mast cell receptors—even when hooked up to the nanoparticle surfaces.
“It is a uniquely dynamic floor,” Scott mentioned. “As an alternative of an ordinary steady floor, it could actually change its floor chemistry. It is product of tiny polymer chains of compounds, which might flip their orientation to maximise favorable interactions with each water and proteins as obligatory.”
When Scott’s staff combined the nanoparticles with antibodies, near 100% of the antibodies efficiently hooked up to the nanoparticles with out dropping their capability to bind to their particular targets. This resulted in a nanoparticle-based remedy using surfaces with densely packed and extremely controllable quantities of a number of distinct antibodies to focus on mast cells.
Selective shut down
To ensure that somebody to develop into allergic, their mast cells seize and show antibodies, particularly immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, for that particular allergen. This allows the mast cells to acknowledge—and react to—the identical allergen upon re-exposure.
“When you’ve got a peanut allergy and have had a response to peanuts up to now, then your immune cells made IgE antibodies in opposition to peanut proteins, and the mast cells collected them,” Scott mentioned. “Now, they’re ready so that you can eat one other peanut. If you do, they will reply inside minutes, and if the response is powerful sufficient, it can lead to anaphylaxis.”
To selectively goal mast cells to answer a selected allergen, the researchers designed their remedy to have interaction solely mast cells carrying IgE antibodies for that allergen. The nanoparticle makes use of a protein allergen to have interaction with IgE antibodies on the mast cells after which makes use of an antibody to have interaction the Siglec-6 receptor to close down the mast cell’s capability to react. And since solely mast cells show Siglec-6 receptors, the nanoparticle can’t bind to different cell varieties—a technique that successfully limits unintended effects.
“You should use any allergen that you really want, and you’ll selectively shut down the response to that allergen,” Scott mentioned. “The allergen would usually activate the mast cell. However on the identical time the allergen binds, the antibody on the nanoparticle additionally engages the inhibitory Siglec-6 receptor. Given these two contradictory alerts, the mast cell decides that it should not activate and may depart that allergen alone. It selectively stops a response to a particular allergen. The fantastic thing about this strategy is that it doesn’t require killing or eliminating all of the mast cells. And, from a security standpoint, if the nanoparticle unintentionally attaches to the mistaken cell kind, that cell simply will not reply.”
Stopping anaphylaxis in mice
After demonstrating success in mobile cultures utilizing human tissue-derived mast cells, the researchers moved their remedy right into a humanized mouse mannequin. As a result of mast cells in mice don’t have the Siglec-6 receptor, Bochner’s staff developed a mouse mannequin with human mast cells of their tissues. The researchers uncovered the mice to an allergen and delivered the nanotherapy on the identical time.
No mice skilled anaphylactic shock and all survived.
“The only technique to monitor an allergic response is to trace adjustments in physique temperature,” Scott mentioned. “We noticed no adjustments in temperature. There was no response. Additionally, the mice remained wholesome and didn’t show any outward indicators of an allergic response.”
“Mouse mast cells don’t have Siglec-6 on their floor like in people, however we obtained as shut as we may for now to precise human research by testing these nanoparticles in particular mice that had human mast cells of their tissues,” Bochner mentioned. “We have been capable of present that these humanized mice have been protected against anaphylaxis.”
Subsequent, the researchers plan to discover their nanotherapy for treating different mast cell-related illnesses, together with mastocytosis, a uncommon type of mast cell most cancers. Additionally they are investigating approaches to loading medication contained in the nanoparticles to selectively kill mast cells in mastocytosis with out injuring different cell varieties.
Extra info:
Fanfan Du et al, Managed adsorption of a number of bioactive proteins allows focused mast cell nanotherapy, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-023-01584-z
Offered by
Northwestern College
Quotation:
Adorned nanoparticles forestall anaphylaxis with out inflicting unintended effects in mouse research (2024, January 16)
retrieved 16 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-nanoparticles-anaphylaxis-side-effects-mouse.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


