Terahertz (THz) radiation is electromagnetic radiation starting from frequencies of 0.1 THz to 10 THz, with wavelengths between 30μm and 3mm. Reliably detecting this radiation may have quite a few helpful functions in safety, product inspection, and high quality management.
As an illustration, THz detectors may permit legislation enforcement brokers to uncover potential weapons on people or in baggage extra reliably. It may be used to watch pure environments with out damaging them or to evaluate the standard of meals, cosmetics and different merchandise.
Latest research launched a number of units and options for detecting terahertz radiation. Whereas a number of of them achieved promising outcomes, their efficiency by way of sensitivity, pace, bandwidth and working temperature is commonly restricted.
Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT), College of Minnesota, and different institutes in the USA and South Korea lately developed a new digital camera that may reliably detect THz radiation at room temperature, whereas additionally characterizing its so-called polarization states. This digital camera, launched in a paper revealed in Nature Nanotechnology, relies on broadly accessible complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors (CMOS), enhanced utilizing quantum dots (i.e., nm-sized semiconductor particles with advantageous optoelectronic properties).
“Our earlier measurements of electroluminescence from quantum dots (QDs) confirmed that cost switch between them may be induced by a THz-frequency mild pulse,” Keith A. Nelson, Sang-Hyun Oh and Jiaojian (Tristan) Shi, three of the researchers who carried out the research, advised Phys.org through electronic mail. “The electrical area of the sunshine pulls an electron off one QD and transfers it to a neighboring QD. After the THz pulse is over (it is often only one cycle of the sector), the electron recombines with its dad or mum QD.”
Of their earlier work, Nelson and his colleagues discovered that an electron’s return to its unique internet hosting quantum dot is often accompanied by the emission of seen mild. Of their new research, they got down to create a tool that may leverage the method they noticed and the ensuing mild emission to detect THz pulses.
“Our goal was to develop a tool that makes use of this mechanism to detect THz pulses, by upconverting them to seen mild emission,” Nelson, Oh and Shi mentioned. “We additionally wished to understand different novel functionalities uniquely enabled by such a novel detection mechanism.”
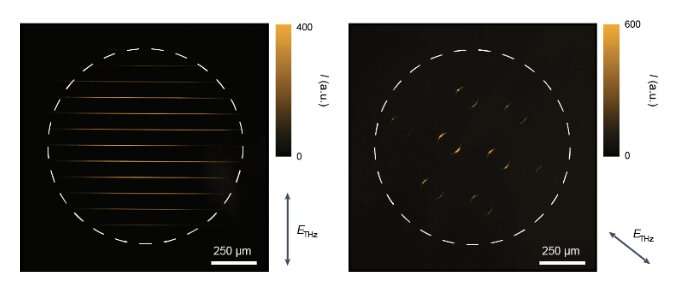
The CMOS-based THz digital camera created by the researcher was assembled in two separate phases. First, Nelson, Oh, Shi and their colleagues fabricated nanoscale area enhancement buildings (i.e., patterned conducting layers with sub-micron insulating gaps by which an incident THz area is strongly enhanced). These buildings had been created utilizing electron-beam lithography, a typical methodology to write down or draw patterns on substates. The second stage of the digital camera’s meeting entailed the synthesis of quantum dots and their deposition onto the sector enhancement buildings.
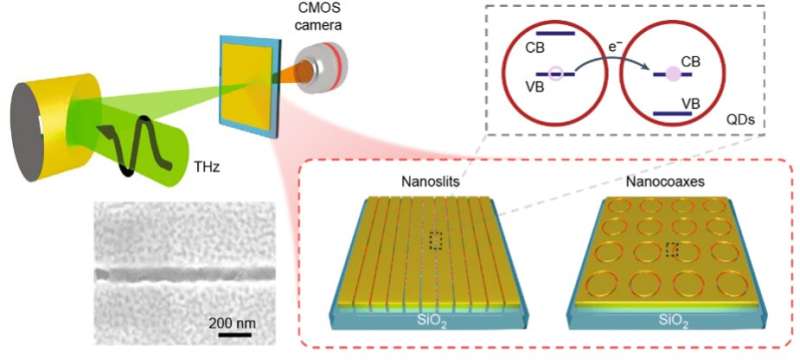
“The QDs that find yourself within the insulating gaps are subjected to the improved THz area. Their electroluminescence produces seen mild that’s detected with a standard CMOS ingredient,” Nelson, Oh and Shi defined. “Its precise fabrication is advanced, however it’s primarily based on two current applied sciences, and the processes may be separated into distinct elements. Thus, streamlined mass manufacturing ought to be doable and low-cost.”
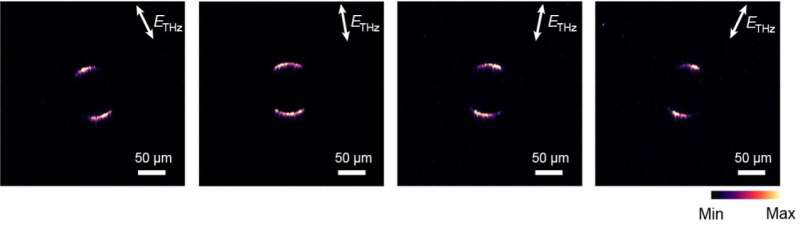
In preliminary evaluations, the THz-detecting digital camera created by this workforce of researchers achieved outstanding outcomes, detecting THz pulses with peak fields as little as 10 kVcm-1 at room temperature, with a quick response charge and excessive bandwidth. The machine can be inexpensive and may be scaled as much as wafer measurement for large-area imaging or different large-scale functions.
In distinction with different THz radiation detectors devised up to now, the digital camera created by Nelson, Oh and Shi can concurrently detect each the depth of THz mild and its polarization states. Sooner or later, it may thus open new thrilling prospects for the sensing and characterization of THz mild.
“We now plan to enhance the qTV efficiency even additional, as an example utilizing completely different QD or OLED (natural LED) supplies, cooled and amplified seen detectors, even narrower insulating gaps, and so on.,” the researchers added. “We carried out preliminary work on integrating qTV units with a DC electrical area, with an concept just like the avalanche detector improvement, which may improve the THz sensitivity and decrease the brink. We plan to discover this path additional to allow CW or quasi-CW THz sensing. The upconversion mechanism we uncovered is so handy that it may even allow the event of an ultrasmall THz spectrometer, combining diameter-varying coax arrays with QDs.”
Extra info:
Jiaojian Shi et al, A room-temperature polarization-sensitive CMOS terahertz digital camera primarily based on quantum-dot-enhanced terahertz-to-visible photon upconversion, Nature Nanotechnology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-022-01243-9
© 2022 Science X Community
Quotation:
A room-temperature terahertz digital camera primarily based on a CMOS and quantum dots (2022, December 8)
retrieved 8 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-room-temperature-terahertz-camera-based-cmos.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


