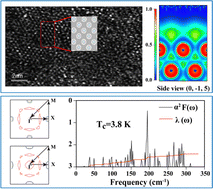
Because the discovery of graphene in an atomic skinny layer format, many investigations have been carried out to seek for two-dimensional (2D) layered supplies, during which 3d-transition metals provide a lot new physics and nice freedom of tunability. On this work, by means of electron-beam irradiation, we allow the manufacture of a brand new 2D Ti nanosheet from a suspension of Ti0.91O2 nanosheets. In state-of-the-art density useful idea (DFT), each empirical and linear response idea predicted that Hubbard Ueff values could be imposed, leading to unstable phonon dispersion curves. In the long run, the newly discovered Ti monolayer is confirmed to be a non-magnetic superconductor, with a medium stage of electron–phonon coupling. The newly established Ti layer is sort of strong beneath pressure, and the evolution of native Dirac factors in digital bands can also be analyzed when it comes to linearity and energetic shift close to the Fermi vitality. As recommended by the Fermi floor, this metallic monolayer experiences an digital topological transition beneath pressure. Our findings will encourage many extra explorations of pure d metal-based isotopic monolayers with numerous constructions and open a brand new playground for 2D superconductors and ultra-thin sensoring elements.