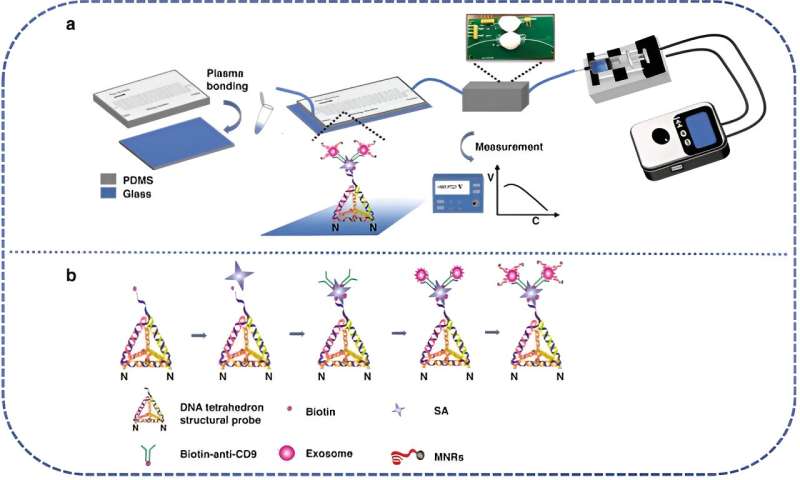
In a research printed on 7 November 2023 within the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Data Know-how, Chinese language Academy of Sciences, and Shanghai Tech College, have developed an revolutionary microfluidic magnetic detection system (μFMS) for analyzing tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs), potential biomarkers for most cancers analysis. This groundbreaking system may enormously improve the early detection and therapy of most cancers.
Within the methodology of the microfluidic magnetic detection system (μFMS), DNA tetrahedral-structured probes (TSPs) and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) modified with CD63 aptamers synergistically create magnetic nano-reporter probes (MNRs). These MNRs are adeptly built-in right into a microfluidic chip, which options serpentine microchannels and an induction coil-based magnetic detector, thereby enabling fast and extremely delicate detection of tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs).
The meticulous preparation course of concerned synthesizing particular DNA sequences to kind the TSPs and MNRs. The microfluidic chips, crafted from polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and aldehyde-modified glass slides, are designed to immobilize TSPs successfully. Extraction of TDEs from U251 cell strains was achieved by way of ultracentrifugation, adopted by detailed characterization utilizing transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic mild scattering (DLS).
Vital findings from this analysis embrace the μFMS’s exceptional detection capabilities, exhibiting a dynamic vary of 1.98 × 10³ to 1.98 × 10⁷ particles/mL and a detection restrict of 1.98 × 10³ particles/mL in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), successfully maintained even in simulated serum samples. The microfluidic chip‘s revolutionary serpentine design considerably enhances the effectivity of TDE seize, whereas the incorporation of DNA TSPs on the chip’s floor augments the specificity of TDE detection.
The μFMS represents a significant leap ahead in TDE evaluation. Its excessive sensitivity and specificity, coupled with its potential for simple integration into scientific settings, pave the best way for its use in early most cancers analysis and monitoring. The success of this technique in simulated scientific serum samples reinforces its potential in real-world functions. Future analysis and growth will concentrate on refining this expertise for widespread scientific use, probably remodeling most cancers diagnostics and therapeutics.
Extra info:
Qiuling Qian et al, Microfluidic magnetic detection system mixed with a DNA framework-mediated immune-sandwich assay for fast and delicate detection of tumor-derived exosomes, Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41378-023-00617-w
Supplied by
Chinese language Academy of Sciences
Quotation:
A microfluidic magnetic detection system for tumor-derived exosome evaluation (2023, December 19)
retrieved 23 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-microfluidic-magnetic-tumor-derived-exosome-analysis.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


