Join day by day information updates from CleanTechnica on e mail. Or observe us on Google Information!
NREL Hyperlinks Quickly Evolving Photovoltaic Module Applied sciences With Potential Reliability Impacts
Traditionally, photovoltaic (PV) modules have demonstrated excessive reliability, making them a reliable and rising a part of international decarbonization efforts. PV module know-how additionally has a historical past of iteration and evolution over time, with potential impacts for module reliability.
With this in thoughts, Nationwide Renewable Vitality Laboratory (NREL) researchers assist to establish potential future reliability impacts in a current assessment article revealed in IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, “Getting Forward of the Curve: Evaluation of New Photovoltaic Module Reliability Dangers Related With Projected Technological Modifications.” The article additionally suggests areas the place further analysis, requirements, and testing might enhance module reliability. The work was carried out as a part of the Sturdy Module Supplies (DuraMAT) Consortium.
“Anticipating and mitigating module reliability dangers is central to DuraMAT’s mission,” mentioned Teresa Barnes, one of many article’s authors and director of the DuraMAT Consortium. “On this article, we begin figuring out future reliability advantages and challenges from module supplies and designs that haven’t been deployed within the area lengthy sufficient for statistically legitimate failure evaluation.”
Multifaceted Sources Join PV Analysis to Market Issues
The article synthesizes details about crystalline silicon modules from PV market studies, interviews with PV researchers and different business stakeholders, and peer-reviewed literature to hyperlink tutorial issues with market issues and to higher seize quickly evolving data and views.
“We’re lucky at NREL to have colleagues with experience encompassing the complete spectrum of module applied sciences and reliability analysis, in addition to entry to further researchers and business viewpoints by DuraMAT,” defined writer Jarett Zuboy, market and coverage analyst for NREL. “Our discussions with many of those specialists helped form and validate our evaluation of know-how tendencies and reliability implications, along with revealed sources.”
Key PV Developments Fall Into 4 Classes: Module Structure, Interconnects, Bifacial Expertise, and Cell Expertise
The synthesis of sources enabled the researchers to establish 11 key know-how tendencies inside 4 classes—module structure, interconnects, bifacial know-how, and cell know-how. For every of the 11 tendencies (listed alongside the underside of the graphic beneath), the authors analyzed know-how drivers (akin to improved efficiency, value, or sustainability), deployment projections, reliability implications, choices for mitigating reliability dangers, and the necessity for extra analysis and testing. Additionally they explored reliability-related interactions amongst a number of tendencies.
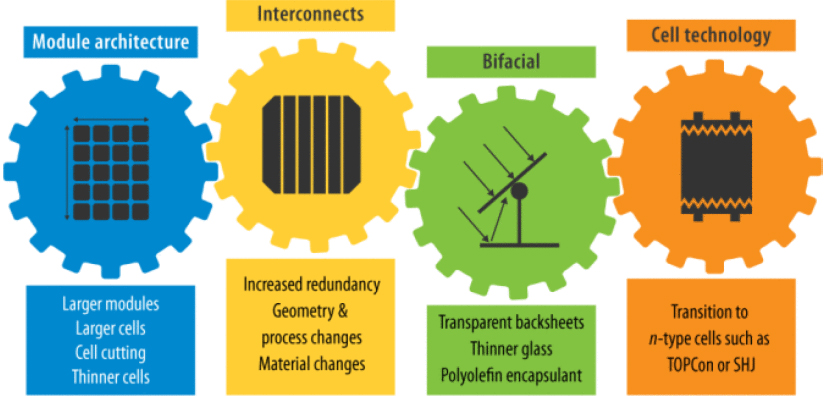
As one instance, the article particulars the continuing change from monofacial designs, which solely convert daylight on the entrance of the module, to bifacial designs, which enhance electrical energy era by changing gentle acquired in the back of the module as nicely. This pattern is driving the alternative of opaque polymers with glass on the again sides of modules. It is usually resulting in using thinner glass on each the back and front of modules, in addition to elevated use of polyolefin-based encapsulants.
This mix of tendencies creates reliability concerns which are completely different from these related to monofacial module designs.
“As a result of distinctive potential-induced degradation mechanisms can happen on the again aspect of bifacial cells and modules, there’s a must develop potential-induced degradation checks particular to this configuration,” mentioned writer Elizabeth Palmiotti, NREL supplies scientist. “Reliability analysis on using thinner glass—associated to each hail impacts and structural integrity—in addition to using combined and coextruded encapsulants and clear polymer backsheets would even be priceless.”
Cyclical Analysis Retains Tempo With Fast Concurrent Modifications
Particular person PV know-how modifications have a variety of potential results on module reliability, from lowering the chance of reliability issues, to having little or no influence, to growing the chance. Extra vital—and extra complicated—are the compounding results of creating a number of modifications without delay. Because of this, the article makes suggestions for addressing the complexity of quite a few, interrelated know-how tendencies, along with the precise suggestions for every know-how class.
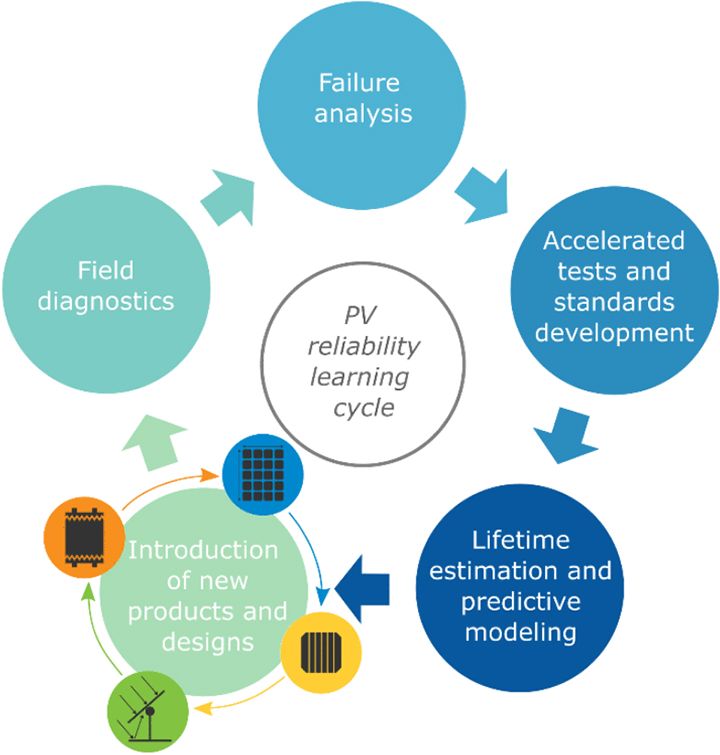
The researchers spotlight the function of the PV reliability studying cycle in holding module high quality in lockstep with technological change. The cycle begins with the introduction of recent merchandise and designs, and the remaining steps present a holistic reliability evaluation that features area diagnostics, failure evaluation, accelerated checks and requirements improvement, and lifelong estimation and predictive modeling. The cycle begins once more when earlier findings are integrated into module efficiency and reliability enhancements by new technological modifications.
Though the revealed article covers solely crystalline silicon modules, the workforce is growing a follow-on article that may embody thin-film applied sciences as nicely, whereas offering further particulars on key tendencies affecting crystalline silicon applied sciences.
“The training cycle—together with the event of predictive fashions—helps us transcend evaluation at any given cut-off date to establish and handle potential reliability issues rapidly, earlier than they’re noticed out there,” mentioned writer Martin Springer, supplies scientist at NREL. “That is what we imply by getting forward of the curve.”
Learn the complete article, “Getting Forward of the Curve: Evaluation of New Photovoltaic Module Reliability Dangers Related With Projected Technological Modifications,” from IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics. Contact report authors Jarett Zuboy and Teresa Barnes for extra data.
Courtesy of NREL. By Sara Fall and Jarett Zuboy
Have a tip for CleanTechnica? Wish to promote? Wish to recommend a visitor for our CleanTech Speak podcast? Contact us right here.
Newest CleanTechnica TV Video
CleanTechnica makes use of affiliate hyperlinks. See our coverage right here.



