Dec 02, 2023
(
Nanowerk Information) The universe is increasing. How briskly it does so is described by the so-called Hubble-Lemaitre fixed. However there’s a dispute about how huge this fixed really is: Totally different measurement strategies present contradictory values.
This so-called “Hubble pressure” poses a puzzle for cosmologists. Researchers from the Universities of Bonn and St. Andrews are actually proposing a brand new answer: Utilizing another concept of gravity, the discrepancy within the measured values will be simply defined – the Hubble pressure disappears.
The examine has now been printed within the
Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (
“Simultaneous answer to the Hubble pressure and noticed bulk circulate inside 250 h-1 Mpc”).
The enlargement of the universe causes the galaxies to maneuver away from one another. The pace at which they do that is proportional to the space between them. As an example, if galaxy A is twice as distant from Earth as galaxy B, its distance from us additionally grows twice as quick. The US astronomer Edwin Hubble was one of many first to acknowledge this connection.
So as to calculate how briskly two galaxies are transferring away from one another, it’s due to this fact essential to know the way far aside they’re. Nevertheless, this additionally requires a continuing by which this distance have to be multiplied. That is the so-called Hubble-Lemaitre fixed, a elementary parameter in cosmology.
Its worth will be decided, for instance, by wanting on the very distant areas of the universe. This provides a pace of virtually 244,000 kilometers per hour per megaparsec distance (one megaparsec is simply over three million gentle years).
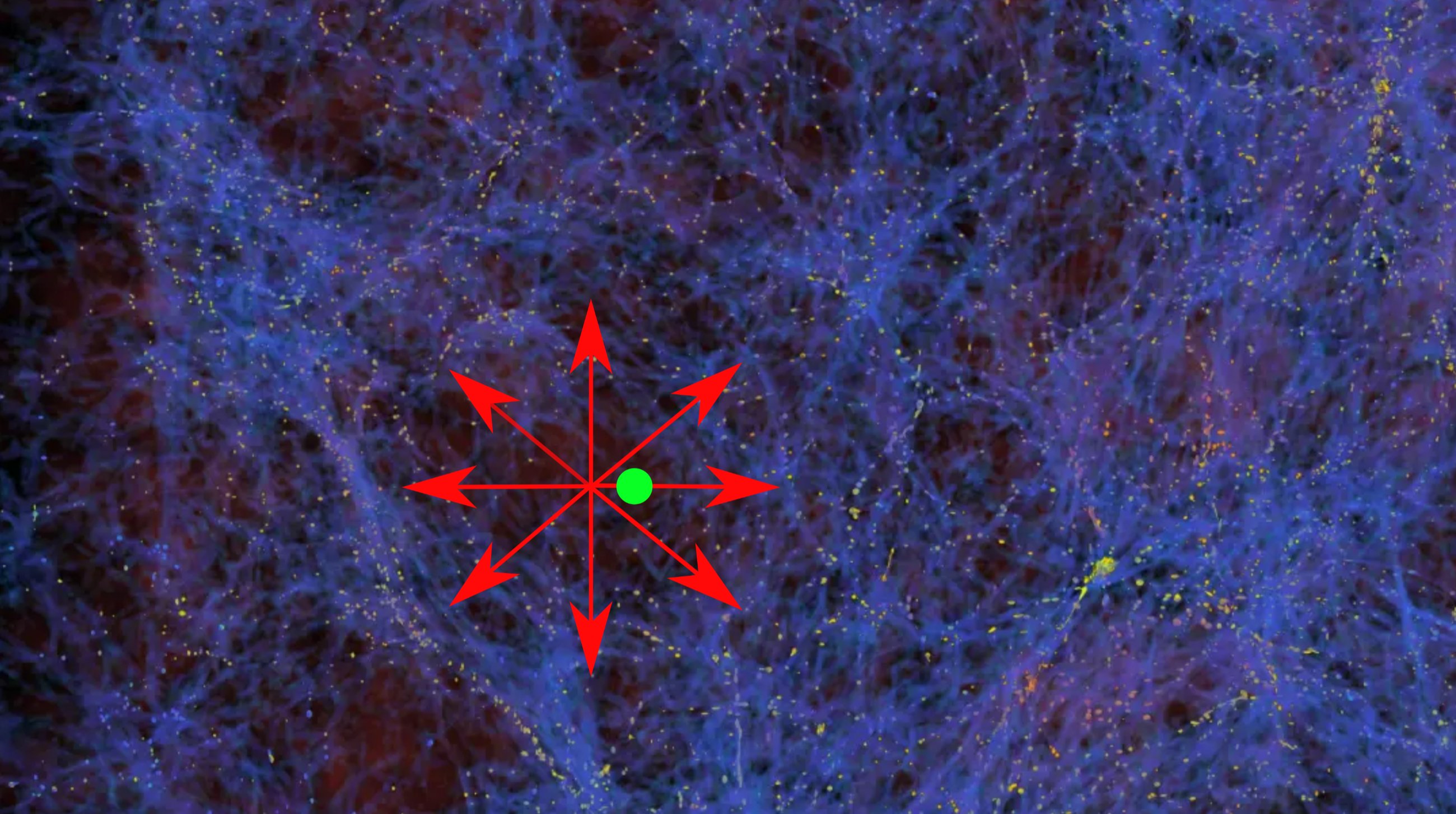
The picture reveals the distribution of matter in area (blue; the yellow dots symbolize particular person galaxies). The Milky Approach (inexperienced) lies in an space with little matter. The galaxies within the bubble transfer within the route of the upper matter densities (pink arrows). The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker contained in the bubble. (Picture: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)
244.000 kilometers per hour per megaparsec – or 264,000?
“However it’s also possible to take a look at celestial our bodies which can be a lot nearer to us – so-called class 1a supernovae, that are a sure kind of exploding star,” explains Prof. Dr. Pavel Kroupa from the Helmholtz Institute of Radiation and Nuclear Physics on the College of Bonn. It’s potential to find out the space of a 1a supernova to Earth very exactly. We additionally know that shining objects change colour once they transfer away from us – and the quicker they transfer, the stronger the change. That is much like an ambulance, whose siren sounds deeper because it strikes away from us.
If we now calculate the pace of the 1a supernovae from their colour shift and correlate this with their distance, we arrive at a distinct worth for the Hubble-Lemaitre fixed – specifically slightly below 264,000 kilometers per hour per megaparsec distance. “The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker in our neighborhood – that’s, as much as a distance of round three billion gentle years – than in its entirety,” says Kroupa. “And that shouldn’t actually be the case.”
Nevertheless, there has lately been an commentary that might clarify this.
Based on this, the Earth is situated in a area of area the place there may be comparatively little matter – corresponding to an air bubble in a cake. The density of matter is greater across the bubble. Gravitational forces emanate from this surrounding matter, which pull the galaxies within the bubble in direction of the sides of the cavity. “That’s why they’re transferring away from us quicker than would really be anticipated,” explains Dr. Indranil Banik from St. Andrews College. The deviations might due to this fact merely be defined by a neighborhood “under-density.”
Actually, one other analysis group lately measured the common pace of a lot of galaxies which can be 600 million gentle years away from us. “It was discovered that these galaxies are transferring away from us 4 occasions quicker than the usual mannequin of cosmology permits,” explains Sergij Mazurenko from Kroupa’s analysis group, who was concerned within the present examine.
Bubble within the dough of the universe
It’s because the usual mannequin doesn’t present for such under-densities or “bubbles” – they need to not really exist. As an alternative, matter must be evenly distributed in area. If this had been the case, nonetheless, it will be troublesome to clarify which forces propel the galaxies to their excessive pace.
“The usual mannequin relies on a concept of the character of gravity put ahead by Albert Einstein,” says Kroupa. “Nevertheless, the gravitational forces could behave in a different way than Einstein anticipated.” The working teams from the Universities of Bonn and St. Andrews have used a modified concept of gravity in a pc simulation. This “modified Newtonian dynamics” (abbreviation: MOND) was proposed 4 a long time in the past by the Israeli physicist Prof. Dr. Mordehai Milgrom. It’s nonetheless thought of an outsider concept right this moment. “In our calculations, nonetheless, MOND does precisely predict the existence of such bubbles,” says Kroupa.
If one had been to imagine that gravity really behaves in accordance with Milgrom’s assumptions, the Hubble pressure would disappear: There would really solely be one fixed for the enlargement of the universe, and the noticed deviations could be because of irregularities within the distribution of matter.
 The picture reveals the distribution of matter in area (blue; the yellow dots symbolize particular person galaxies). The Milky Approach (inexperienced) lies in an space with little matter. The galaxies within the bubble transfer within the route of the upper matter densities (pink arrows). The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker contained in the bubble. (Picture: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)
The picture reveals the distribution of matter in area (blue; the yellow dots symbolize particular person galaxies). The Milky Approach (inexperienced) lies in an space with little matter. The galaxies within the bubble transfer within the route of the upper matter densities (pink arrows). The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker contained in the bubble. (Picture: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)
 The picture reveals the distribution of matter in area (blue; the yellow dots symbolize particular person galaxies). The Milky Approach (inexperienced) lies in an space with little matter. The galaxies within the bubble transfer within the route of the upper matter densities (pink arrows). The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker contained in the bubble. (Picture: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)
The picture reveals the distribution of matter in area (blue; the yellow dots symbolize particular person galaxies). The Milky Approach (inexperienced) lies in an space with little matter. The galaxies within the bubble transfer within the route of the upper matter densities (pink arrows). The universe due to this fact seems to be increasing quicker contained in the bubble. (Picture: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)