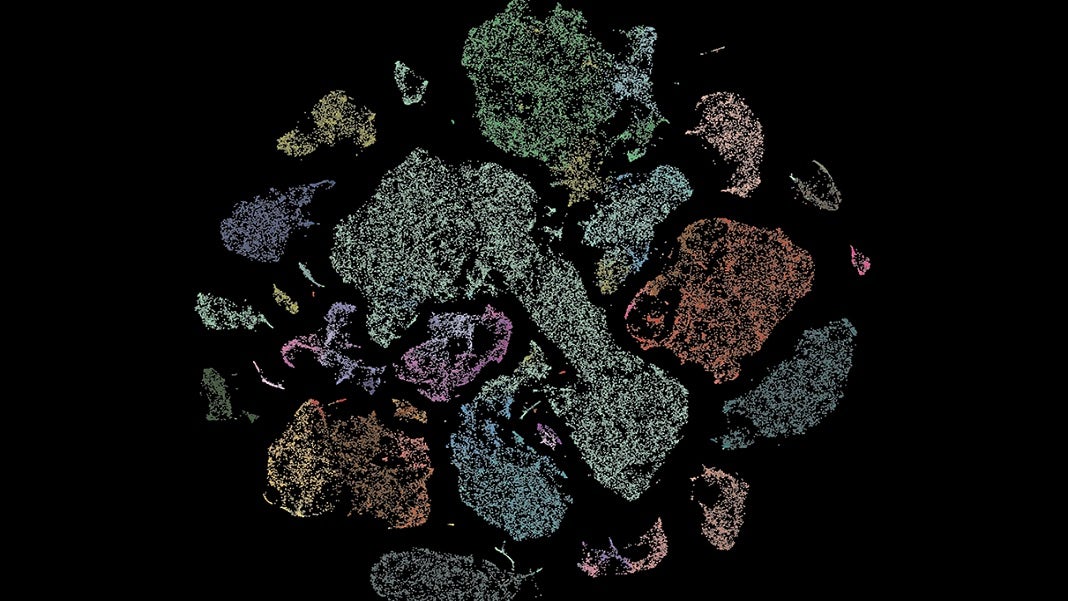
Regardless of a long time of analysis, the human mind stays largely a thriller to science. A brand new $500 million venture to create probably the most complete map of it ever may assist change that.
Our brains are among the many most advanced objects within the recognized universe. Deciphering how they work may convey super advantages, from discovering methods to deal with mind ailments and neurological problems to inspiring new types of machine intelligence.
However a crucial place to begin is developing with a elements checklist. Whereas everybody is aware of that brains are primarily made up of neurons, there are a blinding array of various kinds of these cells. That’s to not point out the assorted sorts of glial cells that make up the connective tissue of the mind and play a vital supporting position.
That’s why the Nationwide Institutes of Well being’s BRAIN Initiative has simply introduced $500 million in funding over 5 years for an effort to characterize and map neuronal and different forms of cells throughout the complete human mind. The venture shall be spearheaded by the Allen Institute in Seattle, however involves collaborations throughout 17 different establishments within the US, Europe, and Japan.
“These awards will allow researchers to discover the multifaceted traits of the greater than 200 billion neurons and non-neuronal cells within the human mind at unprecedented element and scale,” John Ngai, director of the NIH BRAIN Initiative, stated in a press release.
The BRAIN initiative was launched in 2014 by former president Barack Obama to revolutionize our understanding of the human mind. The brand new venture builds on a earlier effort to determine and map greater than 100 cell varieties throughout the motor cortex of a mouse, and can borrow lots of the instruments and strategies developed for that effort.
These embrace approaches like single-cell transcriptomics, which make it potential to measure the gene expression of particular person cells, and spatial transcriptomics, which make it potential to map gene expression over giant sections of tissue and localize gene exercise to particular areas.
A bunch from the Salk Institute in San Diego may also focus particularly on how the mind adjustments as we grow old by measuring adjustments in gene expression over time—generally known as epigenetic adjustments—in mind samples from individuals of various ages.
It is going to be an formidable job, although. The human mind is 1,000 occasions bigger than a mouse mind and way more advanced, so scaling these strategies up gained’t be a easy process. In the event that they succeed, the ensuing cell atlas will turn into a robust and freely-accessible useful resource for neuroscientists all around the world.
“I actually do view this as just like the Human Genome Challenge. We have now the flexibility now to outline cells like we had been in a position to outline genes,” Ed Lein, who’s main the Allen Institute’s contribution, informed STAT. “That is the inspiration to begin to perceive plenty of different features of biology and illness.”
These tasks are a part of a brand new spherical of funding dubbed BRAIN 2.0 that was launched at first of this yr. Alongside the scaling up of efforts to map out completely different sorts of mind cells, $36 million will go in the direction of an initiative referred to as the Armamentarium for Precision Mind Cell Entry, which can use information on mind cell varieties to develop new instruments designed to focus on them for examine and doubtlessly therapy.
And there’s extra funding to come back. Early subsequent yr, the NIH will dole out one other $30 million to tasks looking for to take the subsequent step in mapping out the mind, shifting on from the elements checklist to figuring out the wiring diagrams that govern how completely different cells and areas are linked.
With the venture anticipated to generate petabytes of knowledge, it’s more likely to be years earlier than scientists are in a position to make full use of this new useful resource. But it surely may show to be a crucial piece of the puzzle as we try to unravel the mysteries of the human mind.
Picture Credit score: Allen Institute