Inexperienced synthesis of CuO-Zs-NPs
For the CuO-Zs-NPs to be fashioned, an answer of 90 mL copper sulfate was combined with 10 mL of Zizyphus spina leaf extract at a ratio of 9:1 (v/v) and stirred constantly for 60 min at 80 °C. The colour of the answer modified from blue to darkish inexperienced in the course of the response, indicating the formation of CuONPs. This was confirmed utilizing UV‒vis spectroscopy, which confirmed the digital spectrum brought on by the floor plasmon resonance (SPR) impact [2, 5, 12, 28]. Earlier research have additionally reported the useful function of tannins, saponins, phenols, and alkaloids current in Zizyphus spina aqueous extract which was used as capping and stabilizing brokers for inexperienced synthesis of CuO-Zs-NPs and their doable involvement in decreasing Cu + to Cu0 [1, 45, 68, 93]. The mechanism for the synthesis is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Characterization of the biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles(CuO-Zs-NPs)
UV Absorption of CuO-NPs
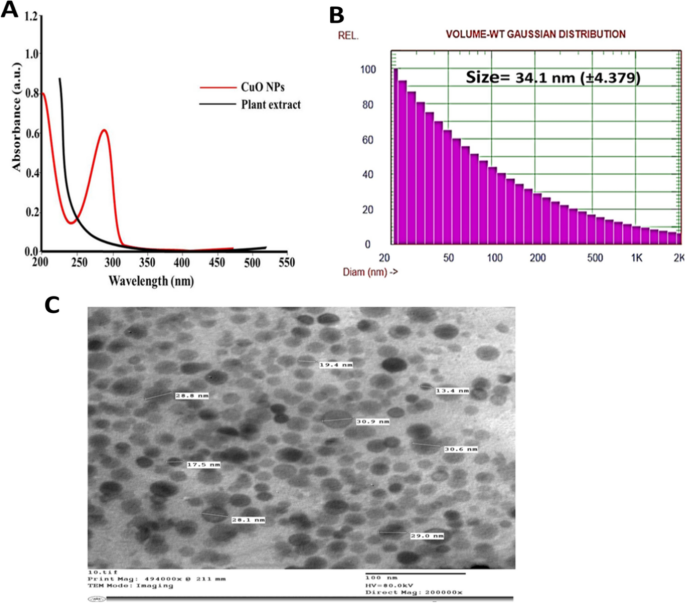
By analyzing the UV‒seen spectrum, a sturdy absorption peak positioned at roughly 290 nm was noticed, which represents the profitable synthesis of CuO nanoparticles (NPs) (Fig. 2A). The height place and width are associated to the typical measurement and measurement distribution of the nanoparticles, respectively. This peak is attributed to the inter-band transition of core electrons in copper and the band hole distinction related to quantum measurement results, which is in step with the formation of varied CuO NPs [27]. Moreover, the absorption peak of excited CuO NPs that was seen at 290 nm at a temperature of 23 °C, signifies a mono-dispersed measurement distribution within the combination [69]. These outcomes are suitable with these reported by Jing et al.(2019),which show the formation of steady CuO NPs [62].
Morphology and measurement distribution of CuO-NPs
The morphology and measurement distribution of CuO-Zs-NPs nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized through a biosynthetic pathway had been examined utilizing Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), a vital characterization approach for acquiring quantitative measures of particle measurement, measurement distribution, form, and lattice fringes. The TEM picture confirmed the looks of spherical-shaped CuO-Zs-NPs with a particle measurement vary of 13.4 − 30.9 nm (Fig. 2C). The dimensions distribution measurements by dynamic gentle scattering had been discovered to agree with the TEM evaluation, yielding a particle measurement of imply at 34.1 ± 4.379 nm (Fig. 2B). Nonetheless, slight variations within the two measurements will be attributable to lots of variables. Dynamic gentle scattering (distribution evaluation) investigates the hydrodynamic particle diameter in resolution, which is predicated on the Brownian movement of particles in a solvent. Moreover, temperature, viscosity, and particle translational diffusion coefficient all affect the hydrodynamic diameter within the solvent. The hydrodynamic diameter additionally takes account of the entire molecular sizes and hydration layers of water molecules.
FT-IR evaluation
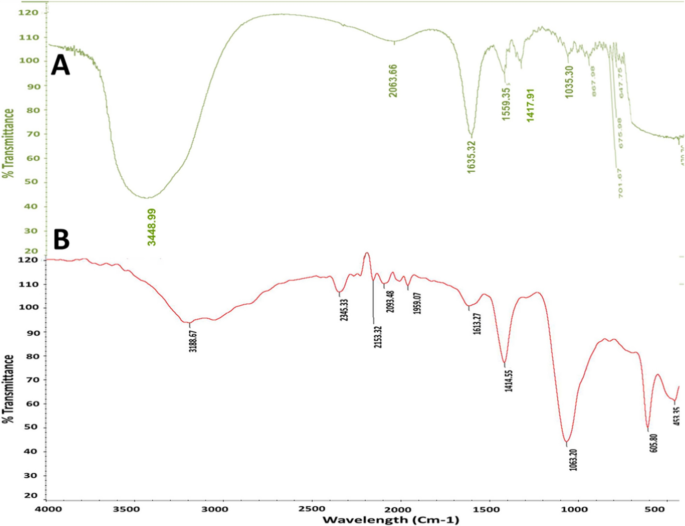
To additional look at the phytochemicals of Zizyphus spina leaf extract and their potential chemical useful teams accountable for the discount and stabilizing of the CuO-Zs-NPs, FT-IR evaluation was additionally carried out on the produced CuO NPs to find out their chemical construction. As depicted in Fig. 3, the FT-IR spectrum reveals absorption bands of Zizyphus spina leaf extract centered at 3448.99, 2063.66, 1635.32, 1559.35, 1417.91, 1035.30, 867.98, 701.67, 676.9, 647.76 and 470.7 cm−1(Fig. 3A). The broad absorption band at 3448.99 cm−1 could also be attributed to the stretching vibrations of (–OH), whereas the height at 2063.66 attributed to alene (C = C), and 1635.32 cm−1 could also be attributed to the amine orenone group. Whereas The height at 1559.35 is as a result of C = C stretching of the fragrant ring, in tertiary amides, flavonoids, terpenoids, tannins, and saponins. As well as, the height at 1417 cm−1 may very well be attributable to C-N stretching in imines or oximes, or C-N stretching in aliphatic amines and 1035.30 are related to C-O stretching in alcohols, phenols, ethers or esters even be attributable to C-N stretching in fragrant amines.
In Fig. 3B, the FT-IR absorption bands of CuO-Zs-NPs had been centered at 3188.67, 2345.33, 2153, 2093, 1959, 1613, 1414,1063, 605, and 453 cm−1(Fig. 3B). The broad absorption band at 3188.67 cm−1could also be attributed to the stretching vibrations of (–OH), whereas the height at 2345.33 attributed to Carbon dioxide (O = C = O), and 2153cm−1 could also be attributed to the presence of Si-based compounds. The height at 1613 is because of N–H bending in main amides, reminiscent of amino acids, and the C = C stretching in tertiary amides— flavonoids, terpenoids, tannins, and saponins. As well as, the height at 1414 cm−1 may very well be attributable to C = N stretching in imines or oximes, or C-N stretching in aliphatic amines, and 1063 may very well be related to C-O stretching in alcohols, phenols, ethers or esters even be attributable to C-N stretching in fragrant amines. Whereas the height at 605 and 453 point out the formation of O bonds, these knowledge had been attributed to [37].
Molecular identification of Fusarium solani
Molecular identification of the causal agent of tomato root rot illness was carried out utilizing the inner transcribed spacer (ITS) area of ribosomal DNA. The ITS sequence of the remoted fungal pressure confirmed 100% similarity with F. solani isolate sequence with the accession quantity (MW216959.1) out there on the GenBank database. The recognized ITS area of F. solani isolate was then assigned within the GenBank database with the accession quantity (OP824846).
In vitro antifungal exercise impact of CuO-Zs-NPs
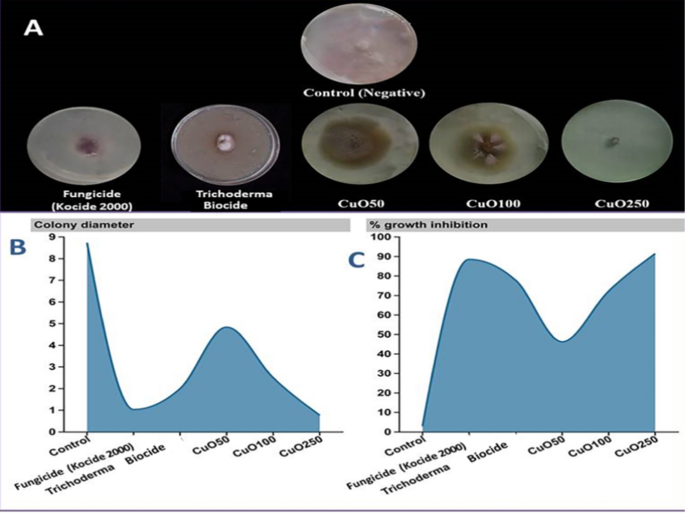
CuO-Zs-NPs anti-fungal exercise was examined at varied concentrations (50, 100, and 250 μg/mL), which are referred to within the manuscript as (CuO50, CuO100, and CuO250) respectively, as compared with their bulk precursor of copper “Kocide 2000” because the chemical fungicide and TricodermaBiocide by way of mycelial development inhibition in opposition to remoted F. solani in vitro. The antifungal exercise of CuO-Zs-NPs elevated with rising focus (Fig. 4). Particularly, the best ranges of development inhibition had been achieved at a focus of 250 mg/l for CuO-Zs-NPs. With a vital worth of 91.17 ± 1.28, in comparison with Kocide 2000 as a chemical fungicide and the Trichoderma Biocide (Trichoderma viride 1.5% WP) confirmed values 88.20 ± 3.57 and 77.09 ± 5.88% after ten days of incubation (Desk 1; Fig. 4). Curiously, statistical evaluation indicated that when analyzing the antifungal impact of the three examined CuO-Zs-NPs concentrations, the NPs focus is a major issue. Moreover, that is in settlement with a number of research displaying that CuO-NPs show a number of inhibitory modes of motion in opposition to microbial pathogens [31]. Moreover, Lopez-Lima et al. [53] examined Cu-NPs at totally different doses for in-vitro antifungal exercise in opposition to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici (FOL). As well as, 0.5 mg/mL CuO-NPs inhibited mycelial FOL development to 67.3%, in comparison with 15.6% for a business fungicide primarily based on copper hydroxide, making them useful in opposition to varied microbial pathogens that assault crops. Moreover, this might significantly assist decrease the chance of publicity to harmful chemical fungicides, Moreover, this might considerably contribute to decreasing the hazardous results of poisonous chemical fungicides, particularly on edible crops and contemporary greens reminiscent of tomatoes [17, 41]. Taken collectively, our findings assist that CuO-Zs-NPs are thought-about a promising alternative for conventional fungicides in crop safety.
Antifungal exercise of CuO-Zs-NPs at totally different concentrations in addition to a business fungicide (Kocide 2000) and Trichoderma biocide in opposition to Fusarium solani on PDA medium A: Inhibitory exercise of CuO-Zs-NPs in opposition to F. solani mycelial development on PDA medium in contrast with Trichoderma biocide and the chemical fungicide, B: On colony diameter (cm) C: On share of development Inhibition (%)
Phytotoxicity take a look at
Influence of CuO-Zs-NPs on the germination of tomato seeds
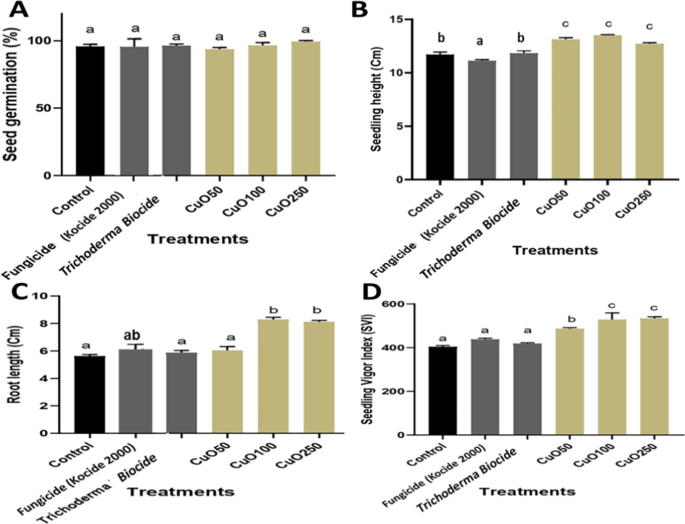
The results of various concentrations of CuO-Zs-NPs and its bulk counterpart (fungicide) in in contrast with Trichoderma biocide on seed germination and seedling size of tomato seeds had been evaluated in vitro. The chances of germination and germination index of tomato seeds handled with 50, 100, and 250 µg/ml CuO-Zs NPs in comparison with untreated management seeds are proven in Fig. 5.
The info offered in Fig. 5 signifies that every one CuO-Zs-NPs therapies significantly had an inductive impression on seed germination starting from 97.02 ± 1.53–98.67 ± 1.53 in in comparison with untreated management seeds giving values ” 97.07 ± 1.54. Though therapies with the chemical fungicide and Trichoderma Biocide gave larger inductive values (98.33 ± 0.00, 98.0 ± 1.15) respectively for tomato seed germination, CuO-Zs-NPs at 250 mg/l confirmed the best inductive impression on seed germination in comparison with different therapies The outcomes additionally indicated that the addition of CuO-Zs-NPs significantly at 100 and 250 μg/mL didn’t negatively have an effect on the variety of germinated seeds in comparison with their bulk counterparts. Though remedy with Trichoderma Biocide confirmed a greater impact on seed germination than remedy with CuO-Zs-NPs at 50 μg/ml.
Impact of CuO-Zs-NPs therapies on seed germination and development vigor
On the 3–5 leaf stage, the impact of CuO-Zs- NPs at concentrations (50, 100, and 250) mg/l on the proportion of tomato seed germination in soil medium was additionally evaluated and in contrast individually with the remedy of their counterpart (business chemical fungicide Kocide 2000) and Trichoderma Biocide (Fig. 5A). The outcomes indicated that every one therapies had no vital stimulating impact on seed germination in comparison with the untreated management. Alternatively, the outcomes additionally point out that the addition of CuO-Zs-NPs significantly at 100 and 50 μg/mL didn’t negatively have an effect on the variety of germinated seeds in comparison with their bulk counterparts. Equally, the distinctive inductive impact of CuO-Zs-NPs significantly at 100 mg/l was additionally seen in different tomato development parameters reminiscent of seedling peak, tomato root development, and the vigor index (Figs. 5(B-D), and 6). A big, dose-dependent impression on seedling peak, root size, and Seedling vigor index was noticed in all therapies with CuO-Zs-NPs in comparison with remedy with both Trichoderma biocide or the kocide fungicide (Fig. 5B–D). Extra curiously therapies with CuO-Zs-NPs confirmed a extra inductive impact on root size and seedling development, in distinction to their bulk counterpart which confirmed a noticeable detrimental impact (Fig. 5). These knowledge had been confirmed by Pradhan et al. [66] examined Cu NPs on mung beans, and located that Cu-NPs stimulated plant development higher than copper sulfate. In distinction, Bakshi and Kumar [8] evaluated the impact of Cu-NPs on oregano, and reported that the damaging or constructive results of nanoparticles rely on the plant kind, nanoparticle focus, and Cu oxidation state (Fig. 6).
Effectiveness of CuO-Zs-NPs in opposition to Fusarium root rot illness infecting tomato crops
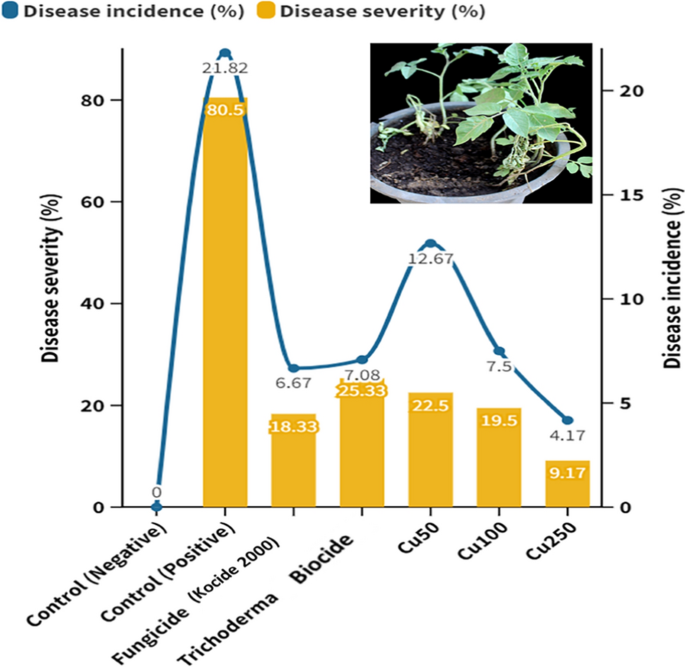
The antifungal exercise of CuO-Zs-NPs at three totally different concentrations (Cu50, Cu 100, Cu250) was additional investigated in vivo experiment performed to find out the efficacy of the remedy in controlling Fusarium root rot that impacts tomato crops (Fig. 7). Illness severity was recorded for 90 days publish inoculation (dpi) in all handled tomato crops. As a comparability, the experiment included crops handled with Kocide 2000 copper fungicide and Trichoderma biocide as chemical and biocide business controls respectively.
As early as 15 days post-inoculation, illness indicators in mock-treated tomato crops had been evident and the crops had been visibly weakened; in distinction, illness signs in tomato-treated crops had been minimal and vastly delayed. Management therapies of tomato crops both with an equal chemical fungicide, Kocide 2000, or Trichoderma Biocide additionally delayed and lowered illness signs, however to a lesser extent than CuO-Zs-NPs. A big discount in Fusarium root rot illness was seen for all concentrations of CuO-Zs-NPs in comparison with the management handled with the pathogen solely (contaminated management) (80.5%). No substantial distinction was noticed within the illness severity share in crops uncovered to 50 or 100 mg/l CuO-Zs-NPs. Though therapies with both the chemical fungicide (Kocide fungicide) confirmed higher illness discount and illness incidence with values of 18.33% and 6.67% respectively, than CuO-Zs-NPs at a focus of 50 mg/l, nonetheless, CuO-Zs-NPs at a dose of 250 mg/l achieved the best illness discount (9.17 ± 2.89%) and lowest illness incidence (4.17 ± 3.80%).
Progress and Physiological parameters
Impact on plant peak, weight, and chlorophyll content material
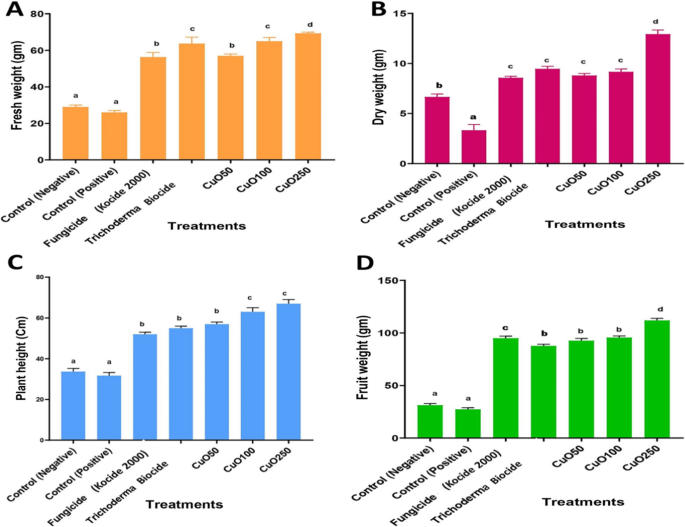
Three months after seeding, the results of CuO-Zs-NPs on tomato seedlings had been examined for plant lengths, contemporary and dry weights, and weight of the ensuing fruit (Fig. 8). The outcomes indicated that every one CuO-Zs-NPs had a selling impact on the plant peak and tomato (contemporary, dry, fruit) weight. On this regard, CuO-Zs-NPs at (50, 100, and 250) mg/l focus confirmed an inductive impact on tomato plant peak with values 57.67 ± 12.5, 62.33 ± 7.37, and 65.33 ± 12.32 respectively, in comparison with 54.67 ± 3.05, 55.67 ± 3.51, and 37 ± 2.65 for remedy with Kocide 2000 fungicide, Trichoderma biocide, and the damaging management respectively (Fig. 9). Equally, the distinctive inductive impact of CuO-Zs-NPs, significantly at 250 mg/l, was additionally seen in knowledge reported for tomato contemporary weight, dry weight, and fruit weight. Total, our knowledge point out the effectiveness of Cu-Zs-NPs in decreasing the illness severity and rising all development parameters and manufacturing, which was confirmed by Hernández-Hernández et al. [34]. As well as, the rise in dry weight could also be a results of the NPs boosting the exercise of photosystems I, II (PSI and PSII), together with the redox state of plastoquinone within the electron transport chain [79].
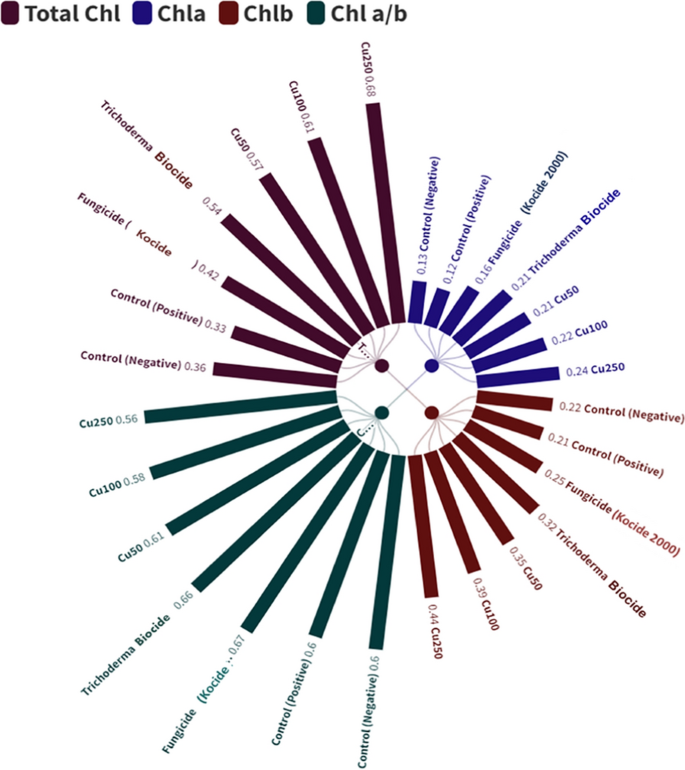
To analyze the impact of various concentrations of CuO-Zs-NPs on chlorophyll focus and composition in tomato plant leaves. The entire chlorophyll focus within the management of tomato plant leaves was 0.36 ± 0.014 mg /g contemporary weight, whereas, in CuO-Zs-NPs (250.100 and 50, respectively), it was 0.68, 0.61, and 0.57. Nonetheless, the composition of chl was considerably totally different, as evidenced by a lower within the chl a/b ratio in CuO-Zs-NPs 250 (0.56), this ratio was elevated when reducing the focus of CuO-Zs-NPs remedy in comparison with the damaging management (0.60) (Fig. 10). Whereas the chl a/b ratio elevated in each the biotreatment and the Cu fungicide remedy to 0.66 and 0.67, respectively, and each the management and CuO-Zs-NPs 50 had comparable cha/chb values.
The improved photosystem exercise noticed in crops uncovered to nanoparticles (NPs) could also be attributed to the up-regulation of genes associated to photosynthesis, reminiscent of psaA (photosystem, I P700chlorophyll an apoprotein A1), pet A (photosynthetic electron switch A), HSP90.1 (warmth chock protein1), and psbA (photosystem, II response middle protein A) [84]. Moreover, NPs might kind complexes with light-harvesting complicated (LHC) proteins within the antennae of photosystems, thereby bettering gentle absorption [85]. Moreover, NPs can enhance CO2 assimilation by enhancing the exercise of beta-carbonic anhydrase (BCA) and Rubisco enzymes in light-independent reactions [42, 43]. The promotion of photosynthetic exercise by NPs can also be accountable for the elevated contemporary and dry biomass of tomato crops in comparison with chemical fungicides or Trichoderma biocides. This impact is because of NPs rising gentle absorption, accelerating power transport between photosystems, selling photolysis of water, and facilitating oxygen evolution [43]. Furthermore, the outcomes revealed a major enhance in chlorophyll a (ch-a), b (ch-b), and complete chlorophyll content material in tomato crops handled with CuO-Zs-NPs in comparison with different therapies. The focus of CuO-Zs-NPs had vital results on chlorophyll content material (Fig. 10), with CuO100 and 250 inducing a rise of roughly 50% in chlorophyll a and about 40% in chlorophyll b in comparison with the management. Equally, CuO50 additionally resulted in a average enhance in chlorophyll a and b, albeit with a comparatively smaller quantity. All therapies confirmed a rise in chlorophyll b content material, however tomato crops handled with both CuO50, CuO100, or CuO250 confirmed vital will increase in comparison with these handled with Kocide 2000 chemical fungicide, biocide, or samples of untreated management. The stimulatory affect of CuO-Zs-NPs on the manufacturing of those pigments could also be attributed to their potential to boost plant vitamin by selling nitrogen absorption. This course of can considerably enhance the focus of vitamins in crops, resulting in improved development and rising phenolic compound concentrations that improve pigment manufacturing [82]. Moreover, the second stage of the bio-stimulation approach for CuO nanoparticles entails the bio-transformation of the core materials into ions contained in the cytoplasm. Particularly, this course of converts CuO nanoparticles into Cu ions. This transformation is probably going related to a rise in chlorophyll ranges, which means that the ions could also be concerned in selling plant development and photosynthesis. Total, this second stage of bio-stimulation seems to be an essential step in enhancing the effectiveness of CuO nanoparticles for agricultural functions [38]. The rise in chlorophyll a and b concentrations could also be defined by the truth that therapies together with diverse doses of CuO50, CuO100, and CuO250 stimulated sturdy root improvement. The place therapies can enhance root vitality as in maize, permitting the crop to soak up vitamins from the rising medium [55]. Along with bettering the crop’s capability to soak up gentle through its photosystems, attributable to will increase in chlorophyll concentrations are regarded as a pure response to environmental stimuli [65].
The ratio of chlorophyll a/b is commonly used as a criterion to estimate crop responses to environmental stresses [78]. Some stresses may cause the conversion of chlorophyll a to b through the enzyme Chl-a oxygenase [13]. The lower within the Chla/Chlb ratio noticed on this research could also be attributable to CuO-Zs-NPs selling the exercise of this enzyme [94]. This leads to a rise in Chlb focus and a discount within the ratio, indicating the next focus of PSII in opposition to PSI. This discovering is supported by earlier analysis displaying that Chlb is considerable in PSII [11, 81]. Elevated PSII ranges in leaves point out larger effectivity in absorbing photo voltaic power. Chl-b additionally performs an essential function in arranging thylakoid membranes and regulating LHCs [90]. These outcomes corroborate the sooner descriptions of plant dry matter enhance and photosynthetic effectivity.
In conclusion, CuO-Zs-NPs have been discovered to advertise sturdy root improvement and enhance chlorophyll concentrations in tomato crops. The lower within the Chla/Chlb ratio noticed could also be as a result of elevated exercise of the enzyme accountable for synthesizing Chlb from Chla. These findings counsel that CuO-Zs-NPs might have potential functions for bettering crop development and productiveness.
Impact of CuO-Zs-NPs on enzymatic actions of handled crops
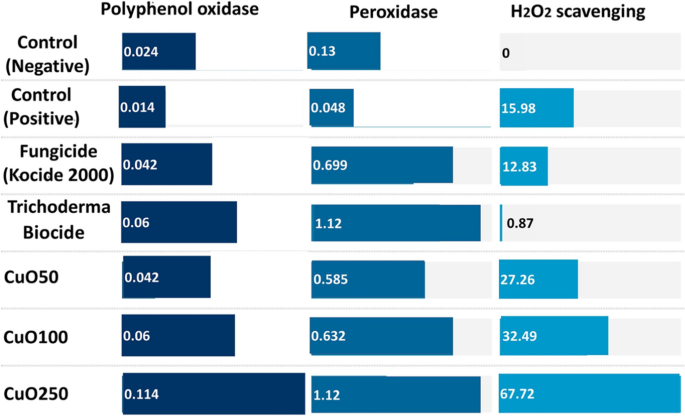
Within the pot experiment, to know extra concerning the interplay of F. solani with tomato crops following the applying of CuO-Zs-NPs at diverse concentrations. A variety of defense-related enzymes had been examined. The info obtained confirmed that the inoculation of F. solani improved the exercise of all of the defense-related enzymes examined in all therapies in comparison with the un-inoculated management crops. The CuO-Zs-NPs considerably modified the enzymatic exercise of polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase in tomato leaves (Fig. 11). The interplay of CuO-Zs-NPs at 50, 100, and 250 mg/l elevated the exercise of the polyphenol oxidase enzyme to 75, 150 and 375% respectively in comparison with the non-treated wholesome and contaminated tomato crops displaying polyphenol oxidase enzymatic exercise of 0.024 and 0.014 U/min/gram respectively. In distinction, remedy with the chemical fungicide and Trichoderma Biocide that elevated polyphenol oxidase exercise to 75, and 150% respectively.
Alternatively, the peroxidase enzyme was elevated to 350, 386, and 762% respectively as compared with the non-treated wholesome and contaminated tomato crops that confirmed peroxidase enzymatic exercise 0.13, 0.048 U/min/gram respectively. In distinction, remedy with the chemical fungicide and Trichoderma Biocide elevated peroxidase exercise to 415, and 762% respectively. Moreover, the exercise of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) scavengers as an antioxidant response to oxidative stress doubtlessly brought on by CuO-Zs-NPs therapies was decided in tomato plant leaves. The outcomes indicated that each CuO-Zs-NPs and the chemical fungicide therapies exhibited larger ranges of H2O2 scavenger exercise than the Trichoderma biocide remedy and the untreated management (Fig. 11).
Total, the outcomes of our research point out that the applying of CuO-Zs-NPs exogenously can improve the resistance of tomato crops in opposition to F. solani an infection. This discovering is in step with earlier experiences demonstrating that sure derived compounds, when utilized externally, can induce resistance in host crops by elevating the degrees of host protection enzymes and pathogen-related (PR) proteins [36]. It’s recommended that CuO-Zs-NPs might set off systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in host crops, thereby decreasing their susceptibility to an infection, as described beforehand [36]. SAR is a plant immune response that forestalls the unfold of an infection or illness to non-infected components of the host plant and is usually characterised by a rise in PR proteins reminiscent of chitinases, -1,3-glucanases, acid invertases, and peroxidases [4, 10, 77]. A number of research have proven that substances derived from crops can stimulate the event of extra resistant crops and scale back illness incidence [61, 67]. The induction of systemic resistance in crops entails the activation of dormant protection genes beneath varied situations.
Quite a few research have reported that elevated ranges of peroxidase, protease, and polyphenol oxidase (POD) enzyme exercise, in addition to the expression of genes for -1,3-glucanase and chitinase, are efficient in opposition to varied fungal illnesses [61, 67]. That is in step with Fernandes, & Ghag, [25] supplied an inclusive evaluation of tomato genes concerned in pathogen detection, protection signaling networks, and the features of enzymes that assist host resistance to Fusarium solani. CuO-Zs-NPs therapies at varied concentrations have been proven to extend defense-related enzymes and pathogenesis-related proteins in tomato crops in opposition to root rot pathogens. These proteins might play a vital function in strengthening the host plant’s cell partitions to withstand F. solani an infection. Moreover, CuO-Zs-NPs might activate protection mechanisms in response to pathogen inoculation by creating extra proteins to forestall pathogen entry or subsequent unfold as a result of significance of Cu as a microelement for crops. Moreover, latest research have additionally demonstrated the function of Cu Bio-nanoparticles in rising H2O2 scavenger exercise as an anti-resistance mechanism in opposition to stress or toxicity [87]. The applying of Cu nanoparticles has been proven to boost antioxidant enzyme exercise and scale back oxidative injury brought on by stress or toxicity. Subsequently, it may be concluded that Cu nanoparticles have potential functions in enhancing plant protection mechanisms in opposition to varied biotic and abiotic stresses.
Willpower of Cu content material in terminal apical tomato tissues
Tomato crop development relies on a spread of important vitamins, each macronutrients (reminiscent of N, P, Okay, Ca, and Mg) and micronutrients (reminiscent of Cu, Fe, B, Mn, and Mo). These vitamins are essential for varied processes together with photosynthesis, mobile respiration, and protection responses. The roots are the first website for nutrient absorption. Cu is especially essential in mitigating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), facilitating photosynthesis, regulating phenol metabolism, and selling protein synthesis [86, 87]. As proven in Desk 2, tomato crops handled with the chemical fungicide Kocide 2000, confirmed the best conc. of Cu with a 17.244 ± 0.22 worth, adopted by 12.372 ± 0.22, 12.516 ± 1.2, and 15.344 ± 0.32 for CuO-Zs-NPs 50, 100, and 250 therapies respectively, in comparison with 10.983 ± 0.40 for remedy with Trichoderma biocide and 10.272 ± 0.24 and 10.297 ± 0.35 for damaging and constructive controls respectively. In view of the obtained outcomes and inconsistent with different analysis [34], rising the conc. of Cu significantly at their nanoscale might promote the expansion of tomato roots which instantly improved seed germination, plant peak, and contemporary and dry weight as indicated above in (Figs. 5, 8) with none adversarial results. That is in settlement with [54] who reported that publicity of plant leaves to various concentrations of Cu NPs didn’t lead to a rise in Cu content material within the fruits. Nonetheless, some research have recommended that the buildup of Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn in leaves might happen by means of uptake by crops through leaf apertures reminiscent of stomata, trichomes, and hydathodes when utilized in foliar or by means of water uptake through root absorption [6]. Micronutrient regulation, significantly Cu, happens throughout totally different pathways of transport that facilitate migration to the wanted areas. Ghasemi et al. [23] discovered that some vitamins might trigger fluctuations in different microelements, which might trigger them to build up in numerous tissues.
This may occasionally clarify the buildup of copper (Cu) in tomato plant leaves when uncovered to the fungicide Kocide 2000 at a excessive focus of two.5 g/L, which can not give the most effective constructive results on some development and physiological parameters in in comparison with decrease dosages of CuO therapies on the nanoscale as indicated above. These findings counsel that CuO-Zs-NPs nanoparticles can improve root development and nutrient absorption, which may very well be thought-about one more reason for selling tomato development in in comparison with different therapies. Moreover, the usage of CuO nanoparticles in soil might mitigate environmental contamination brought on by extreme agrochemical use.
Pollen grain evaluation
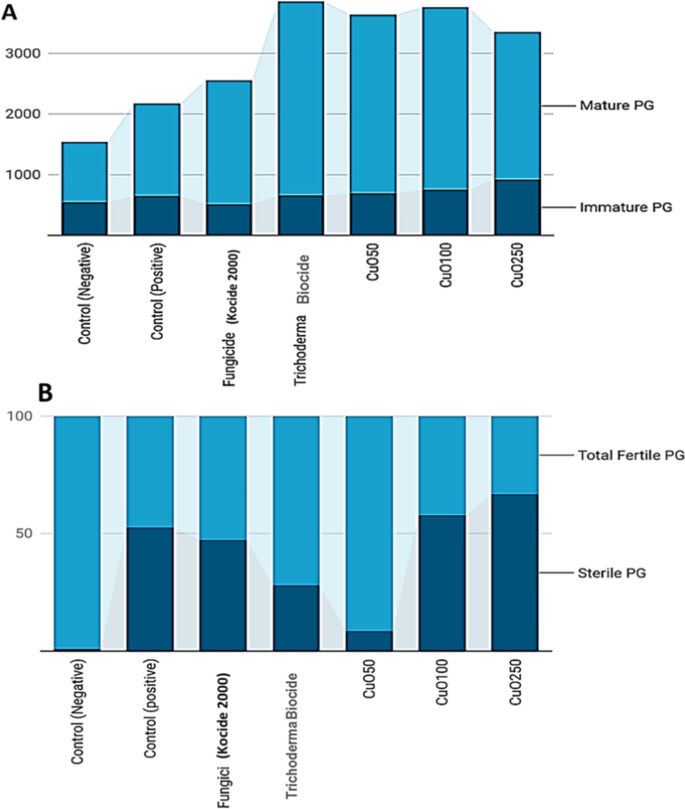
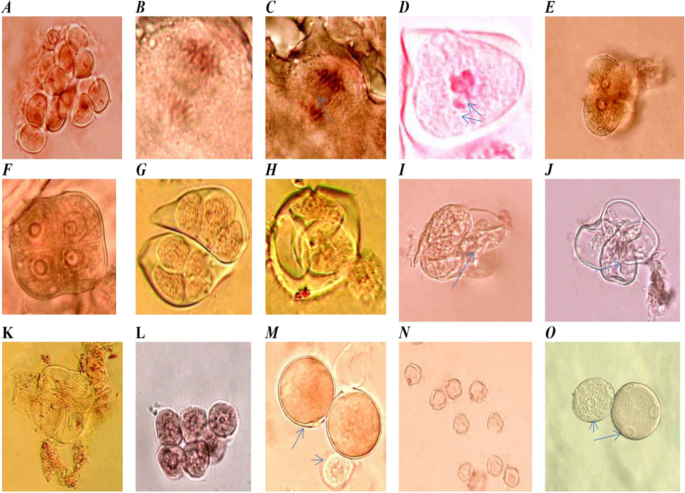
The info in Desk (3) point out that the impact of Cu nanoparticles on the pollen grain fertility of tomato crops was analyzed. The outcomes indicated that therapies with CuO-Zs-NPs on the lowest concentrations led to a rising variety of mature pollen grains (Fig. 13M) in comparison with the immature ones (Figs. 12A and 13L). That is presumably, as a result of early flowering of the crops handled with CuO-Zs-NPs. Which may have an effect on the photosynthesis and respiration strategy of the crops, and affect the manufacturing of sugars and power which might be required for flowering. Equally, remedy with Trichoderma (biocide) confirmed a noticeable enhance in the variety of mature pollen grains in comparison with the management samples. These findings are in settlement with knowledge obtained by Marmiroli et al. [56], who reported that no facet of the plant’s look, improvement, or pollen formation modified after being handled with excessive concentrations (320 mg/kg−1) of nano-CuO. in distinction, some experiences revealed that copper NPs decreased black cumin’s fertility, suggesting that these NPs might have acted as a barrier to pollen formation or to the plant’s regular improvement and maturation [48]. Moreover, fertile pollen grains of irregular measurement in diploid 2n (Fig. 13O arrow) had been noticed in in comparison with regular (n) pollen grains (Fig. 13M), the place meiosis was completely regular within the management remedy (Fig. 13A, B and E). Fertile n was discovered to be elevated to 91.5 in CuO-Zs-NPs at a focus of 50mg/l, approaching the values (99 ± 8.7 of untreated (damaging management, and there was no vital distinction between them. Alternatively, the obtained outcomes indicated that publicity of tomato tissues to Cu-Zs-NPs, significantly on the highest conc. (250 mg/l inhibited pollen improvement within the flowering stage. That is additionally recommended to have an adversarial impact on pollen fertility which was recorded (30.1 ± 1.7% for n fertile pollens and (3.1 ± 0.2for 2n fertile pollens; subsequently, the entire fertile pollens for this remedy had been recorded (33.22% (Desk 3).
A. Divided cell in meiosis I and II; B. Regular anaphase I; C. Anaphase I with lagging chromosome arrow; D. Metaphase I with lagging chromosome and fragment arrow E. Diad pollen grain preparations; F. Regular Microspore tetrad (isobilateral); G. Regular Microspore tetrad (Liner and Decussate) H. Tetrad launch immature PG arrowhead (Tetrahedral); I. Two cells from tetrad lose cytoplasmic granules arrows; J. All cells fashioned tetrad lose cytoplasmic granules; Okay. cytoplasmic granules exterior tetrad arrows; L. immature PGs; M. Mature Fertile PGs (scale back) arrow and immature arrowhead; N. Sterile PGs; O. Mature fertile 2n pollen grain arrow (unreduced)
Whereas the remedy with biocide recorded (68.7 ± 2.9) for the haploid (n) fertile pollen grain and (3.1 ± 0.2) for the diploid pollen, leading to a complete of 71.88% fertile pollen (Fig. 12B). Then, the chemical fungicide was recorded (49.7 ± 4.1) in haploid pollens and (2.9 ± 0.1) in diploid pollens to boost the variety of complete fertile pollens to 52.7%. Moreover, there have been slight will increase within the 2n% worth and no vital distinction among the many therapies with CuO-Zs-NPs at conc. 100 mg/l (2.4 ± 0.1), the chemical fungicide (2.9 ± 0.1), CuO-Zs-NPs at conc. 250 mg/l (3.1 ± 0.2), and Trichoderma biocide (3.1 ± 0.2). Remedy with F. solani solely elevated the diploid 2n to 11.8%. To elucidate this, we propose that the injury brought on by F. solani to tomato root tissues results in a useful impairment that happens from dietary imbalances, which had the best impact on the irregular look [49]. Alternatively, different experiences counsel that the impact of CuONPs presumably prevents centromeric division, resulting in the manufacturing of additional chromosomes (Diplo-chromosomes) [48]. Moreover, polyploid cells and stragglers will be brought on by defects within the spindle course of.
ANOVA statistical analyses indicated a noticeable vital distinction (P < 0.05) between many of the experimental teams in comparison with the management group of sterile PG (Fig. 13N). Nonetheless, when evaluating the fungicide-positive management with the copper-based Cu 100, there was no statistically vital distinction (P > 0.05) (Desk 3). The outcomes indicated a noticeable sterile pollens (unstained pollens, Fig. 13N) which elevated considerably within the remedy with CuO-Zs-NPs at conc. 250 mg/l, which was 66.8 ± 5.6, however there was no vital distinction between the remedy with CuO-Zs-NPs at conc. 100 mg/l, 57.7 ± 2.2, and the constructive management, 52.6 ± 0.7. Alternatively, the biocide remedy recorded a average fee (28.1 ± 2.8). The outcomes additionally confirmed no vital distinction between the constructive management and the remedy with the chemical fungicide (47.3 ± 1.6). Whereas the most effective remedy was CuO-Zs-NPs at a focus of fifty mg/l giving (8.5 ± 0.2), the place there was no noticeable vital distinction with the damaging management (1 ± 0.2).
Though therapies with CuO-Zs-NPs (100, 250 mg/l), and the chemical fungicide decreased the passive impact of F. solani on the tomato host plant, the therapies elevated the damaging impact (sterility) on pollen grains ensuing in chromosomal lagging and fragments that induced mutations (Fig. 13C, and D). The lower within the proportion of viable pollen grains in these handled crops relative to untreated crops will be attributable to their pollen-toxic results. In truth, this dangerous impact turns into extra obvious when fungicides and excessive concentrations of CuO-Zs-NPs are used. Sterility happens in the course of the formation of gametophytes, almost definitely initiating on the microspore stage, and gametophytes are aborted at the start of their improvement. These findings are opposite to knowledge obtained by Marmiroli et al. [56], who reported no adjustments within the improvement or viability of pollen after remedy with excessive concentrations (320 mg/kg) of nano-CuO.
The diploid gametes (Fig. 13O) might outcome from quite a lot of cytological abnormalities as a result of 5 fundamental cytological mechanisms of 2n gamete formation: pre-meiotic chromosome doubling in the course of the transition from mitosis to meiosis, meiosis disturbances, and irregular cytokinesis in the course of the first or second meiosis leading to dyad and triad formation (Fig. 13E, H), adopted by 2n pollen formation. On this regard, some research estimated the frequency of 2n pollen grains and recommended that they got here from restoration nuclei generated throughout meiosis I and II as dyads and triads within the spore stage (Xue, Liu, and Liu [92]). Giant-sized 2n pollen grains had been noticed to be well-filled, pigmented, and viable; therefore, it’s extremely possible that fertilization by these 2n gametes may end up in intraspecific polyploidy. Moreover, Sabrine et al., [74] talked about that larger Cu concentrations disrupt vital features reminiscent of mitosis and photosynthesis, inflicting plant tissue toxicity [70, 74]. Moreover, heavy metals disrupt the mitotic cycle, trigger chromosomal aberrations microtubule injury irregularly formed nuclei, and decompose nuclear materials [91], Eun, Shik Youn, and Lee [22]).
The outcomes recorded a transparent statement within the frequency sample of a traditional tetrad (isobilateral) and tetrads liner and Decussate (Fig. 13F, G) compared to that within the case of the frequency sample of tetrad launch immature PG (Tetrahedral), which confirmed that remedy with CuO-Zs NPs outcomes in a transparent noticed lack of cytoplasmic granules in tetrad cells both exterior or inside cells (Fig. 13H–Okay), such because the non-disjunction of chromosomes in each meiotic divisions. These findings will be defined by manipulations in male meiosis as indicated in Berdnikov et al [9]. Moreover, the therapies induce structural injury to the cell within the tetrad-stage pollen cytoplasm Grain (PCG) are naturally launched from the pollen grain when the cytoplasm is expelled from the pollen grains by means of the pore. Nonetheless, launch might additionally happen by means of cracks of the exine when the pollen was broken. Solely a small proportion of the pollen releases their cytoplasm, and the remaining pollen stays intact. Nonetheless, in fragile pollen, PCG launch may happen by means of breaks of the exine cytoplasmic granules that may be seen subsequent to the pollens that come out of them. Our outcomes confirmed that cytoplasmic granules had been expelled from the cells in tetrad levels. Tetrad cytoplasmic granules will be seen subsequent to tetrad stage additionally. Moreover, the tetrads with two lethal pollen grains might outcome primarily from non-disjunction in anaphase I, and people with one pollen grain might outcome primarily from non-disjunction in anaphase II [9]. This phenomenon outcomes from the interplay of cell division and pollen improvement with some poisonous therapies and will increase the proportion of cytoplasmic granules launched. These causes additionally decreased the ultimate share of complete fertile pollen grains within the handled crops in contrast with the management, which will be attributed to their poisonous impact on pollen.