(Nanowerk Information) Amino acids, reminiscent of tyrosine and tryptophan, are the elemental constructing blocks that make up proteins. These biomolecules have totally different chemical teams on every finish and facet chain, and so, have the pure potential to kind a series by way of the formation of an amide (peptide) bond. Nevertheless, such linkages are weak and simply degraded below physiological situations. That is the place the Fmoc-protected amino acids come into the image.
In a brand new research, a analysis crew led by Dr. Eijiro Miyako, Affiliate Professor, Japan Superior Institute of Science and Know-how (JAIST) and Dr. Alberto Bianco and Dr. Cécilia Ménard-Moyon from the Centre Nationwide de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), France, employed ultraviolet gentle at 254 nm (resulting in CBPUV nanoparticles) and riboflavin-mediated crosslinking at 365 nm (resulting in CBPRibo nanoparticles) to crosslink the Fmoc-protected amino acids.
“Amino acids being the constructing blocks of proteins have quite a few benefits, reminiscent of higher biocompatibility. Subsequently, we wished to create novel self-assembled amino acid-based nanoparticles which may be triggered by way of a number of mechanisms,” says Dr. Eijiro Miyako, explaining the motivation behind their analysis.
The findings of this research are revealed in Small (“Photocrosslinked Co-assembled Amino Acid Nanoparticles for Managed Chemo/photothermal Mixed Anticancer Remedy”).
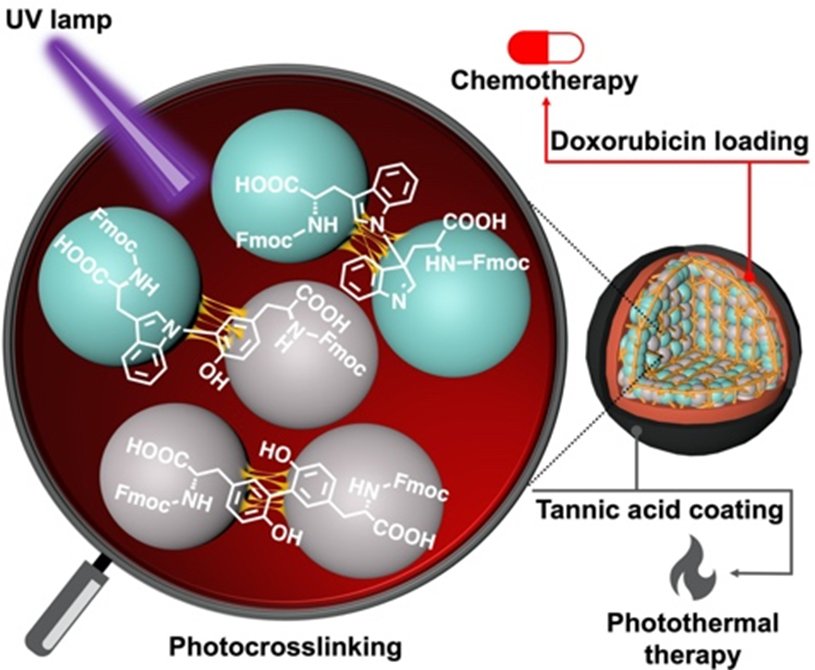 A illustration of the amino acid-based nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and coated with tannic acid complicated for a dual-action mechanism. Picture caption: Nanotechnology confers the flexibility to tailor the floor properties of nanoparticles and improve the general drug launch profile. Using tannic acid coating together with loading of the anticancer drug – doxorubicin, creates a sensible drug supply system that may be triggered to launch the drug in a managed and sustained method, leading to elevated anticancer efficacy. (Picture: Eijiro Miyako, JAIST)
The self-assembled amino acids have been stably crosslinked dimers of Fmoc-Tyr-OH (Tyrosine) and Fmoc-Trp-OH (Tryptophan). Doxorubicin, an anticancer drug, was subsequently loaded into the crosslinked amino acid nanoparticles. To extend the steadiness of the nanoparticles, the researchers used a tannic acid-Iron (Fe3+) complicated (or TAF) because the outer layer of coating. This coating can degrade contained in the cells by way of the glutathione enzymatic launch or by pH distinction within the tumor microenvironment. The tannic acid coating may be additionally utilized in photothermal anticancer remedy, the place exterior gentle can improve the native temperature surrounding the most cancers tissue, inflicting most cancers cell dying.
The synthesized nanoparticles have been then extensively studied for his or her structural integrity, stability, and drug launch below totally different pH situations. The purposeful profile, mobile uptake, and biocompatibility of self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles have been then studied utilizing cell tradition strategies. Lastly, the anticancer efficacy of synthesized nanoparticles was analyzed in tumor-bearing mice. The mixed strategy of chemotherapy, as a consequence of doxorubicin motion, and photothermal remedy due to the tannic acid coating, confirmed wonderful anticancer exercise.
Submit crosslinking, the amino acid-based nanoparticles confirmed notable modifications in coloration, measurement, absorbance, fluorescence, and thermal stability. Moreover, CBPUV exhibited superior stability after crosslinking, in comparison with CBPRibo. CBPUV additionally persistently maintained its construction, whereas CBPRibo confirmed partial disassembly, forming hole spheres. Drug launch research revealed minimal drug launch below physiological pH (7.4), indicating that steady coating is essential for in vivo supply.
At pH 5.5, incomplete coating degradation resulted in negligible drug launch. Nevertheless, the addition of glutathione (GSH) at pH 5.5 considerably boosted drug launch by triggering TAF coating degradation, indicating GSH/pH responsiveness. The mixed acidic and GSH therapy intensified coating degradation. This responsive habits allows managed drug launch in particular physiological situations.
Moreover, in vitro assessments revealed concentration-dependent cytotoxicity and improved efficacy in mixed chemo/photothermal remedy. In vivo research on tumor-bearing mice showcased important tumor progress inhibition, indicating promising anticancer results with out noticed uncomfortable side effects.
Sharing his concluding ideas in regards to the research findings, Dr. Miyako says, “Nanotechnology holds promise of remodeling fundamental laboratory science into a strong instrument for combating complicated ailments like most cancers. We’re optimistic that this pioneering analysis will advance, doubtlessly evolving into cutting-edge most cancers therapy know-how prepared for scientific trials inside ten years.”
The event of those self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles can assist in combating crucial points reminiscent of multi-drug resistance in most cancers and enhance the general efficacy of therapy outcomes.
A illustration of the amino acid-based nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and coated with tannic acid complicated for a dual-action mechanism. Picture caption: Nanotechnology confers the flexibility to tailor the floor properties of nanoparticles and improve the general drug launch profile. Using tannic acid coating together with loading of the anticancer drug – doxorubicin, creates a sensible drug supply system that may be triggered to launch the drug in a managed and sustained method, leading to elevated anticancer efficacy. (Picture: Eijiro Miyako, JAIST)
The self-assembled amino acids have been stably crosslinked dimers of Fmoc-Tyr-OH (Tyrosine) and Fmoc-Trp-OH (Tryptophan). Doxorubicin, an anticancer drug, was subsequently loaded into the crosslinked amino acid nanoparticles. To extend the steadiness of the nanoparticles, the researchers used a tannic acid-Iron (Fe3+) complicated (or TAF) because the outer layer of coating. This coating can degrade contained in the cells by way of the glutathione enzymatic launch or by pH distinction within the tumor microenvironment. The tannic acid coating may be additionally utilized in photothermal anticancer remedy, the place exterior gentle can improve the native temperature surrounding the most cancers tissue, inflicting most cancers cell dying.
The synthesized nanoparticles have been then extensively studied for his or her structural integrity, stability, and drug launch below totally different pH situations. The purposeful profile, mobile uptake, and biocompatibility of self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles have been then studied utilizing cell tradition strategies. Lastly, the anticancer efficacy of synthesized nanoparticles was analyzed in tumor-bearing mice. The mixed strategy of chemotherapy, as a consequence of doxorubicin motion, and photothermal remedy due to the tannic acid coating, confirmed wonderful anticancer exercise.
Submit crosslinking, the amino acid-based nanoparticles confirmed notable modifications in coloration, measurement, absorbance, fluorescence, and thermal stability. Moreover, CBPUV exhibited superior stability after crosslinking, in comparison with CBPRibo. CBPUV additionally persistently maintained its construction, whereas CBPRibo confirmed partial disassembly, forming hole spheres. Drug launch research revealed minimal drug launch below physiological pH (7.4), indicating that steady coating is essential for in vivo supply.
At pH 5.5, incomplete coating degradation resulted in negligible drug launch. Nevertheless, the addition of glutathione (GSH) at pH 5.5 considerably boosted drug launch by triggering TAF coating degradation, indicating GSH/pH responsiveness. The mixed acidic and GSH therapy intensified coating degradation. This responsive habits allows managed drug launch in particular physiological situations.
Moreover, in vitro assessments revealed concentration-dependent cytotoxicity and improved efficacy in mixed chemo/photothermal remedy. In vivo research on tumor-bearing mice showcased important tumor progress inhibition, indicating promising anticancer results with out noticed uncomfortable side effects.
Sharing his concluding ideas in regards to the research findings, Dr. Miyako says, “Nanotechnology holds promise of remodeling fundamental laboratory science into a strong instrument for combating complicated ailments like most cancers. We’re optimistic that this pioneering analysis will advance, doubtlessly evolving into cutting-edge most cancers therapy know-how prepared for scientific trials inside ten years.”
The event of those self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles can assist in combating crucial points reminiscent of multi-drug resistance in most cancers and enhance the general efficacy of therapy outcomes.


