Jan 08, 2024
(Nanowerk Information) A world crew of researchers led by Mungo Frost from SLAC Nationwide Accelerator Laboratory in California and together with DESY scientists used the European X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) in Schenefeld to realize new insights into the formation and incidence of diamond rain in ice giants equivalent to Neptune, Uranus, or exoplanets exterior of our photo voltaic system.
The outcomes, which have now been printed within the scientific journal Nature Astronomy (“Diamond Precipitation Dynamics from Hydrocarbons at Icy Planet Inside Circumstances”), additionally present clues into the origin of their advanced magnetic fields.
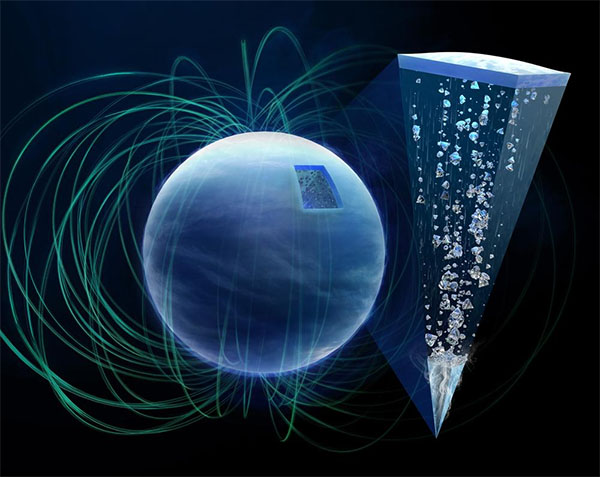 The graphic illustrates the phenomenon of diamond rain inside the planet, whereby diamonds descend via surrounding ice. As these diamonds journey deeper into the planet, each strain and temperature steadily improve. (Picture: European XFEL / Tobias Wüstefeld)
In earlier work utilizing X-ray lasers, scientists had already found that diamonds can kind from carbon compounds on the pressures and temperatures discovered inside massive fuel planets, confirming the potential for diamond formation in ice giants that are primarily composed of water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. Following their formation, diamonds are anticipated to slowly sink deeper into the planetary inside in response to gravitational forces, leading to a ‘rain’ of treasured stones from larger layers.
A brand new experiment on the European XFEL has now proven that the formation of diamonds from carbon compounds happens at decrease pressures and temperatures than beforehand assumed. Within the case of icy Photo voltaic planets, because of this diamond rain can kind at a shallower depth than initially thought, and will subsequently have a stronger affect on the magnetic discipline. As well as, diamond rain also needs to be doable in fuel planets which might be smaller than Neptune and Uranus, the so-called “mini-Neptunes”, that are probably the most frequent sorts of exoplanets discovered exterior of the photo voltaic system.
After their formation, diamond particles can entrain fuel and ice as they descend from the outer to the inside layers of the planet, inflicting currents of ice. The brand new outcomes present that diamonds kind above a layer of conductive ice which shall be stirred because the diamonds fall via them. Currents of conductive fluids act as a type of dynamo via which the magnetic fields of planets are fashioned. “Diamond rain most likely has an affect on the formation of the advanced magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune,” Frost mentioned.
The group used a plastic movie made out of the hydrocarbon compound polystyrene as a carbon supply, which was subjected to the intense pressures and temperatures discovered deep within the inside of those icy planets. First, excessive pressures have been generated by squeezing the foil between the ideas of two diamonds utilizing a so-called ‘diamond anvil cell’, during which the anvils operate like a mini-vice. The foil was then uncovered to a number of doses of excessive power X-rays to warmth it to greater than 2200 levels Celsius, imitating the intense circumstances skilled deep inside these planets.
Then the researchers additionally used the X-ray pulses produced by the European XFEL to look at when and the way the diamonds fashioned throughout their experiments. The strain and temperature at which diamonds have been noticed permits researchers to foretell the depth they are often anticipated to kind contained in the planet.
The graphic illustrates the phenomenon of diamond rain inside the planet, whereby diamonds descend via surrounding ice. As these diamonds journey deeper into the planet, each strain and temperature steadily improve. (Picture: European XFEL / Tobias Wüstefeld)
In earlier work utilizing X-ray lasers, scientists had already found that diamonds can kind from carbon compounds on the pressures and temperatures discovered inside massive fuel planets, confirming the potential for diamond formation in ice giants that are primarily composed of water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. Following their formation, diamonds are anticipated to slowly sink deeper into the planetary inside in response to gravitational forces, leading to a ‘rain’ of treasured stones from larger layers.
A brand new experiment on the European XFEL has now proven that the formation of diamonds from carbon compounds happens at decrease pressures and temperatures than beforehand assumed. Within the case of icy Photo voltaic planets, because of this diamond rain can kind at a shallower depth than initially thought, and will subsequently have a stronger affect on the magnetic discipline. As well as, diamond rain also needs to be doable in fuel planets which might be smaller than Neptune and Uranus, the so-called “mini-Neptunes”, that are probably the most frequent sorts of exoplanets discovered exterior of the photo voltaic system.
After their formation, diamond particles can entrain fuel and ice as they descend from the outer to the inside layers of the planet, inflicting currents of ice. The brand new outcomes present that diamonds kind above a layer of conductive ice which shall be stirred because the diamonds fall via them. Currents of conductive fluids act as a type of dynamo via which the magnetic fields of planets are fashioned. “Diamond rain most likely has an affect on the formation of the advanced magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune,” Frost mentioned.
The group used a plastic movie made out of the hydrocarbon compound polystyrene as a carbon supply, which was subjected to the intense pressures and temperatures discovered deep within the inside of those icy planets. First, excessive pressures have been generated by squeezing the foil between the ideas of two diamonds utilizing a so-called ‘diamond anvil cell’, during which the anvils operate like a mini-vice. The foil was then uncovered to a number of doses of excessive power X-rays to warmth it to greater than 2200 levels Celsius, imitating the intense circumstances skilled deep inside these planets.
Then the researchers additionally used the X-ray pulses produced by the European XFEL to look at when and the way the diamonds fashioned throughout their experiments. The strain and temperature at which diamonds have been noticed permits researchers to foretell the depth they are often anticipated to kind contained in the planet.
 The graphic illustrates the phenomenon of diamond rain inside the planet, whereby diamonds descend via surrounding ice. As these diamonds journey deeper into the planet, each strain and temperature steadily improve. (Picture: European XFEL / Tobias Wüstefeld)
In earlier work utilizing X-ray lasers, scientists had already found that diamonds can kind from carbon compounds on the pressures and temperatures discovered inside massive fuel planets, confirming the potential for diamond formation in ice giants that are primarily composed of water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. Following their formation, diamonds are anticipated to slowly sink deeper into the planetary inside in response to gravitational forces, leading to a ‘rain’ of treasured stones from larger layers.
A brand new experiment on the European XFEL has now proven that the formation of diamonds from carbon compounds happens at decrease pressures and temperatures than beforehand assumed. Within the case of icy Photo voltaic planets, because of this diamond rain can kind at a shallower depth than initially thought, and will subsequently have a stronger affect on the magnetic discipline. As well as, diamond rain also needs to be doable in fuel planets which might be smaller than Neptune and Uranus, the so-called “mini-Neptunes”, that are probably the most frequent sorts of exoplanets discovered exterior of the photo voltaic system.
After their formation, diamond particles can entrain fuel and ice as they descend from the outer to the inside layers of the planet, inflicting currents of ice. The brand new outcomes present that diamonds kind above a layer of conductive ice which shall be stirred because the diamonds fall via them. Currents of conductive fluids act as a type of dynamo via which the magnetic fields of planets are fashioned. “Diamond rain most likely has an affect on the formation of the advanced magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune,” Frost mentioned.
The group used a plastic movie made out of the hydrocarbon compound polystyrene as a carbon supply, which was subjected to the intense pressures and temperatures discovered deep within the inside of those icy planets. First, excessive pressures have been generated by squeezing the foil between the ideas of two diamonds utilizing a so-called ‘diamond anvil cell’, during which the anvils operate like a mini-vice. The foil was then uncovered to a number of doses of excessive power X-rays to warmth it to greater than 2200 levels Celsius, imitating the intense circumstances skilled deep inside these planets.
Then the researchers additionally used the X-ray pulses produced by the European XFEL to look at when and the way the diamonds fashioned throughout their experiments. The strain and temperature at which diamonds have been noticed permits researchers to foretell the depth they are often anticipated to kind contained in the planet.
The graphic illustrates the phenomenon of diamond rain inside the planet, whereby diamonds descend via surrounding ice. As these diamonds journey deeper into the planet, each strain and temperature steadily improve. (Picture: European XFEL / Tobias Wüstefeld)
In earlier work utilizing X-ray lasers, scientists had already found that diamonds can kind from carbon compounds on the pressures and temperatures discovered inside massive fuel planets, confirming the potential for diamond formation in ice giants that are primarily composed of water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. Following their formation, diamonds are anticipated to slowly sink deeper into the planetary inside in response to gravitational forces, leading to a ‘rain’ of treasured stones from larger layers.
A brand new experiment on the European XFEL has now proven that the formation of diamonds from carbon compounds happens at decrease pressures and temperatures than beforehand assumed. Within the case of icy Photo voltaic planets, because of this diamond rain can kind at a shallower depth than initially thought, and will subsequently have a stronger affect on the magnetic discipline. As well as, diamond rain also needs to be doable in fuel planets which might be smaller than Neptune and Uranus, the so-called “mini-Neptunes”, that are probably the most frequent sorts of exoplanets discovered exterior of the photo voltaic system.
After their formation, diamond particles can entrain fuel and ice as they descend from the outer to the inside layers of the planet, inflicting currents of ice. The brand new outcomes present that diamonds kind above a layer of conductive ice which shall be stirred because the diamonds fall via them. Currents of conductive fluids act as a type of dynamo via which the magnetic fields of planets are fashioned. “Diamond rain most likely has an affect on the formation of the advanced magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune,” Frost mentioned.
The group used a plastic movie made out of the hydrocarbon compound polystyrene as a carbon supply, which was subjected to the intense pressures and temperatures discovered deep within the inside of those icy planets. First, excessive pressures have been generated by squeezing the foil between the ideas of two diamonds utilizing a so-called ‘diamond anvil cell’, during which the anvils operate like a mini-vice. The foil was then uncovered to a number of doses of excessive power X-rays to warmth it to greater than 2200 levels Celsius, imitating the intense circumstances skilled deep inside these planets.
Then the researchers additionally used the X-ray pulses produced by the European XFEL to look at when and the way the diamonds fashioned throughout their experiments. The strain and temperature at which diamonds have been noticed permits researchers to foretell the depth they are often anticipated to kind contained in the planet.


