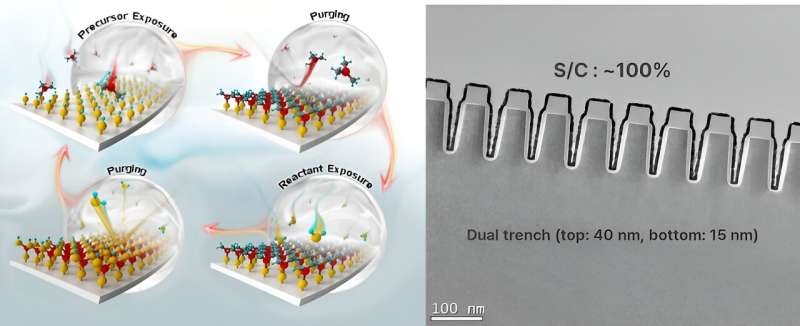
A staff of researchers, led by Professor Soo-Hyun Kim within the Graduate Faculty of Semiconductors Supplies and Gadgets Engineering and the Division of Supplies Science and Engineering at UNIST has made vital progress in exactly controlling valuable metals (Ru, Ir, Pt, Pd) incorporation by atomic layer deposition (ALD).
On this research, revealed in Superior Science, the staff efficiently developed distinctive and unexplored two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials V-MXene for the very first time coupled with valuable metallic ruthenium (Ru) by the ALD course of. This breakthrough holds immense promise for numerous functions, each contact and non-contact mode of real-time temperature sensing on the human-machine interface.
The combination of Ru-engineered V-MXene by ALD has demonstrated a outstanding 300% enhancement in machine sensing efficiency and sturdiness, surpassing the capabilities of pristine V-MXene. This development not solely paves the best way in the direction of the creation multifunctional, cutting-edge private well being care gadgets, but additionally holds nice guarantees for the development of fresh power conversion and storage applied sciences.
Furthermore, the utilization of the industrially scalable ALD method used on this analysis allows exact engineering of MXene surfaces with valuable metals, thereby opening up new prospects for future functions.
-
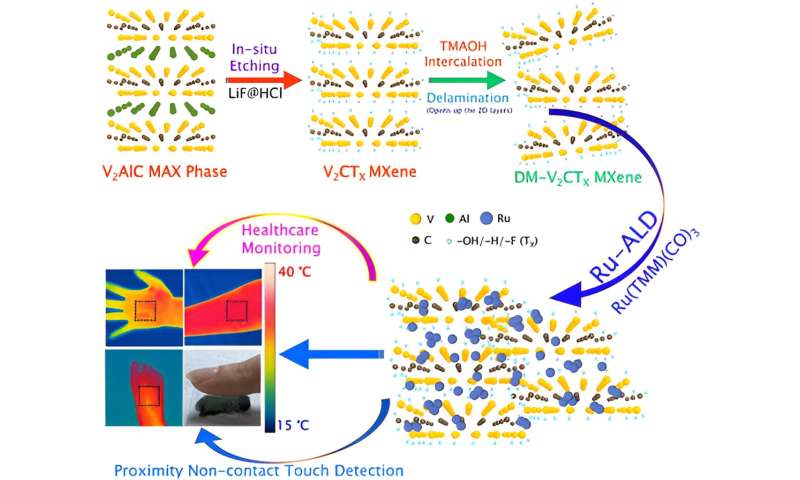
Determine 2. As-synthesized bulk amount delaminated V2CTX MXene (DM-V2CTX) to develop Ru-ALD Engineered DM-V2CTX (Ru@DM-V2CTX) for real-time pores and skin temperature sensing, noncontact contact, proximity sensing, and respiratory monitoring. Credit score: Superior Science (2023). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202206355
-
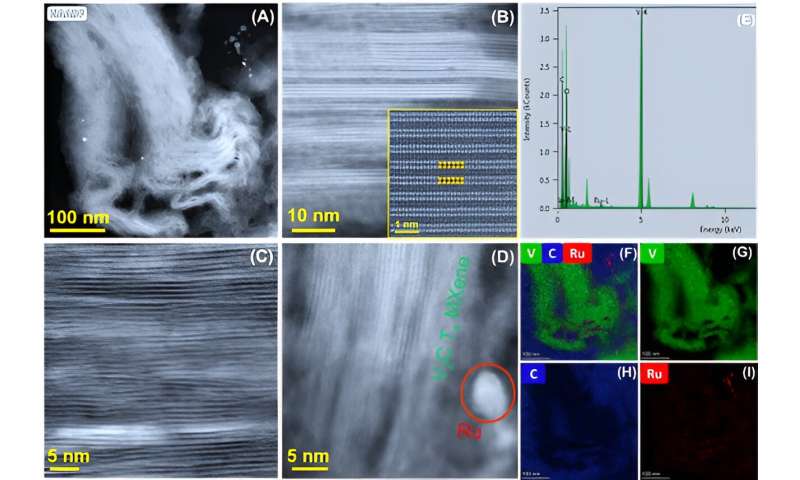
Determine 3. Ru-ALD engineered DM-V2CTX MXene microstructure and elemental mapping. (A) HAADF STEM exhibiting the presence of layered DM-V2CTX MXene construction and the distribution of Ru atoms/clusters, (B, C) HR-STEM of the well-defined layered construction of DM-V2CTX MXene all through the pattern and inset (B) confirms the opening of V2CTX MXene layers after the removing of Al-layers, (D) HR-STEM of each layered DM-V2CTX MXene and Ru lattices, (E) Tremendous-X EDS elemental spectra confirming the weather V, C, Ru, and (F–I) their corresponding elemental mapping photos. The atoms in Fig. 2B inset are proven with the identical colours as illustrated in Determine 1 after the etching and delamination course of. Credit score: Superior Science (2023). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202206355
“We’re thrilled by the potential of this breakthrough,” mentioned Professor Kim. “The precision-enabled integration of valuable metals opens up a complete new world of prospects within the improvement of versatile, next-generation, and protected private well being care gadgets, in addition to clear power conversion and storage programs, with the potential to considerably affect individuals’s lives.”
Dr. Debananda Mohapatra, an Affiliate Analysis Professor within the Graduate Faculty of Semiconductors Supplies and Gadgets Engineering at UNIST, emphasised the convenience and flexibility of engineering MXene surfaces with valuable metals, utilizing industrially favored ALD methods. He additionally highlighted the potential for real-time functions in wearable well being care gadgets and clear power fields. He mentioned, “This profitable work marks the start of a thriving analysis subject of targeted on advancing 2D nanomaterials engineering and functions empowered by ALD.”
The analysis staff additional highlighted the huge potential for exploring the much less investigated non-Ti-MXenes, resembling Mo, V, and Nb-based MXenes, for surface-internal construction engineering utilizing selective valuable metals (Ru, Ir, Pt, Pd) ALD processes.
By incorporating single atoms or atomic clusters of valuable metals (Ru, Ir, Pt, and Pd), the ensuing floor exercise and the sensitivity/power efficiency per atom will be considerably enhanced. This strategy minimizes using these scarce and costly valuable metals.
Extra data:
Debananda Mohapatra et al, Course of Managed Ruthenium on 2D Engineered V‐MXene by way of Atomic Layer Deposition for Human Healthcare Monitoring, Superior Science (2023). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202206355
Quotation:
A novel avenue for engineering 2D MXene household by way of valuable metals atomic layer deposition methods (2024, January 3)
retrieved 7 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-avenue-Second-mxene-family-precious.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


