
Google is downplaying studies of malware abusing an undocumented Google Chrome API to generate new authentication cookies when beforehand stolen ones have expired.
In late November 2023, BleepingComputer reported on two information-stealing malware operations named Lumma and Rhadamanthys, claiming they may restore expired Google authentication cookies stolen in assaults.
These cookies might then be loaded into risk actors’ browsers to realize entry to an contaminated consumer’s Google accounts.
Since then, 4 different data stealers have adopted the identical approach, together with Stealc on December 1, Medusa on December 11, RisePro on December 12, and Whitesnake on December 26.
Final week, cybersecurity agency CloudSEK revealed that these information-stealing malware operations are abusing a Google OAuth “MultiLogin” API endpoint to generate new, working authentication cookies when a sufferer’s authentic stolen Google cookies expire.
This API is believed to be designed for synchronizing accounts throughout totally different Google companies by accepting a vector of account IDs and auth-login tokens.
BleepingComputer’s makes an attempt to study extra about this API from Google have been unsuccessful, and the one documentation could be present in Google Chrome’s supply code.
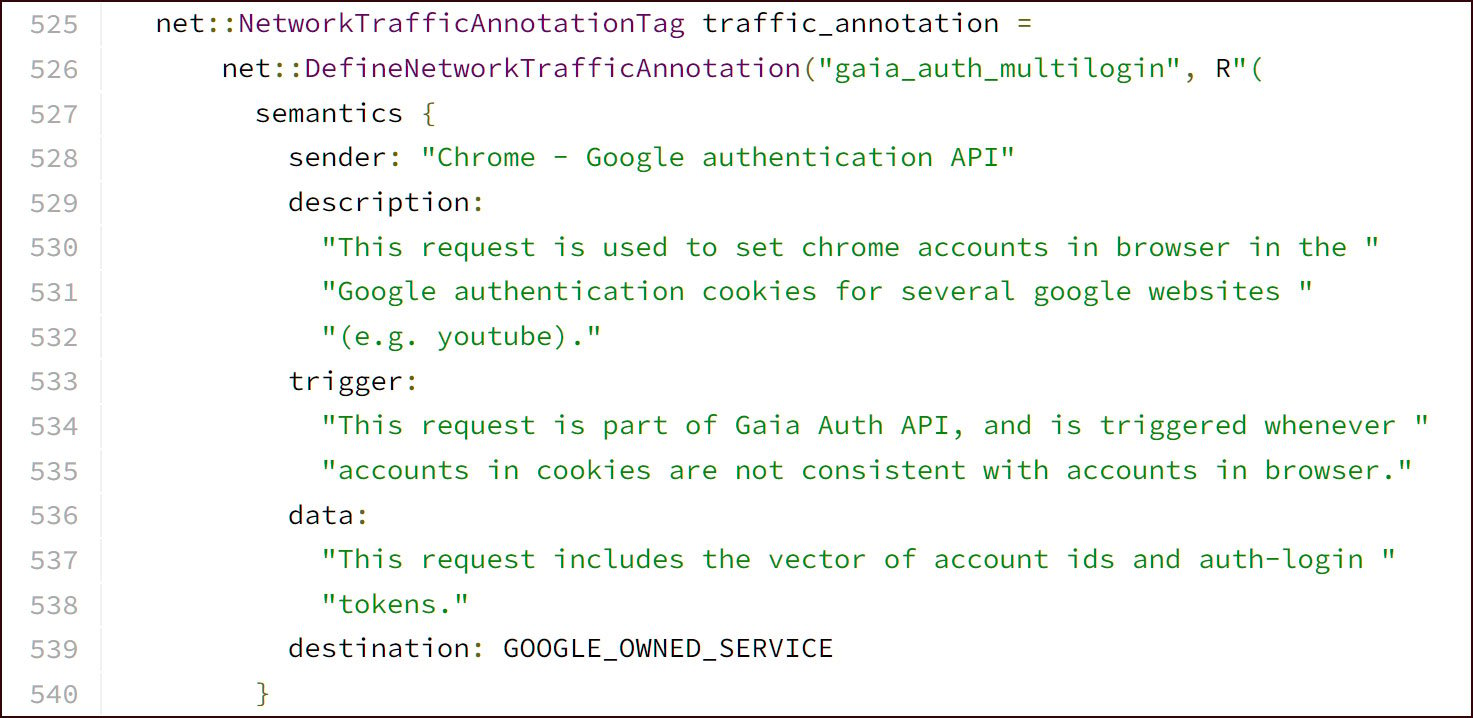
CloudSEK researcher Pavan Karthick instructed BleepingComputer that the information-stealing malware abusing this characteristic will now steal a number of tokens from Google Chrome.
These tokens embrace any authentication cookies for Google websites and a particular token that can be utilized to refresh, or generate, new authentication tokens.
As common authentication cookies expire after a sure period of time, they finally turn into unusable to the risk actor.
Nevertheless, so long as the consumer has not logged out of Google Chrome or revoked all classes related to their accounts, the risk actors can use this particular “Refresh” token to generate model new authentication tokens when the earlier ones have expired.
These new tokens permit them to proceed accessing the accounts for much longer than would often be allowed.
Not simply your normal cookie theft
Sadly, Google sees this API abuse as simply your common, garden-variety malware-based cookie theft.
“Google is conscious of current studies of a malware household stealing session tokens,” Google instructed BleepingComputer in a press release final week.
“Assaults involving malware that steal cookies and tokens usually are not new; we routinely improve our defenses in opposition to such strategies and to safe customers who fall sufferer to malware. On this occasion, Google has taken motion to safe any compromised accounts detected.”
Nevertheless, sources acquainted with this concern have instructed BleepingComputer that Google believes the API is working as supposed and and that no vulnerability is being exploited by the malware.
Google’s resolution to this concern is solely having customers sign off of their Chrome browser from the affected gadget or kill all lively classes by way of g.co/mydevices. Doing so will invalidate the Refresh token and make it unusable with the API.
Because the info-stealing malware stole your credentials, you also needs to change your Google password out of warning, particularly for those who use the identical credentials at different websites.
“Within the meantime, customers ought to regularly take steps to take away any malware from their pc, and we suggest turning on Enhanced Secure Shopping in Chrome to guard in opposition to phishing and malware downloads,” Google additional recommends.
Whereas these really helpful steps will mitigate the affect of information-stealing malware infections, most individuals contaminated with such a malware won’t know when to do these steps.
When individuals are contaminated with information-stealing malware, they sometimes have no idea till their accounts are accessed with out permission and abused in some detectable method.
For instance, an worker for Orange España, the nation’s second-largest cell phone supplier, had their passwords stolen by information-stealing malware.
Nevertheless, nobody knew till stolen credentials have been used to log into the corporate’s RIPE account and modify their BGP configuration, inflicting a 50% efficiency hit and Web outages for Orange prospects.
Whereas Google says that they’ve detected those that have been impacted by this API abuse and notified them, what occurs for future victims?
Moreover, how will customers customers know they need to sign off of their browser to invalidate authentication tokens when they don’t even know they have been contaminated within the first place.
Because of this, a greater resolution could be to limit entry to this API in some method to stop abuse by the malware-as-a-service operations. Sadly, it doesn’t appear to be that is occurring.
BleepingComputer has requested Google what plans they should mitigate this API abuse however has not acquired a response to those questions.

