The malware loader often known as PikaBot is being distributed as a part of a malvertising marketing campaign concentrating on customers looking for reputable software program like AnyDesk.
“PikaBot was beforehand solely distributed through malspam campaigns equally to QakBot and emerged as one of many most popular payloads for a risk actor often known as TA577,” Malwarebytes’ Jérôme Segura stated.
The malware household, which first appeared in early 2023, consists of a loader and a core module that permits it to function as a backdoor in addition to a distributor for different payloads.
This allows the risk actors to achieve unauthorized distant entry to compromised programs and transmit instructions from a command-and-control (C2) server, starting from arbitrary shellcode, DLLs, or executable information, to different malicious instruments corresponding to Cobalt Strike.
From USER to ADMIN: Be taught How Hackers Acquire Full Management
Uncover the key techniques hackers use to develop into admins, easy methods to detect and block it earlier than it is too late. Register for our webinar right this moment.
One of many risk actors leveraging PikaBot in its assaults is TA577, a prolific cybercrime risk actor that has, up to now, delivered QakBot, IcedID, SystemBC, SmokeLoader, Ursnif, and Cobalt Strike.
Final month, it emerged that PikaBot, together with DarkGate, is being propagated through malspam campaigns mirror that of QakBot. “Pikabot an infection led to Cobalt Strike on 207.246.99[.]159:443 utilizing masterunis[.]internet as its area,” Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 disclosed lately.
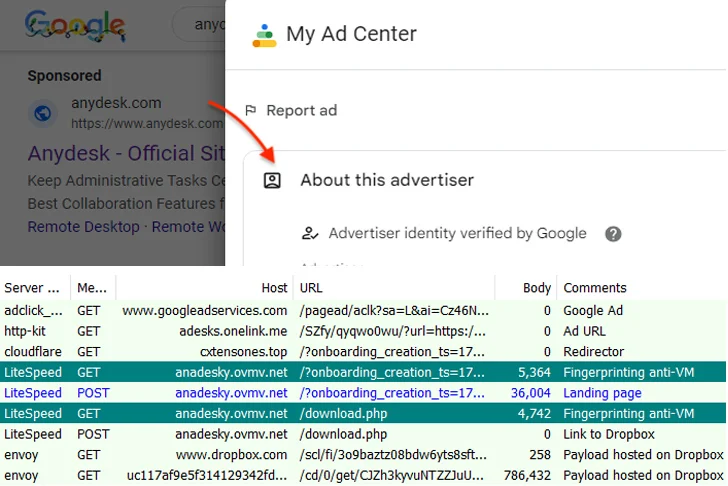
The most recent preliminary an infection vector is a malicious Google advert for AnyDesk that, when clicked by a sufferer from the search outcomes web page, redirects to a faux web site named anadesky.ovmv[.]internet that factors to a malicious MSI installer hosted on Dropbox.
It is value declaring that the redirection to the bogus web site solely happens after fingerprinting the request, and provided that it is not originating from a digital machine.
“The risk actors are bypassing Google’s safety checks with a monitoring URL through a reputable advertising platform to redirect to their customized area behind Cloudflare,” Segura defined. “At this level, solely clear IP addresses are forwarded to the subsequent step.”
Apparently, a second spherical of fingerprinting takes place when the sufferer clicks on the obtain button on the web site, doubtless in an added try to make sure that it is not accessible in a virtualized setting.
Malwarebytes stated the assaults are paying homage to beforehand recognized malvertising chains employed to disseminate one other loader malware often known as FakeBat (aka EugenLoader).
“That is notably attention-grabbing as a result of it factors in the direction of a standard course of utilized by totally different risk actors,” Segura stated. “Maybe, that is one thing akin to ‘malvertising-as-a-service’ the place Google advertisements and decoy pages are offered to malware distributors.”
The disclosure comes because the cybersecurity firm stated it detected a spike in malicious advertisements by means of Google searches for in style software program like Zoom, Superior IP Scanner, and WinSCP to ship a beforehand never-before-seen loader referred to as HiroshimaNukes in addition to FakeBat.
“[HiroshimaNukes] makes use of a number of strategies to bypass detection from DLL side-loading to very giant payloads,” Segura stated. “Its aim is to drop extra malware, usually a stealer adopted by information exfiltration.”
The rise in malvertising is indicative of how browser-based assaults act as channels for infiltrating goal networks. This additionally features a new Google Chrome extension framework codenamed ParaSiteSnatcher, which permits risk actors to “monitor, manipulate, and exfiltrate extremely delicate data from a number of sources.”
Particularly designed to compromise customers in Latin America, the rogue extension is noteworthy for its use of the Chrome Browser API to intercept and exfiltrate all POST requests containing delicate account and monetary data. It is downloaded by means of a VBScript downloader hosted on Dropbox and Google Cloud and put in onto an contaminated system.
“As soon as put in, the extension manifests with the assistance of in depth permissions enabled by means of the Chrome extension, permitting it to govern internet classes, internet requests, and monitor consumer interactions throughout a number of tabs utilizing the Chrome tabs API,” Development Micro stated final month.
“The malware contains numerous parts that facilitate its operation, content material scripts that allow malicious code injection into internet pages, monitor Chrome tabs, and intercept consumer enter and internet browser communication.”