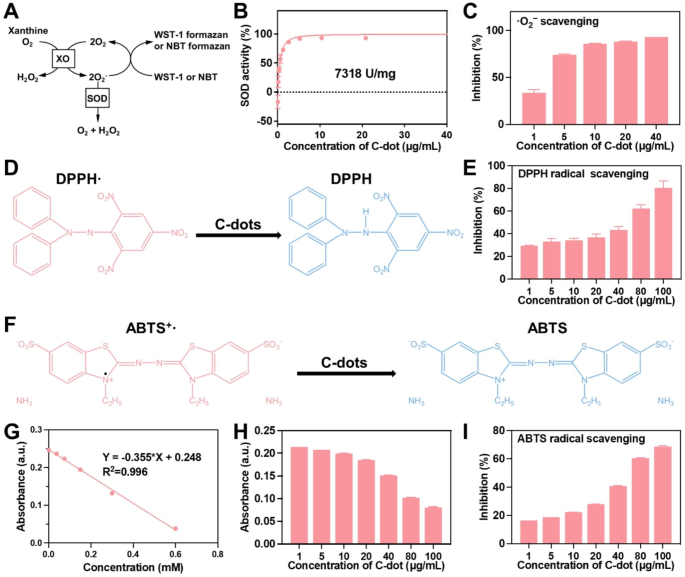
Characterization of C-dots
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs (Fig. S1A-C) confirmed that C-dots have been homogeneous and smaller than 5 nm in diameter. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (C 1 s) was performed to semi-quantitatively analyze the floor constructions of those C-dots (Fig. S1B). The XPS outcomes indicated the presence of C = C, C – O, C = O, and O – C = O on the floor of those C-dots. Enough C = C content material is important for C-dots with excessive SOD enzymatic exercise. Utilizing a available business SOD assay package (WST-1), the SOD-like exercise of the C-dots was assessed (Fig. 2A). As proven in Fig. 2B, the focus of C-dots elevated, the scavenging actions of O2− additionally elevated, suggesting that C-dots exhibit SOD-like exercise. C-dots have been proven to have a SOD-like exercise of 7318 U/mg. Subsequently, two consultant ROS, ·O2− and DPPH(Fig. 2D), have been chosen for investigating the scavenging actions of C-dots. Our outcomes demonstrated a concentration-dependent method in ROS scavenging actions. ~93% of the ·O2− was decomposed by 40 µg/mL of C-dots (Fig. 2C), and over 80% of ·OH was successfully eradicated by 100 µg/mL of C-dots (Fig. 2E). To verify the antioxidant properties of C-dots, the traditional ABTS radical assay was employed on the scavenging of free radicals(Fig. 2F). As proven in Fig. 2G and H, C-dots exhibited notable antioxidant traits, with their capacity to scavenge free radicals changing into extra pronounced because the focus of C-dots elevated. Within the meantime, Trolox, a naturally occurring antioxidant, was employed as a reference. Roughly 8 mmol/g was the decided radical scavenging exercise of C-dots. C-dots (100 µg/mL) scavenged over 68% of the free radicals, surpassing the bulk (Fig. 2I). Collectively, Our outcomes demonstrated that C-dots have wonderful antioxidant actions.
Enzymatic characterization of C-dots. (A) The antioxidant precept of the WST-1 and NBT assay. (B) The WST-1 package was used to evaluate the SOD-like exercise of C-dots. (C) The capability of C-dots to get rid of ·O2−. (D) The antioxidant precept of the DPPH assay. (E) The capability of C-dots to get rid of DPPH radicals. (F) The antioxidant precept of the ABTS assay. (G) A reference antioxidant commonplace curve (Trolox®). (H) The ABTS’s absorbance. (I) The power of C-dots to scavenge ABTS radicals
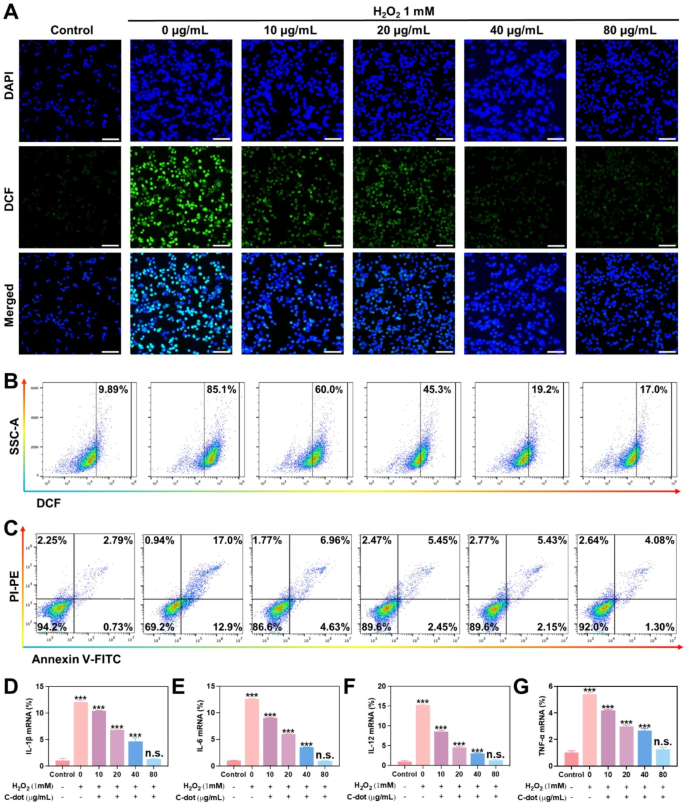
Anti-oxidative stress properties of C-dots in vitro
The influence of C-dots on oxidative stress was examined in L-02 cells. The induction of mobile oxidative stress harm to cells was via publicity to H2O2. Firstly, a prevention mannequin of antioxidant stress harm was induced with H2O2. The ROS indicator employed on this research was DCFH-DA. A robust inexperienced fluorescent sign was noticed after the addition of H2O2 in comparison with the management group with out H2O2 therapy (Fig. 3A). The intracellular fluorescence sign exhibited a big lower because the focus of C-dots elevated, starting from 0 to 80 µg/mL. In accordance with the circulation cytometry assay, the extent of intracellular ROS decreased because the focus of C-dots elevated in cells handled with numerous concentrations of C-dots (0–80 µg/mL), in distinction to cells stimulated with H2O2 (Fig. 3B and Supplementary Fig. 2A). This implies that C-dots possess the power to scavenge ROS. Subsequent, the power of C-dots to guard in opposition to mobile oxidative stress induced by H2O2 was assessed utilizing the usual MTT assay. H2O2 therapy was carried out leading to roughly 50% cell loss of life. Nonetheless, it was famous that cells pre-exposed to various quantities of C-dots (0–80 µg/mL) exhibited a concentration-dependent enhancement in cell viability, suggesting a attainable shielding impact in opposition to oxidative stress effectiveness (Supplementary Fig. 2B). To guage the potential preventive impact of C-dots on cell apoptosis, a cell apoptosis assay was carried out. The outcomes revealed that roughly 30% of cells underwent apoptosis following publicity to H2O2. Nonetheless, within the group pretreated with 80 µg/mL C-dots (Fig. 3C, Supplementary Fig. 2C), the proportion of apoptotic cells decreased considerably to six.28%. These findings counsel that C-dots possess protecting properties in opposition to hepatocyte harm. Subsequently, we assessed the influence of C-dots on inflammatory cytokines expression, resembling IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α. Particularly, we analyzed the expression of mRNAs related to numerous teams of inflammatory cytokines. On the similar time, we examined protein ranges in L-02 cells and RAW264.7 cells utilizing western blotting assays. In accordance with the findings introduced in Fig. 3D-G and Supplementary Fig. S2D-E, the H2O2-induced group exhibited a notable elevation within the ranges of inflammatory cytokines. In distinction, when the H2O2-induced group was pre-treated with various quantities of C-dots (0–80 µg/mL), the inflammatory cytokines decreased progressively, ultimately reaching a variety thought-about to be inside regular ranges.
Antioxidative stress properties of C-dots in vitro. (A) L-02 cells have been uncovered to totally different therapy situations after which stained with consultant ROS (inexperienced fluorescence) and nuclear (blue fluorescence) markers. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) The circulation cytometry outcomes present the degrees of ROS in L-02 cells underneath numerous therapy situations. (C) The circulation cytometry evaluation yielded quantitative information on the distribution of cell apoptosis and necrosis in L-02 cells subjected to numerous therapy situations. The mRNA ranges of IL-1β (D), IL-6 (E), IL-12 (F), TNF-α (G) have been assessed to find out their relative expression as inflammatory cytokines
Moreover, a therapeutic mannequin of antioxidant stress harm was additionally induced with H2O2. Significantly sturdy inexperienced fluorescence was noticed after H2O2 stimulation (Supplementary Fig. 3A). In distinction, the extent of ROS noticeably decreased after the administration of C-dots to the cells. This development was additional corroborated by conducting a quantitative evaluation of ROS ranges utilizing circulation cytometry (Supplementary Fig. 3B, and 4 A). The MTT evaluation outcomes indicated that C-dots had the aptitude to safeguard the cells from hurt brought on by oxidative stress (Supplementary Fig. 4B). To look at the consequences of C-dots on cell apoptosis and necrosis brought on by H2O2, we carried out quantitative evaluation using circulation cytometry. In Supplementary Fig. 3C, and 4 C, additional proof of the cytoprotective properties of C-dots on the mobile stage was supplied by the truth that the proportions of apoptotic and necrotic cells introduced on by H2O2 therapy considerably decreased when C-dots have been added. Moreover, we assessed the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines throughout the cells. In accordance with qPCR outcomes, a big elevation in IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α ranges upon stimulation with H2O2 (Supplementary Fig. 3D-G), which aligns with the outcomes of a earlier assay. Conversely, the presence of C-dot exhibited a exceptional inhibition of inflammatory cytokines. In conclusion, C-dots have the power to efficiently suppress cell apoptosis and considerably lower heightened ranges of inflammatory cytokines. The optimistic impacts aided within the lower of oxidative stress.
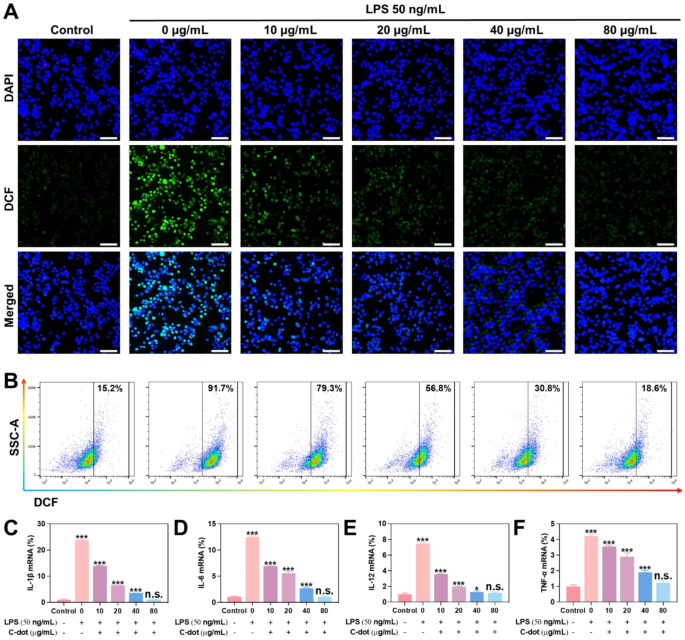
Anti-inflammatory properties of C-dots in vitro
The consequences of C-dots on irritation have been examined in L-02 cells. To create an intracellular irritation mannequin, we subjected cells to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) therapy. Firstly, an in vitro mannequin of the prevention of inflammatory responses was induced with LPS. The degrees of ROS have been evaluated via fluorescence microscopy and circulation cytometry (Fig. 4A and B). The findings indicated that the ROS ranges have been considerably decreased following LPS induction when pretreated with various concentrations (0–80 µg/mL) of C-dots. The circulation cytometry assay demonstrated that the extent of intracellular ROS decreased because the focus of C-dots elevated in cells handled with numerous concentrations of C-dots (0–80 µg/mL) compared to cells stimulated with LPS (Supplementary Fig. 5A). So as to achieve a deeper comprehend the anti-inflammatory properties of C-dots, we examined the impact on the concentrations of varied essential inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-α). Particularly, we analyzed the expression of mRNAs related to numerous teams of inflammatory cytokines. On the similar time, we examined the protein ranges of varied essential inflammatory cytokines in L-02 cells and RAW264.7 cells utilizing Western Blotting assays. In accordance with the findings introduced in Fig. 4C-F and Supplementary Fig. 5B-C, the LPS-induced group exhibited a notable elevation within the ranges of inflammatory cytokines. Curiously, when the LPS-induced group was pretreated with numerous doses of C-dots (0–80 µg/mL), the inflammatory cytokines decreased progressively, ultimately reaching a variety thought-about to be inside regular ranges.
Anti-inflammatory properties of C-dots in vitro. (A) L-02 cells have been uncovered to totally different therapy situations after which stained with consultant ROS (inexperienced fluorescence) and nuclear (blue fluorescence) markers. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) The circulation cytometry outcomes present the degrees of ROS in L-02 cells underneath numerous therapy situations. The mRNA ranges of IL-1β (C), IL-6 (D), IL-12(E), TNF-α (F) have been assessed to find out their relative expression as inflammatory cytokines
Additional, we induced an in vitro mannequin for the therapy of inflammatory responses with LPS. Appreciable depth of inexperienced fluorescence was noticed following LPS stimulation (Supplementary Fig. 6A). After the cells have been handled with C-dots, it was evident that the ROS stage considerably decreased as compared. Therefore, it was demonstrated that C-dots have the power to significantly lower the ROS stage. The development was additional confirmed by circulation cytometry, which concerned quantitative evaluation of ROS ranges (Supplementary Fig. 6B and Fig. 7). Subsequently, we measured the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines throughout the mobile surroundings. Stimulation of cells with LPS led to a big rise in ranges of inflammatory cytokines, as indicated by qPCR findings (Supplementary Fig. 6C-F), which is per the findings of a earlier assay. Then again, inflammatory cytokines have been remarkably inhibited by C-dots. It demonstrated the numerous anti-inflammatory properties of C-dots. In conclusion, C-dots considerably suppressed the manufacturing of inflammatory cytokines. The research showcased the noteworthy anti-inflammatory traits of C-dots. To summarize, C-dots have the power to considerably lower heightened ranges of inflammatory cytokines. The optimistic impacts aided within the lower of inflammatory reactions. In laboratory settings, C-dots exhibit a notable protecting impact on liver cell harm by successfully mitigating oxidative stress and irritation.
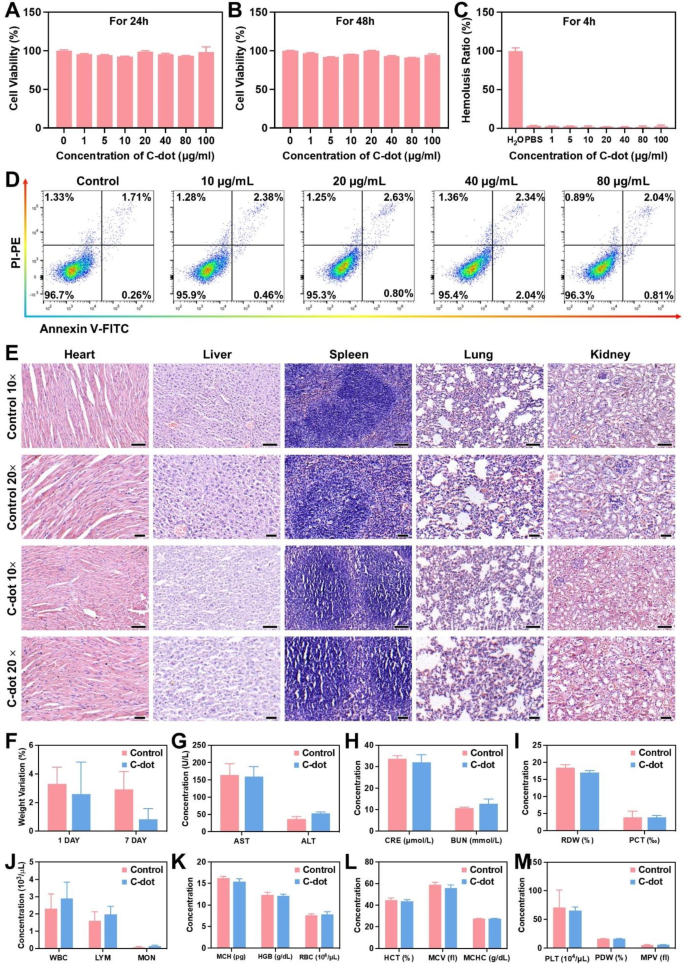
Biocompatibility of C-dots
Contemplating the essential position of biocompatibility within the attainable scientific makes use of of nanomaterials, we assessed the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of C-dots. Initially, we uncovered L-02 cells to C-dots and incubated them for twenty-four and 48 h, respectively. Subsequently, we assessed the cell viability utilizing the MTT assay. C-dots with totally different concentrations of (0-100 µg/mL) confirmed negligible cytotoxicity to L-02 cells (Fig. 5A and B). The hemolysis price of nanomaterials is essential and it should stay under 5% to ensure security when administering them intravenously [27]. A hemolysis assay was performed on C-dots, and the findings indicated minimal hemolysis of C-dots (Fig. 5C). We incubated totally different concentrations of C-dots (0-100 µg/mL) with cells for twenty-four h. Movement cytometric assays have been performed, revealing that the presence of C-dots didn’t exhibit any toxicity in direction of the cells and didn’t influence cell development (Fig. 5D).
Biocompatibility of C-dots. The viability of L-02 cells was assessed after incubation with C-dots for twenty-four h (A) and 48 h (B). (C) The ratio of hemolysis within the subgroups. (D) Distribution of cell apoptosis and necrosis in L-02 cells as indicated by FACS outcomes. (E) Evaluation of the toxicity of C-dots to important organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney) in vivo, performed 24 h following intravenous injection. Scale bar: 50 μm. (F) Modifications in weight of typical mice 24 h after being administered with C-dots. (G) Ranges of liver perform markers, resembling AST and ALT, within the serum. (H) Serum ranges of BUN and CRE function indicators of kidney perform. (I-M) Blood values in mice that have been both intravenously handled with C-dots or regular animals (the management group), 24 h after injection
Moreover, throughout our experiments, we administered C-dots at a therapeutic dosage of 1 mg/kg. Subsequently, all of our in vivo biocompatibility analysis experiments have been carried out at this focus. Afterwards, we examined the consequences of C-dots on the blood chemistry and histopathology of main organs in wholesome mice to be able to uncover their compatibility inside a dwelling organism. H&E staining of main organs 1 day after C-dots injection confirmed no apparent indicators of injury, indicating that C-dots have been biocompatibility (Fig. 5E). Then, as proven in Fig. 5F, the mice injected with C-dots confirmed an identical diploma of physique weight change because the management group, there was no important distinction between the teams. In accordance with the serum biochemistry evaluation’s findings, the C-dots therapy group’s serum concentrations of renal perform indicators (BUN and CRE) and liver perform indicators (AST and ALT) have been similar to these within the management group. This means that C-dots exhibit advantageous compatibility with each the liver and kidney (Fig. 5G, H). In distinction, the whole blood panel evaluation ends in mice didn’t exhibit any statistically important variations in comparison with the management group (Fig. 5I-M).
Moreover, we performed an examination of the in vivo toxicity of C-dots that had amassed within the principal organs subsequent to the repeated each day administration of C-dots over a interval of seven consecutive days. The guts, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney confirmed no indicators of necrosis, congestion, or hemorrhage after the repeated intravenous injection, in keeping with our observations (Supplementary Fig. 8A). Moreover, the outcomes of the analyses of the serum biochemistry and the entire blood panel confirmed additional help for the dearth of detectable toxicity linked to C-dots (Supplementary Fig. 8B-H). All of the findings constantly indicated that the synthesized C-dots demonstrated minimal in vivo toxicity, each within the quick and long run.
Protecting results of C-dots on HIRI in vivo
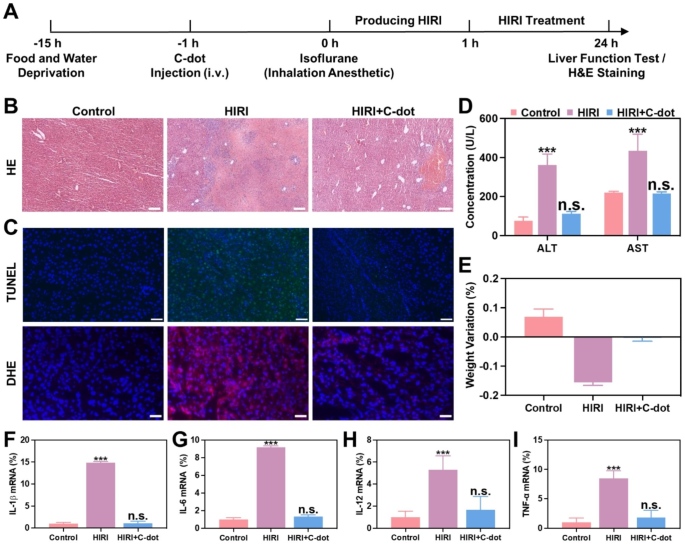
The present investigation seeks to look at the attainable safeguarding influence of C-dots in a mouse mannequin of HIRI, increasing on prior discoveries regarding their in vitro capacity to counteract oxidative stress and cut back irritation. As a contributory issue within the pathology of HIRI, extreme oxidative stress, and extreme irritation are properly acknowledged [28]. Primarily based on our earlier research [26], it was noticed that C-dots exhibited important accumulation throughout the mitochondria. This indicated that C-dots can overcome the harm to cell and mitochondrial membranes by excessive ranges of ROS, thus focusing on mitochondria. Moreover, two hours following the injection of C-dots, the liver and kidney exhibited the best accumulation of C-dots, whereas smaller portions have been discovered within the spleen and lung. In accordance with the Fig. 6A, BALB/c mice have been administered C-dots for a period of 1 h previous to the clamping of porta hepatis. After experiencing 1 h of ischemia and subsequent reperfusion, blood and liver samples have been obtained, and liver features have been subsequently analyzed on the 24-hour mark post-surgery.
Protecting results of C-dots on HIRI in vivo. (A) The diagram depicts the setup and plan for treating HIRI mice. (B) H&E staining was carried out on liver tissues. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Liver tissues have been subjected to TUNEL assay and Dihydroethidium (DHE) staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) After numerous remedies, the degrees of ALT and AST within the serum of HIRI mice have been measured at 24 h. (E) The change in weight of HIRI mice 24 h after being administered with C-dots. Expression ranges of mRNAs for cytokines of IL-1β (F), IL-6 (G), IL-12 (H), TNF-α (I) mRNA have been comparatively analyzed
The analysis of therapeutic effectiveness by conducting hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on liver tissues of HIRI mice after pretreatment with C-dots (Fig. 6B and Supplementary Fig. 9). As anticipated, the PBS-treated HIRI group exhibited important hepatocyte necrosis and cytolysis inside 24 h. Subsequently, we recognized the best dosage of C-dots. Within the HIRI mouse mannequin, the world of hepatocyte necrosis and cytolysis was minimal when administered with 1 mg/kg of C-dots. When the dose of C-dots is lower than 1 mg/kg, it could not exert sufficient nanozymes exercise to get rid of ischemia. Curiously, when the dose of C-dots is greater than 1 mg/kg, it could trigger additional liver harm as a result of manufacturing of poisonous H2O2 within the catalytic course of. Then, fluorescence imaging was carried out on liver tissue. We used dihydroethidium (DHE), a purple fluorescent probe particular for ·O2−, to evaluate the power of C-dots to scavenge ·O2−. DHE staining outcomes confirmed a big discount in ROS ranges in liver tissue after therapy with C-dots. In the meantime, the TUNEL evaluation outcomes indicated a notable lower in cell loss of life when pretreated with C-dots (Fig. 6C).
So as to additional consider the influence of C-dots on therapy, ALT and AST ranges are utilized as markers for liver harm. The HIRI mice group exhibited a notable rise in ALT and AST ranges, suggesting the presence of intensive liver harm when in comparison with the management group. The group of HIRI mice handled with C-dots had considerably decrease ranges of ALT and AST in comparison with the group of HIRI mice, after pretreatment with C-dots (Fig. 6D). Moreover, HIRI mice encountered notable discount in weight inside 24 h, whereas HIRI mice that acquired prior therapy with C-dots confirmed minimal alteration in weight (Fig. 6E).
Subsequently, we examined the consequences of C-dots on inflammatory cytokines in HIRI mice. As proven in Fig. 6F-I, within the HIRI group, the degrees of those inflammatory cytokines have been markedly elevated in comparison with the management group, whereas within the C-dots pretreatment group, they decreased to a comparatively regular vary. In conclusion, C-dot exerted a distinguished protecting impact on HIRI mice.
Therapeutic mechanisms of C-dots on HIRI
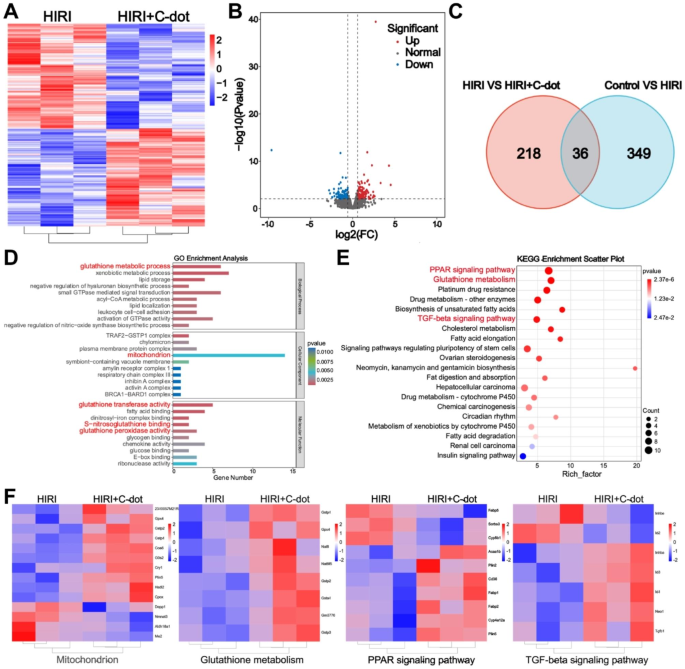
So as to present a extra complete understanding of the potential therapeutic mechanisms, transcriptomic evaluation was performed within the subsequent experiments. There have been 385 genes considerably totally different between HIRI and controls utilizing DESeq2_edgeR evaluation, demonstrating the success of the HIRI mannequin (Supplementary Fig. 10). A complete of 254 genes exhibited differential expression between the HIRI and C-dots therapy teams (Fig. 7A). The volcano plot illustrated that there have been 122 genes that exhibited important upregulation and 132 genes that exhibited important downregulation in differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (Fig. 7B). Concurrently, as proven in Fig. 7C, within the Venn diagram, it was evident that the management, HIRI, and C-dots therapy teams had 36 genetic alterations in widespread, indicating the useful therapeutic influence of C-dots on HIRI mice. In accordance with the obtained sequencing outcomes, we performed gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses as properly. Initially, primarily based on GO evaluation, the outcomes verify that there existed modifications in glutathione metabolism and mitochondria-related genes, suggesting that the C-dots probably perform because the position of regulating the liver inflammatory community within the therapy of HIRI (Fig. 7D). Primarily based on KEGG evaluation, the highest 20 pathways are listed individually in Fig. 7E, and it was noticed that there existed modifications within the PPAR signaling pathway and the TGF-β signaling pathway, which additional confirmed that C-dots therapy regulated the liver inflammatory community and inhibited apoptosis. In accordance with a earlier research [26], C-dots may overcome the harm to cell and mitochondrial membranes by excessive ranges of ROS, thus focusing on mitochondria and ultimately accumulating in mitochondria. It has additionally been proven that mitochondrial metabolism is intimately linked to inflammatory responses. Subsequently, mitochondria-related genes are extremely related to the therapeutic mechanism of C-dots (Fig. 7F). Notably, glutathione regulates cell proliferation and immune responses [29]. PPARs, as a bunch of nuclear receptors, play an important position within the regulation of irritation. As well as, a direct correlation was additionally noticed between the expression of TGF-β and the inflammatory responses [30]. Subsequently, the glutathione metabolism, PPAR and TGF-β signaling pathway have been proven to be extremely related to the therapeutic mechanism of C-dots (Fig. 7F). We additionally validated the important thing genes of those three pathways on the mRNA stage (Fig. S11A-C). The outcomes confirmed the identical development because the sequencing outcomes. From the above proof and outcomes, the potential therapeutic mechanisms of C-dots therapy for HIRI embody regulating the liver inflammatory community and inhibiting apoptosis.
Therapeutic mechanisms of C-dots on HIRI. (A) Warmth maps displaying the expression ranges of noteworthy genes following C-dots administration (fold change ≥ 2 and P < 0.01). (B) The volcano plots displayed the genes that have been upregulated and downregulated by C-dots. (C) The Venn diagram of RNA sequencing evaluation of the complete transcriptome revealed variations in gene expression between the HIRI group and the management group, in addition to between the C-dots group and the HIRI group. (D) Evaluation of gene ontology (GO) together with Molecular Perform (MF), Organic Course of (BP), and Mobile Elements (CC). (E) Evaluation of enrichment in KEGG pathways. Displayed have been the highest 20 pathways that exhibited the best stage of enrichment. (F) After therapy with C-dots, warmth maps displaying important genes associated to the mitochondrion, glutathione metabolism, PPAR signaling pathway, and TGF-β signaling pathway have been generated