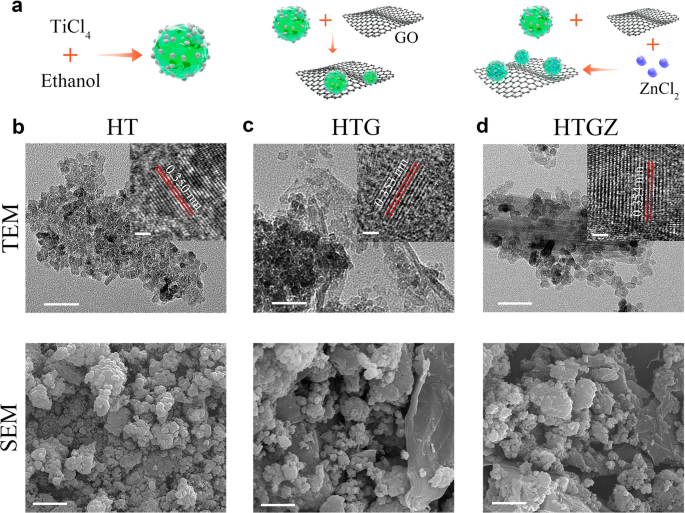
Morphology and construction characterization
Determine 1a schematically illustrates the preparation process of the HTGZ nano-system. HT was initially ready from TiCl4 and ethanol utilizing a nonaqueous sol–gel technique. Subsequently, graphene oxide and ZnCl2 have been added into HT to supply HTG and HTGZ, respectively.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) photographs revealed that HT was composed of agglomerated particles (Fig. 1b). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs confirmed compact nanoparticles with the dimensions of roughly 10 nm. A lattice spacing of 0.350 nm was noticed utilizing high-resolution TEM (HR-TEM), which corresponded to the (101) crystal aircraft of anatase TiO2. TEM picture of HTG confirmed some particles embedded within the wrinkled thin-layers, demonstrating the profitable mixture of rGO (Fig. 1c). Power dispersive spectroscopy (EDS)-mapping photographs additional manifested the homogeneous distributions of C, N, O, and Ti parts throughout the entire HTG (Extra file 1: Fig. S1). The morphology of HTGZ was much like that of HTG (Fig. 1d), and the fundamental mapping confirmed the efficiently Zn doping with the composition ratio of two.6 wt% (Extra file 1: Fig. S2). HR-TEM evaluation of HTGZ revealed a lattice fringe with a calculated spacing of 0.354 nm, indicating a definite lattice distortion of TiO2 attributed to the introduction of Zn [26]. Moreover, X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of HT displayed attribute diffraction peaks of anatase TiO2 (Fig. 2a), which remained unaffected by way of place and intensities of HTG and HTGZ, suggesting that the crystal construction of TiO2 was unaltered by the presence of rGO and Zn. Raman spectroscopy was employed to look at the vibration modes of rGO, revealing attribute peaks at roughly 151, 391, 512, and 636 cm−1 that have been in keeping with TiO2 options. The peaks at 1370 cm−1 and 1581 cm-1 represented the rGO in HTG (Fig. 2b). These outcomes preliminarily indicated that HTGZ had been efficiently synthesized.
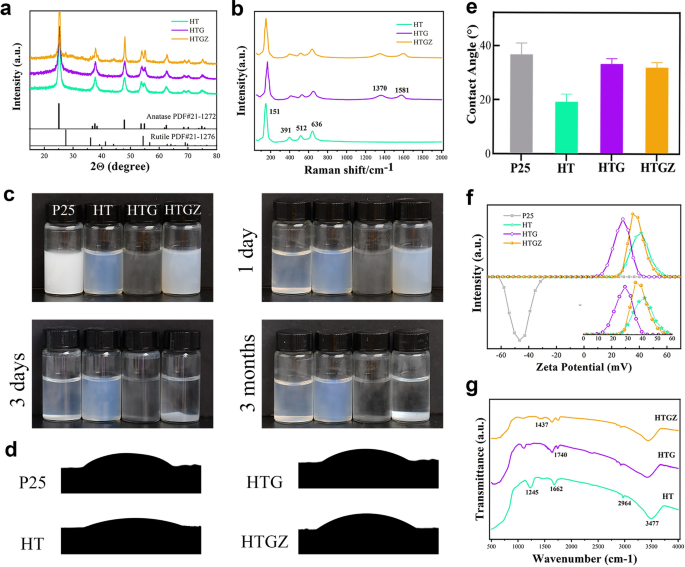
Characterization of nanomaterials. a XRD patterns of nanomaterials. b Raman spectra of nanomaterials. c Pictures of nanomaterials with concentrations of 1% (w/v) left to relaxation for 1 day, 3 days and three months, respectively. d, e Contact angle take a look at for nanomaterials. The information are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). f The zeta potential of nanomaterials. g FTIR spectra of nanomaterials
As proven in Fig. 2c. The P25 (business TiO2) nanoparticle, at a suspension focus of 0.1% (w/v), precipitated fully after 1 d of relaxation with none stirring or disturbance, whereas suspensions of HTG and HTGZ remained steady for roughly 3 d. Notably, HT exhibited long-term excessive dispersibility for as much as 3 months. Erratically dispersed particles attributable to sedimentation lower the organic operate of nano-systems dramatically; subsequently, the excessive dispersibility of the nano-system is favorable for organic functions. Contact angles have been decided to judge the hydrophilicity of the nanomaterials (Fig. 2d, e). HT had a smaller water contact angle (31.5°) than that of P25 (37.5°). Nonetheless, the contact angles of HTG and HTGZ elevated to 36.1° and 34.8°, respectively, which will be ascribed to the addition of hydrophobic graphene. Not like P25 (− 46.4 mV), HT, HTG, and HTGZ exhibited constructive zeta potentials of 28.6, 41.2, and 35.7 mV, respectively (Fig. 2f). The constructive cost of nanomaterials facilitates adherence to bacterial surfaces with a destructive cost. A excessive constructive zeta potential additionally reduces aggregation and maintains bodily stability [27]. Based mostly on these findings, the mix of the favorable hydrophilicity, dispersibility, and constructive potential synergistically promote the whole and tight interplay between HTGZ and cells, probably resulting in enhanced antibacterial results and the dependable analysis of its organic exercise.
Fourier rework infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) have been additional used to discover the chemical compositions of the nanomaterials. The FTIR spectrum of HT revealed C-H stretching vibrations at 2926 cm−1 attributed to the hydrocarbon moiety. Peaks at 1715 cm−1 and 1104 cm−1 corresponded to C=O in oxygenated practical teams and C–O teams, respectively (Fig. 2g). These outcomes urged that carbon oxide compounds have been generated in HT throughout the carbonization of ethanol [28]. The peaks at roughly 1635 cm−1 in HTG and 1652 cm−1 in HTGZ corresponded to the stretching vibrations of C=C in rGO. XPS survey spectra (Extra file 1: Fig. S3a) indicated related peaks for C, Ti, and O parts in HTG and HTGZ. The Ti 2p peaks in HT could possibly be divided into Ti 2p1/2 (464.3 eV) and Ti 2p3/2 (458.6 eV) of Ti4+ in TiO2 (Extra file 1: Fig. S3b). The dominant peak at 529.8 eV within the O 1s was associated to the lattice oxygen in TiO2, and the opposite peak urged the presence of different oxygenated compounds (Extra file 1: Fig. S3c) [29]. Curve becoming of the C 1s spectra resulted in three peaks at 284.4, 285.6, and 288.9 eV (Extra file 1: Fig. S3d), the place the peaks at 285.6 and 288.9 eV have been assigned to the carbon certain to oxygen (C–O and C=O), and the extra peak presumably originated from carbon on the nanoparticle floor.. These outcomes have been in keeping with the FTIR outcomes, confirming that carbonaceous species and oxygenated practical teams existed on the floor of HT, which resulted in a excessive floor potential, prevented nanocrystal agglomeration, and finally led to glorious hydrophilicity and dispersibility. Within the HTG spectrum, the C=C bond within the rGO could have contributed to the considerably elevated peak at 284.7 eV (Extra file 1: Fig. S3e). Concerning HTGZ, two peaks with binding energies of 1022.2 and 1045.2 eV represented Zn 2p1/2 and Zn 2p3/2, demonstrated that Zn was bivalent (Extra file 1: Fig. S3f). Outcomes of chemical composition evaluation for nanomaterials additional demonstrated that the HTGZ nano-system had been efficiently synthesized as we designed.
Photodynamic properties and mechanism
To judge the PDA exercise of the nanomaterials, the corresponding photodynamic efficiency have been systematically evaluated. The HTGZ exhibited one of the best degradation effectivity on RhB underneath seen mild (Fig. 3a), indicating its superior photocatalytic exercise. Equally, as proven in Fig. 3b, the upper fluorescence depth of the HTGZ indicated higher ROS manufacturing than these of P25 and different distinction samples. Moreover, electron spin resonance spectra revealed that ·OH and ·O2− manufacturing within the HTGZ was drastically enhanced in comparison with different contrasts (Fig. 3c, d). The outcomes present direct proof that HTGZ displays an excellent photodynamic efficiency underneath seen mild.
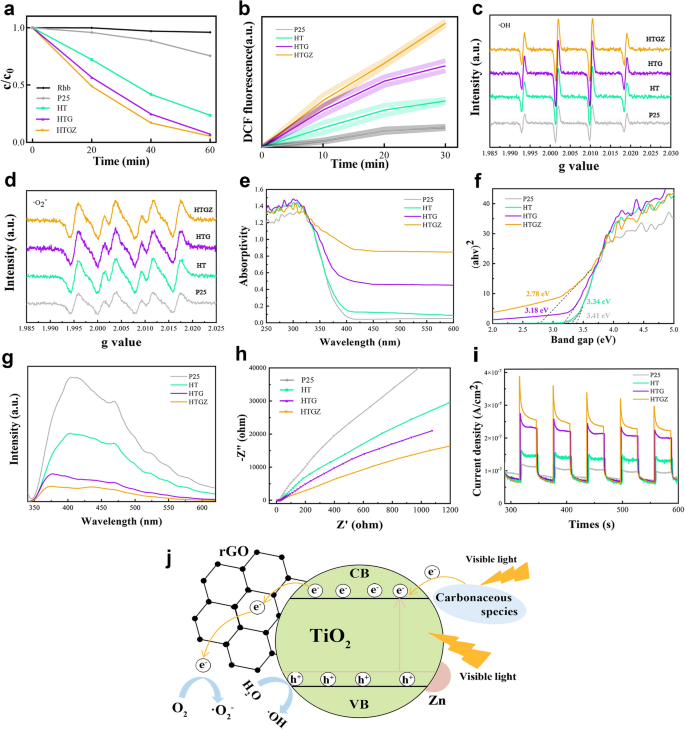
Photodynamic properties of nanomaterials. a Absorbance of RhB self-degradation within the absence of sunshine, in addition to underneath seen mild irradiation for nanomaterials. b ROS manufacturing of nanomaterials underneath seen mild irradiation. c, d ESR for ·OH and ·O2− technology of nanomaterials. e UV–vis–NIR absorption curves of nanomaterials. f Bandgap of nanomaterials. g PL spectra of nanomaterials. h Electrochemical impedance values of nanomaterials underneath seen mild irradiation. i Photocurrent curves of nanomaterials. j Proposed schematic diagram of HTGZ for ROS manufacturing
To elucidate the mechanism of the improved photodynamic efficiency, UV–vis–near-infrared and photoluminescence (PL) spectra have been carried out. The sunshine absorption of P25 was poor within the vary 300–700 nm, and the enhancement of HT was additionally restricted. Nonetheless, a redshift within the absorption edge occurred and the next absorption charge was clearly noticed for HTG and HTGZ (Fig. 3e). Correspondingly, the band hole steadily lowered from 3.41 to 2.78 eV, main to raised absorption effectivity within the seen mild vary (Fig. 3f). The earlier research indicated {that a} vital discount of band hole could enhance the photogeneration of electron–gap pair [30]. Due to this fact, the HTGZ facilitates the enhancement of the sunshine absorption capability and the separation effectivity of electron-hole pairs, thus could lead to enhanced photocatalytic efficiency. PL spectra can be utilized to detect the separation effectivity of photogenerated carriers primarily based on the fluorescence depth. Stronger fluorescence signifies that electrons and holes usually tend to be compounded [31]. As proven in Fig. 3g, the as-prepared TiO2-based nanomaterials exhibit weaker fluorescence and lowered recombination effectivity in comparison with P25. Later, photocurrent and electrochemical impedance measurements have been carried out to probe the electron-hole pair separation skill. The Nyquist plot from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (Fig. 3h) reveals that the HTGZ possess the bottom resistance owing to the smaller circle diameter than these of distinction samples, indicating the quickest cost switch effectivity underneath seen mild irradiation. Moreover, the improved photocurrent density of HTGZ (Fig. 3i) was a lot increased than these of distinction samples, demonstrates an elevated photogenerated provider separation [32]. Basically, the accelerated electron switch and plentiful oxygen provide are thought-about as essential elements to enhance photodynamic efficiency [33]. The above outcomes affirm that the HTGZ displays higher ROS manufacturing, quick electron switch, and a decreased power barrier, thus resulting in a quicker photodynamic response.
The improved photodynamic mechanism of HTGZ is illustrated in Fig. 3j. On the one hand, the electrons transferred to the conduction band of TiO2 via the sensitization of the carbonaceous species on the floor of HTGZ underneath seen mild irradiation. The doping of Zn2+ introduces an impurity power degree and extra defects. A narrower bandgap might enhance the optical absorption to supply extra cost carriers. Then again, rGO can act as an acceptor in electron switch that receiving photogenerated electrons on TiO2, thereby reaching extra environment friendly separation of photogenerated electron–gap pairs and restraining their recombination. These elements synergistically enhance the ROS yields and promote the photodynamic functionality of HTGZ underneath seen mild.
Photocatalytic antibacterial exercise in vitro
Gram-positive cocci (Streptococcus mutans) and gram-negative coliform micro organism (Escherichia coli) have been used to find out antibacterial actions. First, the bacterial development curve at an optical density (OD) of 600 nm was measured after seen mild irradiation for 15 min (Fig. 4a, Extra file 1: Fig. S4a). The outcomes confirmed that the nanomaterials had a big inhibitory impact on each forms of micro organism. The relative bacterial viability was detected on the colony-forming unit (CFU) counts. 200 µg mL−1 HT successfully killed S. mutans at an antibacterial charge of 70.26%. Owing to the elevated manufacturing of ROS, the speed of HTG and HTGZ reached 87.64% and 98.25%, respectively. For E. coli, the antibacterial charge was 61.23%, 78.17%, and 99.15% for HT, HTG, and HTGZ, respectively (Fig. 4b). The pictures of bacterial colonies have been proven in Fig. 4c. As well as, the lack of bacterial viability occurred in a concentration- and time-dependent method (Extra file 1: Fig. S4b). Apparently, the HTGZ exhibited stronger antibacterial results in opposition to S. mutans than in opposition to E. coli. That is most likely as a result of gram-negative micro organism with dense outer membranes comprising lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins present sturdy PDA resistance [34].
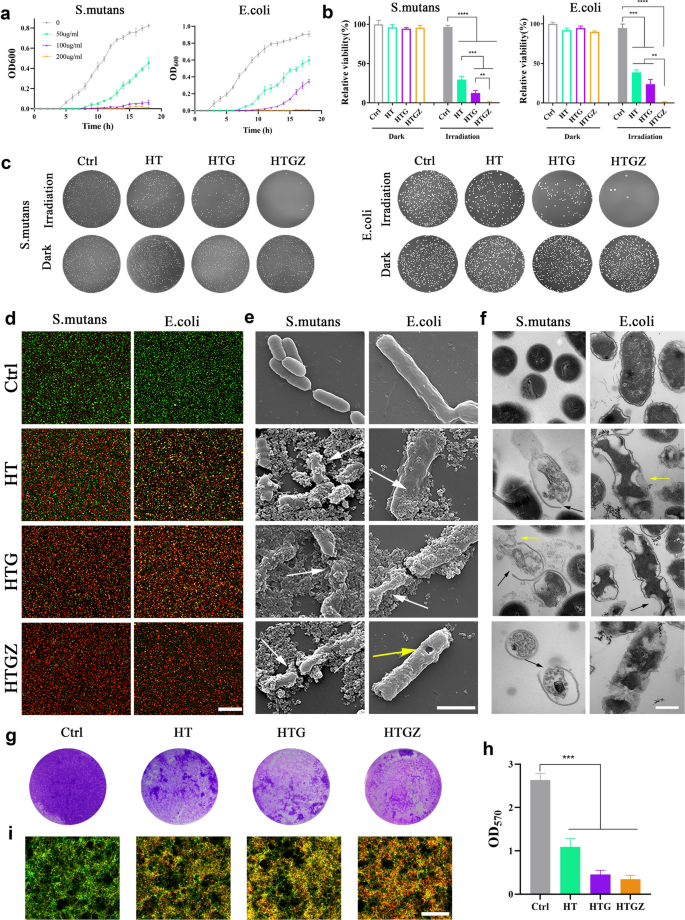
In vitro antibacterial results of nanomaterials towards laboratory micro organism strains of S. mutans and E. coli. a The expansion curve of micro organism after therapy with 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials for 15 min. b Antibacterial ratios of 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials in opposition to micro organism for 15 min. c Plate pictures of 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials in opposition to micro organism for 15 min. d Stay/useless staining photographs of micro organism after therapy with 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials underneath 15 min of irradiation. Scale bars are 20 μm. e SEM photographs of micro organism after therapy with 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials underneath 15 min of irradiation. Scale bars are 1 μm. f TEM photographs of micro organism after therapy with 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials underneath 15 min of irradiation. Scale bars are 300 μm. g, h Pictures of crystal-violet-stained S. mutans biofilms with totally different remedies and its quantitative evaluation. i Stay/useless staining photographs of S. mutans biofilms after therapy with 200 µg mL−1 nanomaterials underneath 15 min of irradiation. Scale bars are 20 μm. The information are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001
The dwell/useless bacterial fluorescence staining assay outcomes have been in accordance with the CFU assays. Vibrant inexperienced fluorescence indicated micro organism with intact membranes within the management group, whereas pink fluorescence revealed broken cells within the therapy teams (Fig. 4d).
SEM and TEM photographs have been used to visualise the impact of nanomaterials on the morphological modifications in micro organism. SEM photographs reveal that micro organism after therapy exhibited obvious wrinkling of the cell partitions (white arrows), damaged form, and visual perforations (yellow arrow) As well as, the nanomaterials tightly adhered to the micro organism due to their hydrophilicity, which ensured that their PDA capability was efficient (Fig. 4e). TEM photographs clearly show the micro organism within the handled group confirmed distorted or damaged membranes/cell partitions (black arrows), and the intracellular materials dispersed with outflow of the cytoplasm (yellow arrow) (Fig. 4f). It may be speculated that the PDA properties of nanomaterials are seemingly attributed to the direct harm to the bacterial buildings.
The degrees of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), as an important power molecule for microorganisms, decreased considerably, suggesting a stronger inhibitory impact on the viability of micro organism (Extra file 1: Fig. S5a). As well as, when the bacterial membrane/partitions have been damaged, intracellular protein leaked from cells. The rise of extracellular protein focus indicating that structural damages (Extra file 1: Fig. S5b).
In some circumstances, micro organism kind an ordered and defensive biofilm that may stop antibiotic penetration, lowering the bactericidal skill of the antibiotics [35]. Thus, the power of nanomaterials to inhibit S. mutans biofilm formation was investigated utilizing crystal violet staining. Within the therapy group, the staining of the biofilm was incomplete and light-weight purple, indicating that biofilm formation was considerably inhibited; this was quantitatively confirmed by the OD570 worth (Fig. 4g, h). Furthermore, dwell/useless assays have been used to detect the power of nanomaterials to disrupt mature biofilms. The rise in pink fluorescence within the therapy teams indicated that the nanomaterials might successfully remove biofilms, which can also be in keeping with the CFU outcomes (Fig. 4i).
These outcomes point out that nanomaterials have good antibacterial properties, presumably as a result of skill of ROS to disrupt bacterial membranes/cell partitions and buildings whereas additionally interfering with metabolic actions. As well as, rGO not solely will increase ROS manufacturing, but in addition has sure antibacterial properties. Sharp edge-mediated slicing and mechanical wrapping can harm the micro organism, which additionally contributes to the wonderful antibacterial skill of HTGZ [36].
As a result of glorious antibacterial potential of GO, there have been many studies on GO-TiO2 photodynamic antibacterial composites [37, 38]. The mixture of carbon and Zn2+ doping permit HTGZ to have glorious antibacterial exercise even underneath low energy irradiation (300 mWcm−2) and quick motion instances (15 min). As well as, as a result of antibacterial skill of Ag+, GO–TiO2–Ag composites have improved PDA results [39]. Guo reported that 100 mg L−1 of this materials might scale back E. coli survival to 12.2% in 10 min [40]. In distinction, HTGZ has decrease organic toxicity and the power to advertise wound therapeutic as a result of operate of Zn2+, thus having higher organic software prospects.
Exploration of antibacterial mechanism
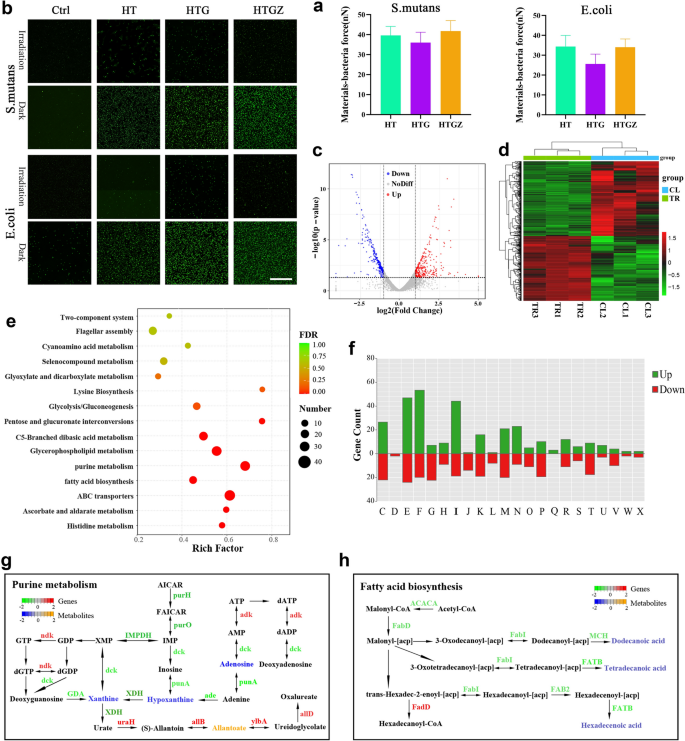
First, we examined the interplay power between micro organism and supplies by atomic power microscopy (AFM) [41]. The outcomes confirmed that the power was above 25 nN for E. coli, and reached about 40 nN for S. mutans (Fig. 5a, Extra file 1: Fig. S6). The nanomaterials with constructive cost can simply obtain shut integration with the negatively charged bacterial cells, thus finally enhancing bacterial inactivation effectivity.
Exploration of antibacterial mechanisms of nanomaterials primarily based on PDA. a Quantitative evaluation of the interplay power between nanomaterials and bacterial cells examined by AFM. The information is introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). b ROS statement of micro organism incubated with nanomaterials with or with out seen mild irradiation. Scale bars are 50 μm. c Volcano plots recognized the DEGs for CL vs. TR. d Heatmap of the DEGs. e KEGG enrichment for the DEGs of CL versus TR. f DEGs in CL versus TR by the COG practical classes. g, h Built-in purine metabolism and fatty acid biosynthesis pathways evaluation of metabolome and transcriptome information. Gene expression with vital variations (P < 0.05) and distinct metabolic profiles have been quantified as log2Foldchange
We speculate that the antimicrobial impact of the nanomaterials was primarily as a result of great amount of ROS. To confirm this concept, the DCFH-DA probe was used to detect intracellular ROS ranges [5]. As depicted in Fig. 5b, enhanced fluorescence depth was noticed in nanomaterial-incubated bacterial cells underneath illumination.
Accrued intracellular ROS can overwhelm the bacterial antioxidant protection system and induce extreme harm to numerous mobile substances essential for regular mobile physiological actions. To additional consider the modifications in micro organism throughout this course of, we carried out transcriptomic and untargeted metabolic analyses of E. coli. Principal part evaluation (PCA) confirmed that gene expression within the HTGZ-treated (TR) group was effectively distinguished from that within the management (CL) group (Extra file 1: Fig. S7a). In complete, 566 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) have been recognized as proven within the volcano plot and warmth map (Fig. 5c, d). The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) practical enrichment evaluation revealed that purine metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, glycolysis, amino acid metabolism and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter household pathways have been considerably affected (Fig. 5e). Based on the clusters of orthologous teams (COGs) evaluation, the genes concerned in power manufacturing and conversion (C), amino acid transport and metabolism (E), nucleotide transport and metabolism (F), and lipid transport and metabolism (I) have been considerably modified (Fig. 5f). Branched-chain amino acids are mandatory for the synthesis of membrane fatty acids [42], subsequently, modifications in lipid metabolism could end result from the disruption of the cell membrane by ROS. As a transport ATPase on the cell membrane, ABC transporters have been additionally affected [43]. As well as, extreme ROS disturbed purine metabolism and glycometabolism and in addition considerably lowered the manufacturing of ATP, which was additionally in keeping with the outcomes proven in Extra file 1: Fig. S5a.
Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant evaluation (OPLS-DA) demonstrated a transparent distinction between the metabolites within the TR and CL teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S7b). Among the many in another way expressed metabolites (DEMs), lipids and lipid-like molecules was the dominant class (Extra file 1: Fig. S7c). These outcomes urged that the synthesis of lipids and nucleosides was considerably affected by PDA. Subsequently, the mixed KEGG pathway evaluation of transcriptomics and metabolomics confirmed that the purine metabolism and fatty acid biosynthesis pathways have been enriched with DEGs and DEMs (Fig. 5g, h). Most gene expression modifications in these two pathways end result within the decreased expression of a number of metabolites, akin to hypoxanthine, adenine, and dodecanoic acid, finally resulting in metabolic issues and cell harm.
Based mostly on these outcomes, the potential PDA mechanism of nanomaterials underneath seen mild will be summarized as follows: Attributable to their glorious hydrophilicity, dispersibility, and constructive potential, nanomaterials can successfully accumulate on bacterial surfaces. Subsequently, extreme ROS past the mobile elimination capability results in the disruption of cell membranes and launch of mobile contents. In the meantime, regular metabolic processes, particularly of purine metabolism and fatty acid biosynthesis pathways of micro organism is severely disrupted, finally resulting in bacterial loss of life.
Cytotoxicity and cell migration skill evaluation in vitro
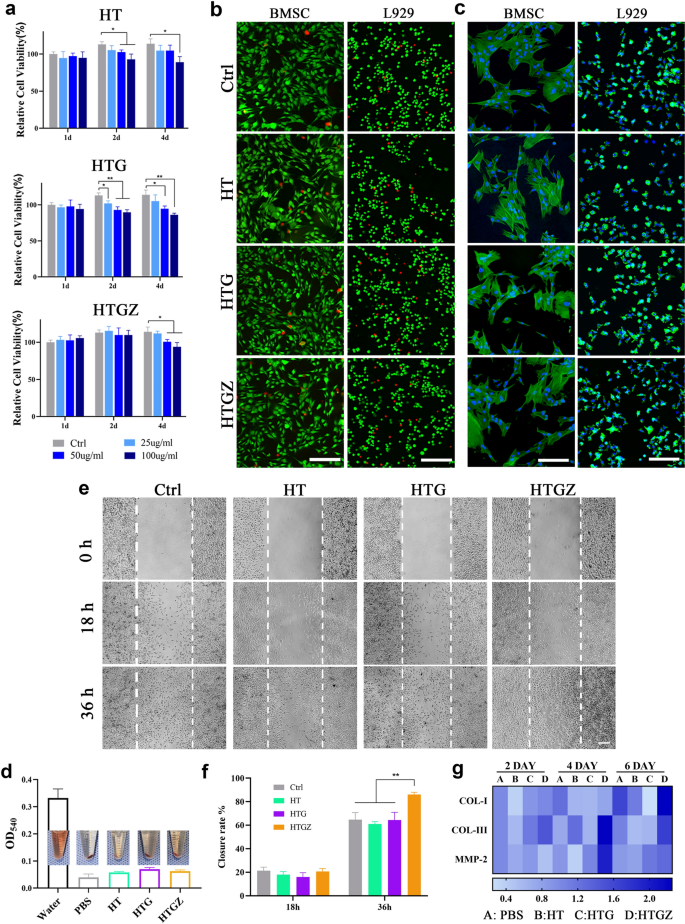
L929 cells and rat bone marrow stem cells have been used to evaluate cytotoxicity. HT and HTG confirmed no apparent cell development inhibition after 1 d however exhibited some toxicity at 2 and 4 d when uncovered to 50 or 100 µg mL−1. HTGZ promoted cell proliferation at decrease concentrations, and the inhibitory impact of excessive concentrations on cell development was weaker than that of HT or HTG (Fig. 6a, Extra file 1: Fig. S8). This enhancement could also be ascribed to Zn2+ promotes cell development and suppresses apoptosis. The dwell/useless cell fluorescence staining assay confirmed related outcomes (Fig. 6b). The morphology confirmed that cells within the handled teams unfold effectively with plenty of lamellipodia, much like the management group. (Fig. 6c). These outcomes point out that the nanomaterial had no vital cytotoxicity.
In vitro cytotoxicity and wound healing-related gene expressions. a CCK-8 outcomes of L929 cells co-cultured with nanomaterials. b Stay/useless staining photographs of cells co-cultured with nanomaterials for sooner or later. Scale bars are 500 μm. c Morphology of cells co-cultured with nanomaterials for sooner or later. Scale bars are 100 μm for BMSCs and 200 μm for L929 cells. d Hemolytic assessments information and pictures of nanomaterials with rat blood cells. Scale bars are 100 μm. e, f Cell scratch assay of L929 cells photographs and the statistical evaluation of closed space share. g Warmth map of gene expression in L929 cells co-cultured with nanomaterials. The expression of PBS teams are the management teams. The information are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001
Hemolytic take a look at was carried out to evaluate blood biosafety. The absorbance of the answer within the handled teams was much like that of the destructive management group (Fig. 6d), demonstrating negligible harm to the erythrocytes and good blood compatibility of the nanomaterials.
Scratch experiments can visually show the power of cells to proliferate and migrate, which is essential for wound therapeutic. As a result of launch of Zn2+, the migration and proliferation skill of cells within the HTGZ group was considerably improved when in comparison with the HT, HTG, and management teams (Fig. 6e, f).
To additional examine the mechanism of HTGZ in selling wound therapeutic, we carried out qRT-PCR to evaluate the expression of a number of tissue restore genes together with matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and sort I (COL-I) and sort III (COL-III) collagen. After co-cultured with HTGZ for 4 d, the expression of COL-III elevated by practically two instances in comparison with the opposite teams. After 6 d, COL-I and MMP-2 expression additionally considerably elevated (Fig. 6g). MMP-2 is a form of polypeptides relying on Zn2+, which is necessary to the activation/migration of fibroblast over the extracellular matrix [44]. Collagen protein is the primary constituent of pores and skin connective tissue, so the excessive expression of COL-I and COL-III is necessary for wound restore [45]. This upregulated gene expression could clarify why Zn2+ stimulates fibroblast motion. As well as, as a result of their increased floor power, hydrophilic surfaces can improve interactions between cells and proteins within the early phases of tissue regeneration [16]. The 2-dimensional porous construction of rGO can function a scaffold for cell migration and adhesion [46]. These all contribute to how HTGZ therapy promotes cell migration.
In the course of the wound therapeutic course of, the quicker cell migration and improved collagen deposition induced by HTGZ can speed up tissue regeneration, and the biosafety and biocompatibility of HTGZ make it a promising versatile platform for future biomedical anti-infective functions.
Contaminated wound therapeutic efficacy and toxicity in vivo
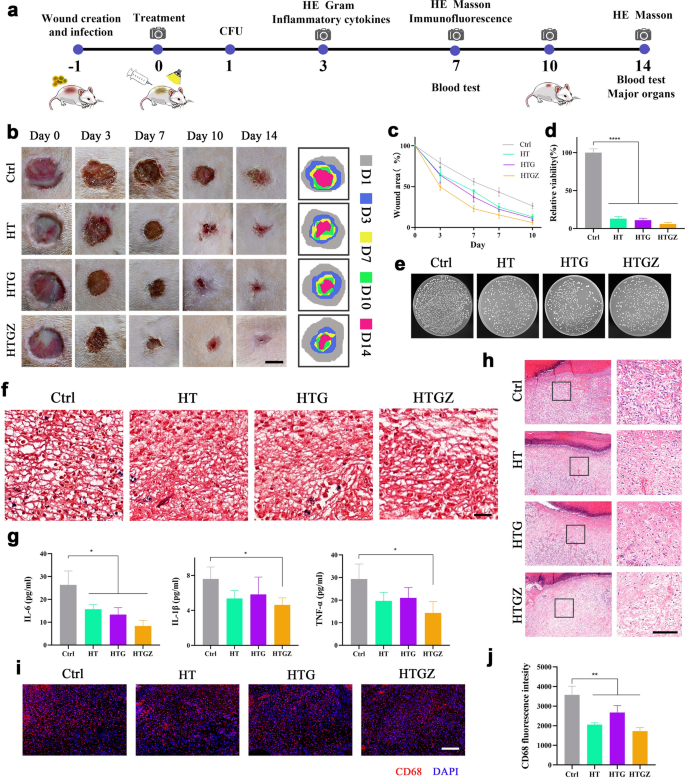
We selected a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-infected pores and skin wound mannequin in rats to discover the in vivo antibacterial and wound therapeutic skill of the nanomaterials (Fig. 7a). After 24 h of an infection, wounds have been handled (day 0) with 100 µg mL−1 nanomaterials underneath 15 min irradiation. These parameters have been chosen primarily based on in vitro antibacterial and toxicity testing. In comparison with the management group, the nanomaterials accelerated the wound therapeutic course of, and HTGZ confirmed optimum skill owing to the discharge of Zn2+ (Fig. 7b, c). Moreover, as proven by gram-positive micro organism staining and CFU counting, the variety of residual micro organism from the wound websites was considerably decreased (Fig. 7d–f). Bacterial infections can severely have an effect on wound therapeutic, whereas the wonderful antibacterial actions of nanomaterials can successfully resolve this challenge through PDA within the preliminary stage.
Antibacterial exercise of nanomaterials within the contaminated wound mannequin in vivo. a Schematic illustration exhibiting the method of experiments about wound restore analysis. b Consultant pictures and schematic presentation of wound therapeutic websites. Scale bars are 5 mm. c Quantitative evaluation of wound space. d, e Quantitative evaluation of CFUs and pictures of bacterial colonies of the contaminated wounds on day 1. f Gram staining of contaminated pores and skin tissues on day 3. Scale bars are 50 μm. g Serum ranges of IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-α in blood samples collected on day 3. h H&E staining of the contaminated tissues on day 3. Left scale bars are 200 μm and proper scale bars are 100 μm. i Immunostaining of contaminated pores and skin tissues stained with CD68 and DAPI on day 7. Scale bars are 100 μm. j Quantifications of macrophages (CD68) within the contaminated pores and skin tissues. The information are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 5). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001
After eliminating an infection, ample irritation management is one other barrier in wound therapeutic. The inflammatory standing of wounds is necessary for exploring the diploma of wound therapeutic. Inflammatory cytokine ranges function indicators of inflammatory development [47]. After 72 h of therapy, the serum degree of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1ß and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-a) within the management group was considerably increased than that within the therapy teams (Fig. 7g). To additional consider the inflammatory circumstances, histopathological and immunofluorescence methods have been employed. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on day 3 confirmed fewer neutrophils emerged from the handled wounds (Fig. 7h). Moreover, on day 7, weaker sign for cluster of differentiation 68 was noticed within the handled teams relative to the management group, indicated fewer macrophages (Fig. 7i, j). In the course of the preliminary phases of wound therapeutic, neutrophils migrate from circulating blood to the wound mattress, decreasing microbial ranges [48], whereas macrophages play a task in eliminating necrotic and apoptotic cells [49]. The lowered numbers of neutrophils and macrophages on the wound web site counsel that therapy with nanomaterials successfully diminishes an infection and irritation throughout the early and center phases of wound restoration via PDA, thereby selling wound therapeutic.
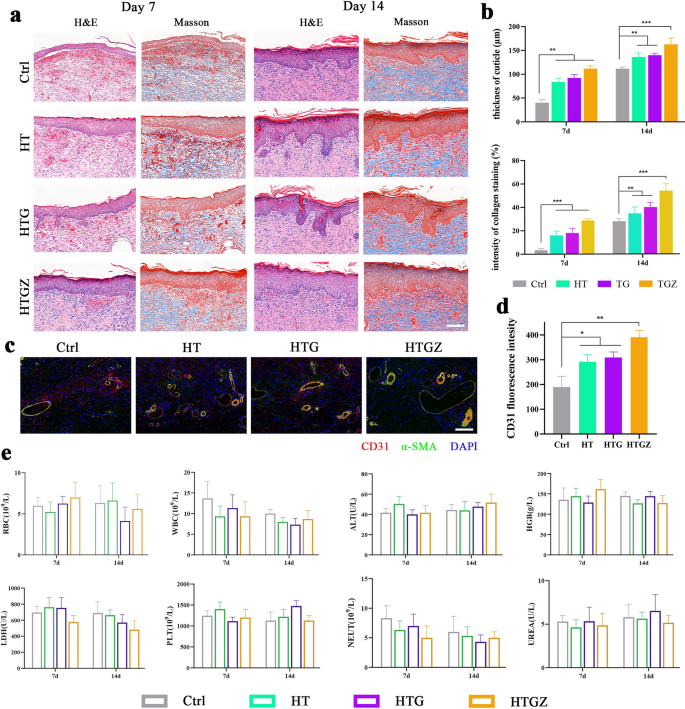
Moreover, we evaluated the results of the nanomaterials on tissue regeneration utilizing H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining. On day 7, the dermis and dermis weren’t tightly bonded within the management group, whereas collagen deposition was considerably decrease than that within the handled teams. On day 14, well-organized collagen fibers and the formation of pores and skin appendages, akin to follicles, have been noticed within the therapy teams (Fig. 8a). The quantitative evaluation of epidermal thickness and collagen staining depth are proven in Fig. 8b. Subsequently, we carried out immunofluorescence staining to discover angiogenesis. CD31 is a marker for newly-formed endothelial cells [50]. whereas α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) is a marker of myofibroblasts in vascular {smooth} muscle [51]. The upregulation fluorescence depth within the handled teams indicated enhanced angiogenesis (Fig. 8c, d). A thicker dermis and elevated collagen deposition indicated that the tissue was present process superior restore, which was not directly confirmed by the presence of native vessels which transport the oxygen and vitamins mandatory for wound therapeutic [52].
Antibacterial exercise of nanomaterials within the contaminated wound mannequin and periodontal irritation mannequin in vivo. a H&E and Masson staining of the contaminated tissues on days 7 and 14. Scale bars are 100 μm. b Statistical evaluation of cuticle thickness and depth of collagen staining. c Immunostaining of contaminated pores and skin tissues stained with CD31, α-SMA and DAPI on Day 7. Scale bars are 100 μm. d Quantifications of CD31 within the contaminated pores and skin tissues. e The blood routine examination and main blood biochemical values of the management and handled teams in rats. The information are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 5). Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001
Basically, bacterial infections and subsequent irritation severely hinder wound restore [53]. The speedy and efficient PDA properties of nanomaterials can remove detrimental elements that hinder wound therapeutic by killing micro organism and assuaging irritation. Furthermore, the discharge of Zn2+ in HTGZ promotes tissue regeneration and additional accelerates the general therapeutic course of.
Moreover, the cytotoxicity of the nanomaterials was evaluated in vivo via hematological examination and histological evaluation of main organs. Histological evaluation utilizing H&E staining revealed no discernible histological abnormalities within the main organs throughout all experimental teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S9). On day 7, the management group exhibited increased white blood cell and neutrophil counts in comparison with the handled teams, attributable to the presence of extreme irritation; nevertheless, all different hematological parameters remained inside the regular vary (Fig. 8e). These findings present compelling proof of the excellent biosafety and promising software potential of nanomaterials in vivo.
Attributable to its monumental potential in treating contaminated wounds and good biosafety, HTGZ-related medication have nice sensible software prospects. Due to its glorious hydrophilicity, HTGZ will be added to antibacterial patches or gels, and even instantly made into aerosolized formulations.
Assuaging periodontal irritation in vivo
Periodontitis is a power irritation characterised by lack of periodontal tissue. Plaque biofilm is a crucial pathogenic issue for periodontitis [54]. Due to this fact, the periodontitis mannequin might additional confirm the antibacterial and tissue restore capability of nanomaterials. Following totally different remedies, the CFU depend of residual bacterial in periodontal tissue confirmed a big discount in therapy teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S10a, b). Moreover, as proven in three-dimensional reconstructed micro-CT photographs, in contrast with the management group, bone resorption space was considerably smaller within the handled teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S10c). Quantitative evaluation of distance between the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and alveolar bone crest (ABC) at furcation of first molar confirmed this end result (Extra file 1: Fig. S10d). Corresponding two-dimensional cross-sectional photographs revealed significantly increased bone density within the therapy teams in comparison with that within the management group inside the area beneath the apex of the bone septum, between the mesial and distal roots of the primary molar. The bone quantity/complete quantity (BV/TV) inside this area displayed related developments (Extra file 1: Fig. S10e). Histopathological evaluation utilizing H&E staining revealed extreme periodontal ligament width skilled and bone loss on the molar furcation space of the management group, whereas these signs have been notably alleviated within the therapy teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S10f, g). Many constructive osteoclasts (yellow arrows) have been evident within the tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining picture of the management group, whereas they have been scarcely seen within the therapy teams (Extra file 1: Fig. S10h), suggesting the suppression of bone destruction in periodontitis. Collectively, HTGZ might remove biofilm via PDA, and additional absorption of alveolar bone was inhibited after the initiating elements of periodontitis have been eliminated. The signs of periodontitis have been relieved, and periodontal tissue was regenerated.