Design, synthesis, and characterization of poly(α-lipoic acid)-polyethylene glycol grafted rhein and geraniol (PPRG) nanoprodrug
The impact of rhein with geraniol together on the expansion of Gram-negative mannequin micro organism, S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028, was investigated within the microplates. These outcomes indicated {that a} typical synergistic impact between the candidate rhein and geraniol have been noticed with FICI at 0.5 ± 0.072 (Extra file 1: Determine S1A). To strengthen the notion of synergism between the candidate rhein and geraniol, a direct synergistic bactericidal assay was carried out. Within the monotherapy assay, the appliance of rhein and geraniol alone exhibited restricted bactericidal exercise over time. In distinction, the mixture of rhein and geraniol quickly eradicated the S. Typhimurium strains, resulting in a discount in bacterial masses by 103–108-fold inside 4 h after therapies (Extra file 1: Determine S1B).
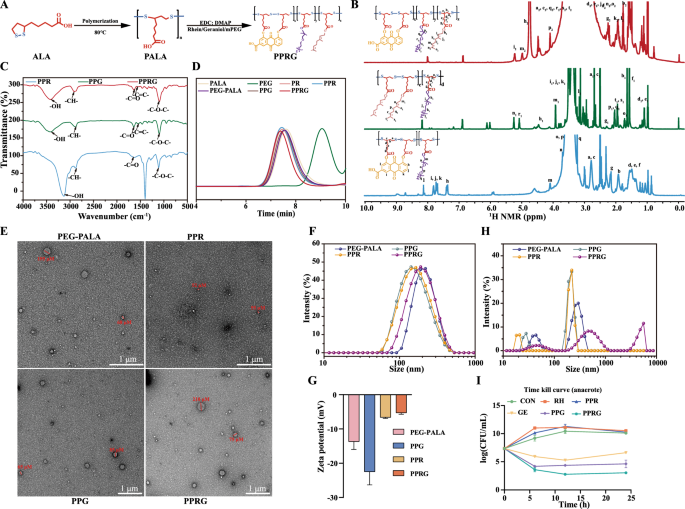
The poly(α-lipoic acid)-polyethylene glycol grafted rhein and geraniol (PPRG) nanoprodrug, was ready by covalently conjugating poly (α-lipoic acid) and PEG to the hydroxyl (-OH) teams of rhein and geraniol through ester bond as a linker. The synthesis processes of PPRG are proven in Fig. 1A and Extra file 1: Determine S2. The 1H NMR spectrum of PPRG reveals the presence of eight distinct kinds of hydrogen atoms, with extra proton peaks from geraniol denoted as h2, i2, j2, okay2, l2, m2, n2 and o2 (δ4.75, δ5.24, δ1.56, δ1.94, δ1.78, δ4.99, δ1.49 and δ1.48 ppm, respectively), grafted onto PEGylated PALA grafted rhein (PPR) skeleton (Fig. 1B). Within the FTIR spectrum, when in comparison with these of PPR, PEGylated PALA grafted geraniol (PPG), PPRG important shifts have been noticed. Particularly, two necessary bonds comparable to the ether bond (-C–O–C-) and the -OH teams have been exhibited at 1060 cm−1 and 3200 cm−1. The depth of -OH group in PPRG decreased compared to that of PPR and PPG, whereas the depth of -COOR elevated compared to that in PPR and PPG. The peaks at 1096 cm−1 and 3133 cm−1 additional validated the construction of PPRG (Fig. 1C). Moreover, the molecular weight of PPRG was decided to be 88674 g·mol−1, which is larger than that of PPR, indicating that 59.3% geraniol grafted within the PALA skeleton (Fig. 1D). These outcomes verify the profitable synthesis of PPRG. The 1H NMR spectra of PR, PPR and PPG exhibit profitable preparation of those compounds.
Synthesis and traits of PPR, PEGylated PALA, and PPRG. A Structural system of PPRG. B 1H NMR. C FTIR. D GPC. E TEM. F particle dimension. G zeta potential. H nanoparticles cope with 1 mM·L−1 Na2S decided by Zetatrac particle dimension analyzer of PEGylated PALA, PPR, PPG, and PPRG. (I) Time-killing curve of S. Typhimurium ATCC 14028 beneath anaerobic situation for twenty-four h. (CON management, SAL Salmonella, RH rhein, PPR PEGylated PALA grafted rhein, GE geraniol, PPG PEGylated PALA grafted geraniol, and PPRG poly(α-lipoic acid)-polyethylene glycol grafted rhein and geraniol, respectively)
X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) evaluation supplied the chemical oxidation state of components current within the samples. The S2p spectrum of the PPR demonstrated the presence of C-S and S–S bonds (161.38 and 163.28 eV), respectively. Whereas the S2p spectrum of the PPRG confirmed the C-S and S–S bonds (161.48 and 163.28 eV), which represented the PALA current in PPR and PPRG. The C-S bonds of PPR and PPRG are shifted, which additionally signifies the considerably modifications in bond construction (Extra file 1: Determine S3). X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns additional look at on the existence of cross-linking response on PALA (Extra file 1: Determine S4), and the crystalline state of α-lipoic acid at 22.8º is nearly remodeled into the amorphous state [28]. The PPR contained PEG and rhein displayed extra peaks at 19.2º and 23.4º, 27.4º, respectively [29]. Geraniol containing in PPRG doesn’t change the height of PPR, which is analogous to different research [30]. These outcomes additional verify the profitable synthesis of PPRG.
HPLC–UV evaluation at 258 nm and 210 nm indicated that the content material of rhein and geraniol in PPR and PPG have been 15.81 ± 5.5% and 48 ± 0.12%, respectively. Within the PPRG, the content material of rhein and geraniol was decided to be 10.56% ± 1.39% and 13.85% ± 0.87%, respectively. The rhein and geraniol from PPR, PPG and PPRG exhibited hardly launched in each simulated gastric fluid (SGF) and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF). To set off the discharge of those as-prepared nanoprodrugs, they have been allotted into options containing dithiothreitol (DTT) served as an in vitro H2S donor, following strategies described in earlier research [31, 32]. Rhein and geraniol have been nearly fully launched inside 2 h in PPR and PPG nanoprodrugs at 1 mM·L-1 DTT resolution. The PPRG nanoprodrug launched 68.6% rhein and nearly all of geraniol inside 4 h (Extra file 1: Determine S5). Then, the assembled morphology of those nanoprodrugs fashioned by PEGylated PALA, PPR, PPG and PPRG indicated particle sizes about 50–200 nm, and PPR was the smallest at 50 nm examined by TEM (Fig. 1E). The common sizes ranged from 142 to 220 nm and the zeta potentials ranged from − 22.5 ± 2.67 to − 5.30 ± 0.30 mV (Fig. 1F–G). These nanoprodrugs exhibited wonderful storage stability no observable precipitation or delamination was noticed after centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 min. And the drug content material remained nearly unchanged within the room temperature after a 14-day storage interval (Extra file 1: Determine S5C).
The as-prepared nanoprodrugs have been noticed to be decomposed in response to sodium sulfide (Na2S) as a H2S donor (Fig. 1H). To additional look at whether or not tradition of the nanoparticles with S. Typhimurium would yield bactericidal impact via the discharge of rhein and geraniol, time-killing curves have been generated beneath anaerobic cultivation to imitate the in vivo intestinal surroundings. As anticipated, the bacterial numbers considerably decreased by 4.31log10(CFU·mL−1) after remedy with PPRG for twenty-four h. In distinction, PPG remedy resulted in a discount of two.72 and 1.99 log10(CFU·mL−1) in comparison with the management and geraniol therapies, respectively. This demonstrates a big impact of the mixture of rhein and geraniol (Fig. 1I).
Permeability assay, in vitro cell viability, and anti inflammatory exercise analysis
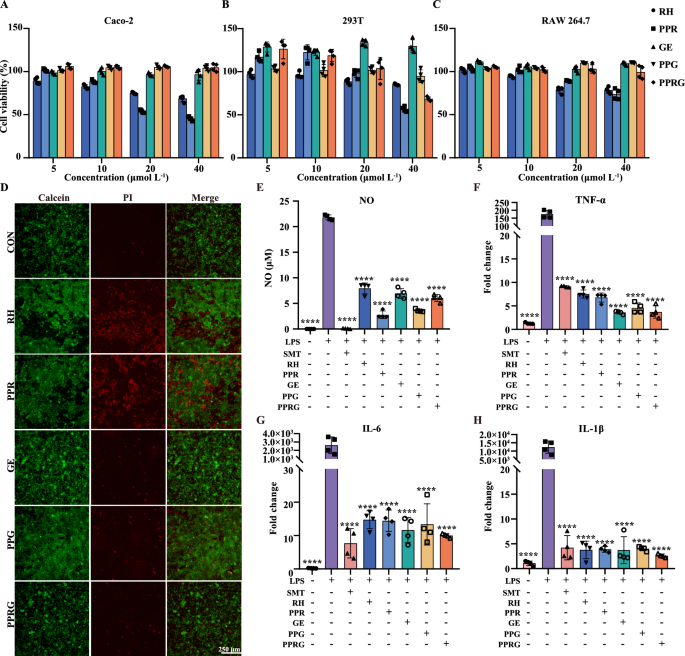
To research the biosafety of those nanoprodrugs, cell viability was decided utilizing the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8). The viability of Caco-2, 293 T, RAW 264.7, HepG2, HGF-1 have been examined by including rhein, PPR, geraniol, PPG, PPRG to the tradition medium at concentrations starting from 5 to 40 μmol·L−1, respectively. Cell viability ratio was normalized with the viability of DMSO-treated cells. At a focus of 40 μmol·L−1, the cell viability of Caco-2 uncovered to rhein, geraniol, PPR, PPG and PPRG have been 63.91, 96.39, 45.34, 103.92, and 104.75%, respectively. Rhein and PPR exhibited low toxicity, particularly at concentrations over 20 μmol L−1 (Fig. 2A). For 293 T cells, the viability uncovered to rhein, geraniol, PPR, PPG, PPRG at 40 μmol L−1 have been 85.10, 56.72, 129.50, 94.84, and 68.36% (Fig. 2B). RAW 264.7 cell viability remained above 70% throughout the examined focus vary (Fig. 2C). Hep G2 and HGF-1 cells exhibited considerably lowered viability upon publicity to excessive doses of rhein and PPR, however no modifications in cells viability have been noticed with different therapies (Extra file 1: Determine S6A–B). Moreover, the dwell/useless cell staining for Caco-2 and 293 T at 40 μmol·L−1 indicated minimal toxicity for rhein and PPR (Fig. 2D, Extra file 1: Determine S6C). These above outcomes confirmed that PPRG successfully reduces the cytotoxicity of rhein.
The cell viability and LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cellls. Cell viability for A Caco-2. B 293 T.and C RAW 264.7. D Dwell/useless cell staining of Caco-2 cells utilizing 40 μM·L−1 check samples. LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells incubated with check samples and measurements of E NO. F TNF-α. G IL-6. and H IL-1β
Contemplating the impact of PPRG on the transport of intestinal epithelial cells, a Caco-2 cell Transwell mannequin [33] was established to discover the intestinal permeability options of rhein, PPR, geraniol, PPG and PPRG. The Trans-Epithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) was measured at 226.7 ± 3.1 Ω /cm2 (Extra file 1: Determine S7A). The consequence confirmed that the PPR, PPRG, PPG and PPRG considerably decreased the permeability in comparison with rhein and geraniol (Extra file 1: Determine S7B-7C). The as-prepared compounds at 10 μmol·mL−1, which exhibits not adversely affected of cells, have been chosen to judge the anti-inflammatory impact. The inflammatory course of is activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated, resulting in the secretion of nitric oxide (NO) and cytokines akin to IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. To guage the anti-inflammatory efficacy of the PPRG nanoprodrug, the NO, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β have been decided utilizing an LPS-induced RAW 264.7 mannequin to judge the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression ranges. Curcumin (CUR), well-documented for its means to scale back NO manufacturing and its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, served as a optimistic management within the research [34]. All of the check compounds exhibited important inhibition of NO manufacturing when in comparison with cells handled with LPS alone (P < 0.0001). In contrast with rhein remedy, PPR, PPG and PPRG exhibited a big discount in NO manufacturing (P < 0.01), whereas geraniol demonstrated no substantial distinction (Fig. 2E). In contrast with the LPS-stimulated alone, all of the therapies have been considerably down-regulated the manufacturing of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Nevertheless, in contrast with rhein or geraniol, CUR, PPR, PPG and PPRG didn’t exhibit important variations (Fig. 2F–H). To sum up, these outcomes indicated that PPRG maintained a high-level anti-inflammatory exercise whereas lowering the toxicity of rhein.
In vivo therapeutic efficacy of the PPRG nanoprodrug in opposition to Salmonella an infection in mice
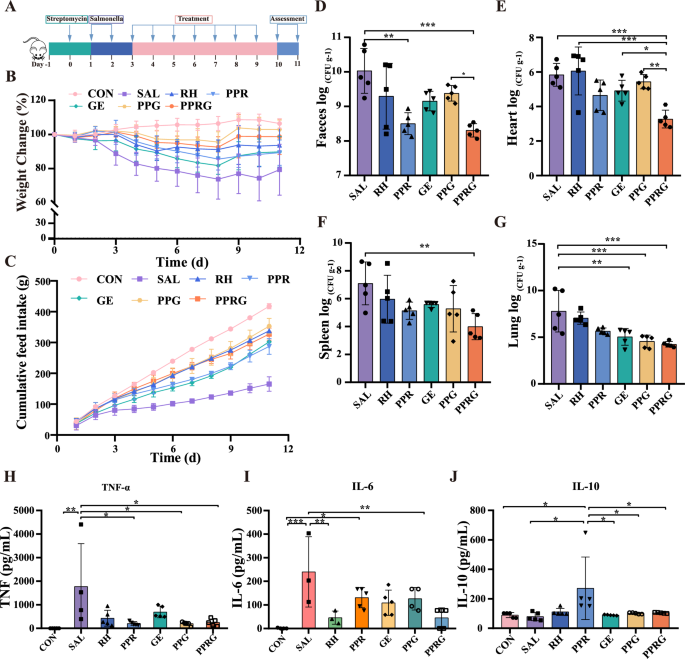
To guage the potential impact of PPRG in vivo, an acute Salmonella an infection mouse mannequin was constructed (Fig. 3A). PPRG considerably alleviated infection-induced discount in physique weight in comparison with Salmonella group (P < 0.0001), whereas PPG alone didn’t considerably enhance in physique weights (P = 0.29) (Fig. 3B–C). The bacterial load of Salmonella within the feces, hearts, spleens, and lungs have been considerably lowered by 1.72, 2.56, 3.11 and three.55log10 CFU· g−1 after receiving PPRG remedy. These outcomes exhibit the substantial efficacy of the PPRG in eradicating Salmonella from contaminated hosts (Fig. 3D–G). Salmonella colonization within the feces, hearts, spleens, and lungs have been lowered by 1.52, 1.18, 1.96, 2.13log10CFU·g−1 and 0.65, 0.40, 1.82, 3.24 log10 CFU·g−1, respectively, after receiving PPR and PPG remedy. These outcomes indicated that the PPRG nanoprodrug exhibited a synergistic impact in vivo by releasing rhein and geraniol after Salmonella an infection. As to the results on modulating intestinal inflammatory response, PPRG was noticed to considerably down-regulate the extent of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6. Moreover, PPRG notably elevated the degrees of the anti-inflammatory issue IL-10, which performs a vital position in modulating the host inflammatory (Fig. 3H–J). To additional examine the affect of in situ effectiveness of the PPRG nanoprodrug at an infection websites, immunohistochemistry evaluation to evaluate the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 within the ceca have been carried out. Geraniol remedy up-regulated the expression of inflammatory components TNF-α and IL-1β, whereas rhein remedy up-regulated expression of IL-6. PPRG remedy down-regulated the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 within the ceca in contrast with Salmonella group (Fig. 4B).
Therapeutic efficacy in an acute Salmonella an infection in vivo mannequin. A The research protocol included streptomycin pretreatment adopted by Salmonella an infection, remedy with rhein (25 mg·kg−1), PPR (250 mg·kg−1), geraniol (12.5 mg·kg−1), PPG (26 mg·kg−1) and PPRG (21 mg·kg−1), every day. B Variations of mouse physique weights over time and normalized to the share of day zero physique weight. C Cumulative meals consumption of per group from day 1 to 11. Quantification of bacterial burdens in D faeces. E coronary heart. F spleen. and G lungs of contaminated mice with completely different therapies. Serum inflammatory issue ranges of H TNF-α. I IL-6. J IL-10 in vivo for Salmonella-infected mice
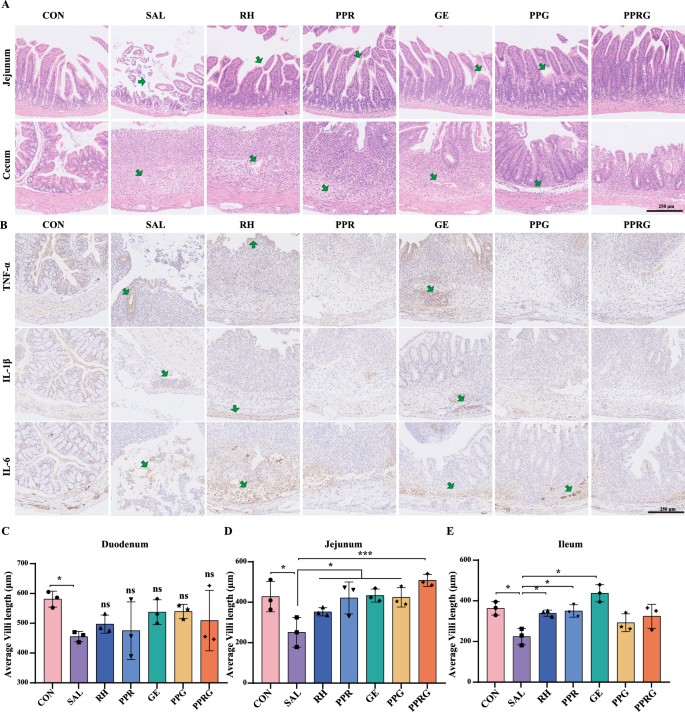
To additional evaluation the histopathologic modifications after Salmonella, H&E (hematoxylin and eosin) staining was carried out. In contrast with the management group, PPRG remedy confirmed lowered tissue destruction brought on by Salmonella within the jejunum and cecum. Particularly, Salmonella an infection mice exhibited a considerably thinner serosal layers with proof of breakage, loss, and irregular association of intestinal villi. In distinction, rhein, PPR, geraniol, PPG, and PPRG remedy confirmed different lengths of intestinal villi. PPRG remedy resulted in a big discount within the severity of an infection within the jejunal tissues in comparison with Salmonella an infection (Fig. 4A and D). Furthermore, the cecal partitions appeared thinner and the muscularis propria was disrupted within the Salmonella, rhein, PPR or geraniol group. Goblet cells within the submucosa of PPG- and PPRG-treated mice have been fewer in comparison with the management teams, and the boundary between the mucous and submucosa was vague (Fig. 4A, Extra file 1: Determine S8). The jejunal, cecal and colonic tissues within the PPRG group carefully resembled these of the management group (Fig. 4D). Curiously, the PPR group displayed considerably elevated villi lengths within the ileum (Fig. 4E). In distinction, Salmonella an infection led to a considerably lower in small bowel villi size within the duodenum. And the rhein, PPR, geraniol, PPG or PPRG remedy had a restorative impact on the size of small intestinal villi, though these modifications have been no statistically important variations (Fig. 4C and Extra file 1: Determine S8).
Intestine microbiota homeostasis of the PPRG nanoprodrug remedy
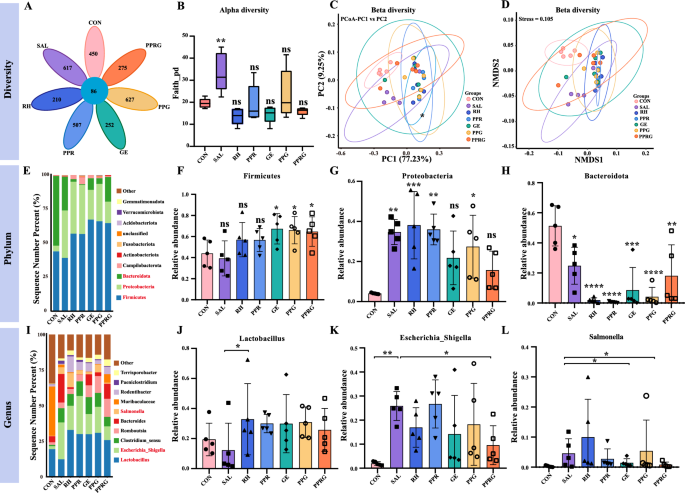
To additional assess whether or not PPRG nanoprodrugs have been in a position to keep the intestine microbiome homeostasis, ceca samples from 7 teams have been collected. A complete of 5322 operational taxonomic models (OTUs) have been recognized, with 210 to 627 OTUs being particular to group acquired completely different therapies, and 86 OTUs being shared amongst all 7 teams. In comparison with the management group, an increment in OTUs was noticed in mice acquired remedy, whereas the RH or PPRG remedy decreased the microbiota abundances (Fig. 5A). The taxonomic evaluation recognized a complete of 4618 taxa on the phylum degree, 4596 on the class degree, 4453 on the order degree, 3626 on the household degree, 1826 on the genus degree, and 507 on the species degree. In contrast with the uninfected mice, the Salmonella an infection lowered the intestine microbial α-diversity (Religion index) (P < 0.01) at species abundance degree (Fig. 5B). UniFrac distance-based principal Coordinate Evaluation (PCoA) and non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots indicated that microbiota composition was centralized in rhein and geraniol remedy teams, which led to a discount to microbiota range in comparison with the PPRG remedy group (Fig. 5C, D). Linear discriminant evaluation Impact Measurement (LEfSe) is usually utilized for evaluating the predominant intestine microbiota amongst completely different teams. The abundance evaluation revealed that the Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes have been essentially the most dominant phyla within the intestine microbiota. These phyla have been possible susceptible to Salmonella an infection, resulting in alterations within the phylum-level construction of the microbial neighborhood. Firmicutes and Proteobacteria considerably elevated at expense of Bacteroidetes compared to the management group (Fig. 5E). Particularly, the abundance of Firmicutes considerably elevated in response to PPRG in comparison with management group (P = 0.08). In comparison with the management group, the abundance of Proteobacteria was considerably elevated within the Salmonella, rhein, PPR, geraniol and PPG teams (P = 0.0002, P < 0.0001, P = 0.0001, P = 0.0001, P = 0.02, P = 0.0029, respectively), whereas no important distinction was noticed within the PPRG teams (P = 0.12, Fig. 5F). As well as, Salmonella an infection led to important improve within the abundance of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, however PPRG remedy was efficient in reversing these alteration microbiota (Fig. 5G–H). Furthermore, Salmonella an infection remedy with medicine considerably elevated the abundance of varied genera of Enterobacteriaceae. To additional outline whether or not PPRG was in a position to keep intestine microbiota at genus degree, the intestine microbiota at genus degree have been analyzed. As proven in Fig. 5I, Escherichia_Shigella, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Romboutsia and Salmonella have been considerably elevated, whereas Lactobacillus and Muribaculaceae have been considerably decreased. Salmonella an infection receiving rhein remedy can considerably improve within the relative abundance of Lactobacillus spp. (P = 0.047, Fig. 5J), whereas PPRG remedy sharply decreased the relative abundance of Escherichia_Shigella brought on by Salmonella an infection (P = 0.024). Salmonella an infection receiving PPRG and GE therapies considerably decreased the relative abundance of Salmonella (P = 0.049, P = 0.0353), which indicated the therapeutic impact of PPRG in vivo.
Intestine microbiota evaluation of contaminated mice after therapies. A Venn diagram indicating completely different OTU quantity for the 4 remedy teams. B Common bacterial taxonomic profiling of the intestine microbiota in seven teams. C Nonmetric multidimensional scaling rating plot primarily based on Bray–Curtis distances. D UniFrac-based PCoA rating plot primarily based on weights. E Common bacterial taxonomic profiling of the intestine microbiota in seven teams at phylum degree. F–H Relative abundance of bacterial phylum obtained from LefSe outcomes. I Common bacterial taxonomic profiling of the intestine microbiota in seven teams on the genus degree. J–L Relative abundance of the bacterial genera obtained from the LefSe outcomes
The Morris water maze check, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of PPRG
To comprehensively assess the results of the nanoprodrug on the themes, we carried out pre-treatment, spatial acquisition, and probe trial classes within the Morris water maze (see Extra file 1: Determine S9A). Our findings indicated that there have been no important modifications in weight in the course of the early days of oral administration (Extra file 1: Determine S9B). The spatial studying and reminiscence skills of the rats subjected to drug pre-treatment have been evaluated utilizing the Morris water maze experiment. These outcomes revealed that the spatial studying skills of mice with rhein, geraniol, or PPRG have been no important impact (Extra file 1: Determine S9C). In contrast with the management group, the swimming distance, swimming time and the variety of instances of swimming throughout within the goal quadrant of mice have been no important modifications (Extra file 1: Determine S9D-9H). These outcomes indicated that the rhein, geraniol or PPRG remedy had no important impact on the cognition and habits of mice.
Plasma pharmacokinetics was evaluated after oral (70 mg/kg) administration in SD rats [35]. Plasma samples of PPRG, rhein, and geraniol have been analyzed at preset time factors. After PPRG administration, plasma focus of rhein and geraniol elevated progressively inside 5 h (Cmax-rhein, 0.85 ± 0.03 µg/mL; Cmax-geraniol, 155.20 ± 43.9 µg/mL), then declined to 0.22 ± 0.037 and 59.81 ± 28.4 0.46 μg/mL inside 8 h, and remained largely fixed as much as 24 h. The calculated pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) parameters are proven in Extra file 1: Desk S3 and Determine S10. In comparison with PPRG, plasma focus of rhein administration alone elevated progressively inside 45 min (Cmax, 3.28 ± 0.17), then declined to 0.64 ± 0.086 μg/mL inside 3 h. Plasma focus of geraniol administration alone elevated progressively 104.32 ± 11.35 μg/mL inside 45 min, then declined to just about 0 inside 3 h. These knowledge have been in contrast with the reported knowledge free of charge rhein and geraniol [20, 35]. The comparability confirmed that it takes very long time to succeed in Cmax at oral administration of PPRG. Equally, half-life (t1/2) of PPRG was for much longer, displaying over fourfold and threefold improve in comparison with free rhein and geraniol. The lower in plasma focus of rhein from PPRG confirmed that the gastrointestinal tract absorbed rhein at a slower price examine to free rhein. Elevated plasma focus of geraniol from PPRG is a transparent indication of the decrease clearance from circulation in comparison with free geraniol. Moreover, we noticed larger t1/2, tmax, and MRT values in contrast PPRG to free rhein or geraniol. Additionally, the numerous lower in space beneath the focus–time curve (AUC) values for rhein from PPRG have been noticed in comparison with free rhein (25.61 ± 18.88 vs 5.73 ± 0.53 μg/h/mL). Whereas the geraniol from PPRG was displayed considerably elevated in AUC values in comparison with free geraniol. These outcomes indicated that PPRG nanoprodrug can successfully keep Tmax of absorption and distribution for rhein and geraniol, contributing to boost their synergy.