MongoDB.dwell came about final week, and Rockset had the chance to take part alongside members of the MongoDB group and share about our work to make MongoDB information accessible through real-time exterior indexing. In our session, we mentioned the necessity for contemporary data-driven functions to carry out real-time aggregations and joins, and the way Rockset makes use of MongoDB change streams and Converged Indexing to ship quick queries on information from MongoDB.
Information-Pushed Purposes Want Actual-Time Aggregations and Joins
Builders of data-driven functions face many challenges. Purposes of at the moment usually function on information from a number of sources—databases like MongoDB, streaming platforms, and information lakes. And the information volumes these functions want to investigate sometimes scale into a number of terabytes. Above all, functions want quick queries on dwell information to personalize consumer experiences, present real-time buyer 360s, or detect anomalous conditions, because the case could also be.
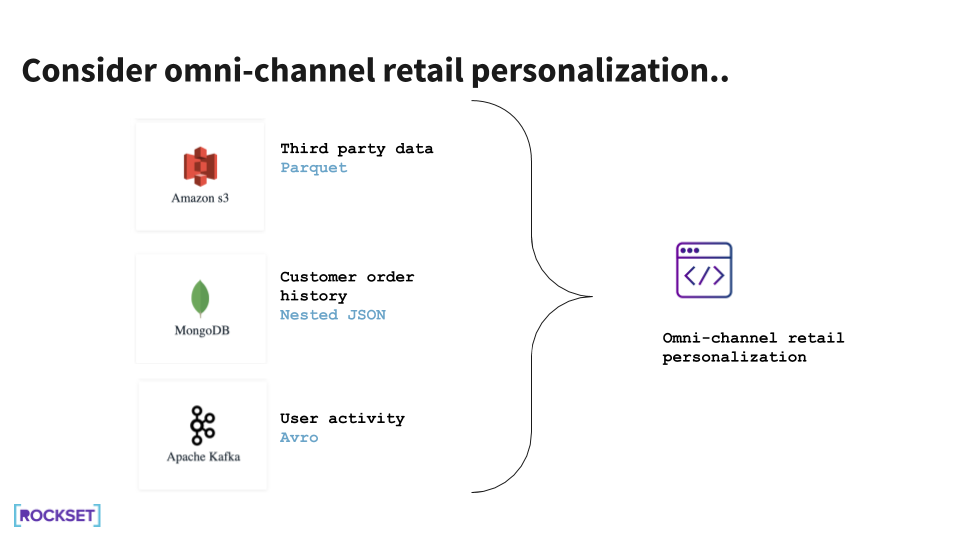
An omni-channel retail personalization software, for instance, could require order information from MongoDB, consumer exercise streams from Kafka, and third-party information from a knowledge lake. The applying should decide what product suggestion or provide to ship to prospects in actual time, whereas they’re on the web site.
Actual-Time Structure At present
One among two choices is often used to help these real-time data-driven functions at the moment.
- We will constantly ETL all new information from a number of information sources, comparable to MongoDB, Kafka, and Amazon S3, into one other system, like PostgreSQL, that may help aggregations and joins. Nonetheless, it takes effort and time to construct and keep the ETL pipelines. Not solely would we now have to replace our pipelines usually to deal with new information units or modified schemas, the pipelines would add latency such that the information can be stale by the point it could possibly be queried within the second system.
- We will load new information from different information sources—Kafka and Amazon S3—into our manufacturing MongoDB occasion and run our queries there. We’d be accountable for constructing and sustaining pipelines from these sources to MongoDB. This answer works effectively at smaller scale, however scaling information, queries, and efficiency can show tough. This could require managing a number of indexes in MongoDB and writing application-side logic to help complicated queries like joins.
A Actual-Time Exterior Indexing Strategy
We will take a special method to assembly the necessities of data-driven functions.
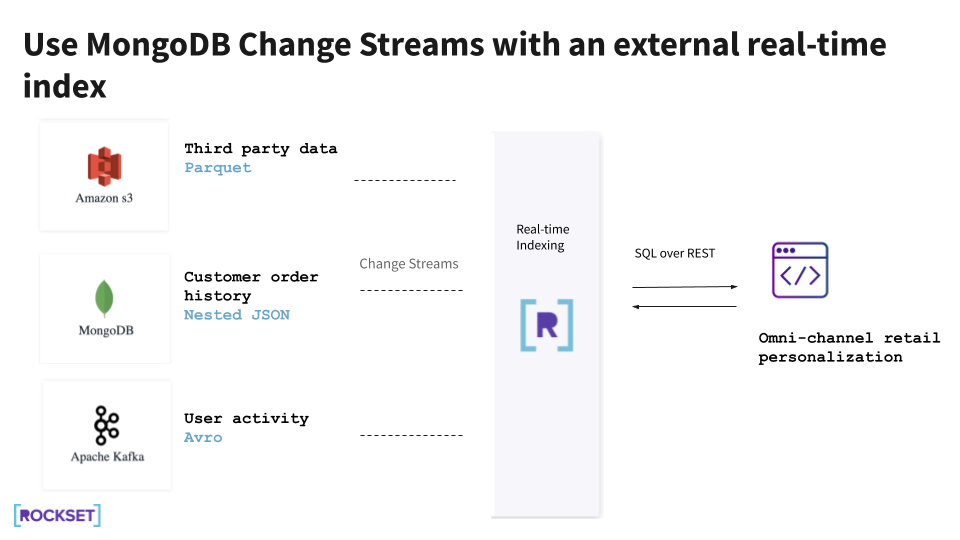
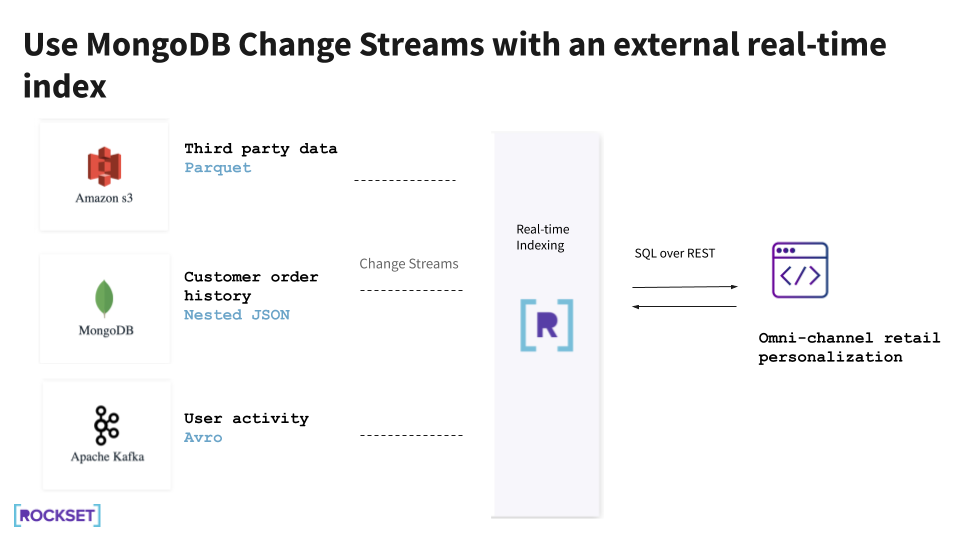
Utilizing Rockset for real-time indexing permits us to create APIs merely utilizing SQL for search, aggregations, and joins. This implies no further application-side logic is required to help complicated queries. As an alternative of making and managing our personal indexes, Rockset robotically builds indexes on ingested information. And Rockset ingests information with out requiring a pre-defined schema, so we are able to skip ETL pipelines and question the most recent information.
Rockset supplies built-in connectors to MongoDB and different frequent information sources, so we don’t must construct our personal. For MongoDB Atlas, the Rockset connector makes use of MongoDB change streams to constantly sync from MongoDB with out affecting manufacturing MongoDB.
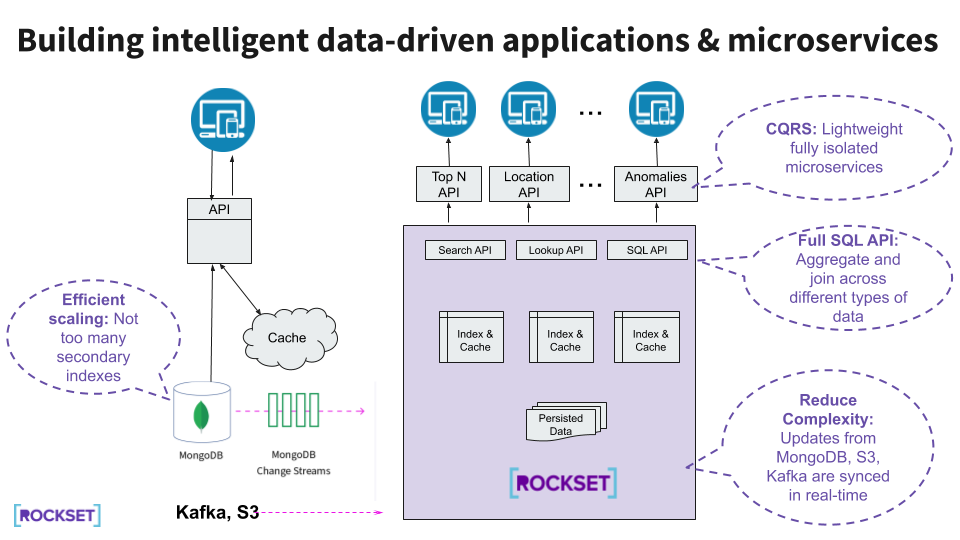
On this structure, there isn’t any want to change MongoDB to help data-driven functions, as all of the heavy reads from the functions are offloaded to Rockset. Utilizing full-featured SQL, we are able to construct various kinds of microservices on prime of Rockset, such that they’re remoted from the manufacturing MongoDB workload.
How Rockset Does Actual-Time Indexing
Rockset was designed to be a quick indexing layer, synced to a main database. A number of features of Rockset make it well-suited for this function.
Converged Indexing
Rockset’s Converged Index™ is a Rockset-specific function through which all fields are listed robotically. There isn’t a have to create and keep indexes or fear about which fields to index. Rockset indexes each single discipline, together with nested fields. Rockset’s Converged Index is essentially the most environment friendly technique to arrange your information and permits queries to be obtainable virtually immediately and carry out extremely quick.
Rockset shops each discipline of each doc in an inverted index (like Elasticsearch does), a column-based index (like many information warehouses do), and in a row-based index (like MongoDB or PostgreSQL). Every index is optimized for various kinds of queries.
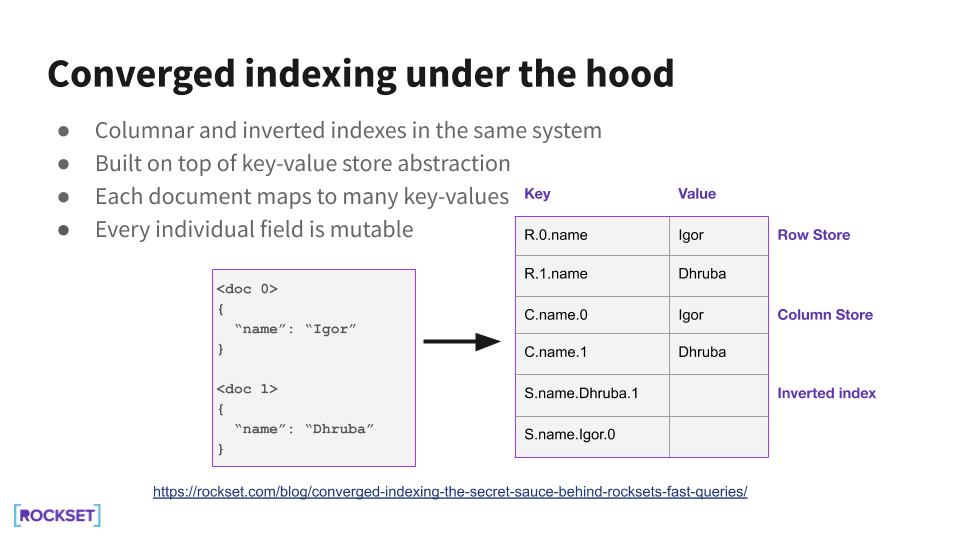
Rockset is ready to index all the pieces effectively by shredding paperwork into key-value pairs, storing them in RocksDB, a key-value retailer. In contrast to different indexing options, like Elasticsearch, every discipline is mutable, that means new fields might be added or particular person fields up to date with out having to reindex the whole doc.
The inverted index helps for level lookups, whereas the column-based index makes it simple to scan by way of column values for aggregations. The question optimizer is ready to choose essentially the most acceptable indexes to make use of when scheduling the question execution.
Schemaless Ingest
One other key requirement for real-time indexing is the power to ingest information with no pre-defined schema. This makes it potential to keep away from ETL processing steps when indexing information from MongoDB, which equally has a versatile schema.
Nonetheless, schemaless ingest alone is just not notably helpful if we’re not in a position to question the information being ingested. To unravel this, Rockset robotically creates a schema on the ingested information in order that it may be queried utilizing SQL, an idea termed Sensible Schema. On this method, Rockset permits SQL queries to be run on NoSQL information, from MongoDB, information lakes, or information streams.
Disaggregated Aggregator-Leaf-Tailer Structure
For real-time indexing, it’s important to ship real-time efficiency for ingest and question. To take action, Rockset makes use of a disaggregated Aggregator-Leaf-Tailer structure that takes benefit of cloud elasticity.
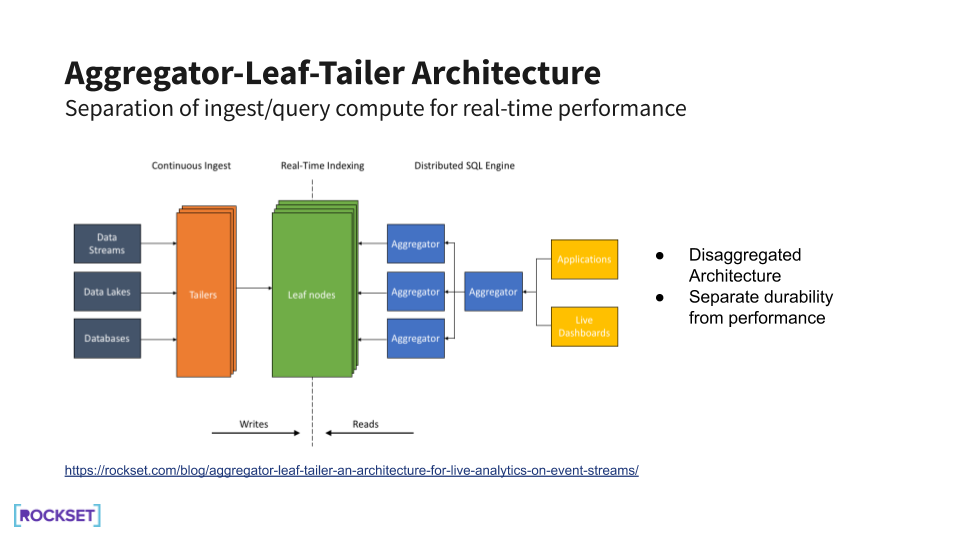
Tailers ingest information constantly, leaves index and retailer the listed information, and aggregators serve queries on the information. Every element of this structure is decoupled from the others. Virtually, which means that compute and storage might be scaled independently, relying on whether or not the appliance workload is compute- or storage-biased.
Additional, inside the compute portion, ingest compute might be individually scaled from question compute. On a bulk load, we are able to spin up extra tailers to attenuate the time required to ingest. Equally, throughout spikes in software exercise, we are able to spin up extra aggregators to deal with the next fee of queries. Rockset is then in a position to make full use of cloud efficiencies to attenuate latencies within the system.
Utilizing MongoDB and Rockset Collectively
MongoDB and Rockset just lately partnered to ship a absolutely managed connector between MongoDB Atlas and Rockset. Utilizing the 2 providers collectively brings a number of advantages to customers:
- Use any information in actual time with schemaless ingest – Index constantly from MongoDB, different databases, information streams, and information lakes with build-in connectors.
- Create APIs in minutes utilizing SQL – Create APIs utilizing SQL for complicated queries, like search, aggregations, and joins.
- Scale higher by offloading heavy reads to a velocity layer – Scale to hundreds of thousands of quick API calls with out impacting manufacturing MongoDB efficiency.

Placing MongoDB and Rockset collectively takes a number of easy steps. We recorded a step-by-step walkthrough right here to indicate the way it’s achieved. It’s also possible to take a look at our full MongoDB.dwell session right here.
Able to get began? Create your Rockset account now!
Different MongoDB sources: