This sponsored article is delivered to you by NYU Tandon College of Engineering.
With so most of the objects we work together with in our each day lives — from soaps and fertilizers to prescription drugs to petrochemicals — deriving from merchandise of the chemical {industry}, the sector has change into a significant supply of financial exercise and employment for a lot of nations, together with the US and China. However as the worldwide demand for chemical merchandise continues to develop, so do the {industry}’s emissions.
These emissions are approaching a tipping level, and the businesses accountable for creating these needed merchandise are more and more choices to assist offset their air pollution outputs.
A variety of presidency laws aimed toward attaining zero-carbon emissions are driving this migration. These greenhouse emissions laws will progressively come into impact within the coming many years, culminating, for instance, within the European Union’s intention to scale back 95 p.c of 1990 stage greenhouse emissions by 2050. These and different worldwide laws on greenhouse emissions might threaten as much as 12 p.c of all U.S. exports (US $220 billion). The duty is clearly huge, not only for the chemical manufacturing {industry} itself however for the bigger economic system.
 André Taylor (middle), Heart Director for DC-MUSE, working with college students from the unit operations senior lab course at NYU Tandon.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
André Taylor (middle), Heart Director for DC-MUSE, working with college students from the unit operations senior lab course at NYU Tandon.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
Now, a brand new analysis group has arisen to sort out essentially the most daunting job looming over the {industry}: Easy methods to make industrial chemistry — particularly petrochemistry — greener and extra sustainable, partly to satisfy the escalating calls for of those greenhouse emission laws. The multi-institutional effort known as Decarbonizing Chemical Manufacturing Utilizing Sustainable Electrification, or DC-MUSE, based on the NYU Tandon College of Engineering and encompassing quite a lot of colleges and establishments.
“The chemical {industry} has distinctive wants, as a result of there are completely different necessities inside the sector,” says André Taylor, Heart Director and Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NYU Tandon. “On one facet, you will have excessive quantity, commodity chemical compounds which have low margins — merchandise like feed shares for instance. And these are the merchandise that generate a lot of the greenhouse fuel emissions. However then you will have specialty chemical corporations that work with just a little bit extra greater finish merchandise which can be low quantity however extremely worthwhile, like medication and drugs. They’ve the identical downside with sustainability, however the options are completely different. That’s what DC-MUSE is addressing.”
A brand new begin for decarbonizing chemical manufacturing
DC-MUSE was conceived in the summertime of 2020 in a workshop attended by over 40 corporations and establishments, and arranged by a planning grant from the Nationwide Science Basis to construct capability in convergent analysis. Its intention is to develop applied sciences and methods to assist the U.S. chemical {industry} migrate from thermal-based manufacturing processes to electricity-based ones.
Many specialists imagine that step one in overhauling the chemical {industry} will contain transferring away from thermally-driven chemical reactions and separation processes that require warmth from fossil gas combustion and transferring in direction of reactions that use electrical energy generated by renewable assets, like wind and photo voltaic.
“DC-MUSE brings a singular contribution to the sector of electrification of the chemical {industry} via our multidisciplinary strategy,” says Elizabeth Biddinger, Deputy Director of DC-MUSE. “We’re in a position to work on the nuances of electrified reactions from a elementary via utilized scale. We’re in a position to mannequin how these reactions can be carried out within the chemical plant and we’re in a position to think about how the grid and chemical plant would work synergistically collectively.”
Whereas this migration has already began to happen, with penetration of renewable sources into the U.S. electrical grid doubling prior to now decade, the applied sciences for integrating these sources into cost-effective electrified chemical processes has remained virtually non-existent.
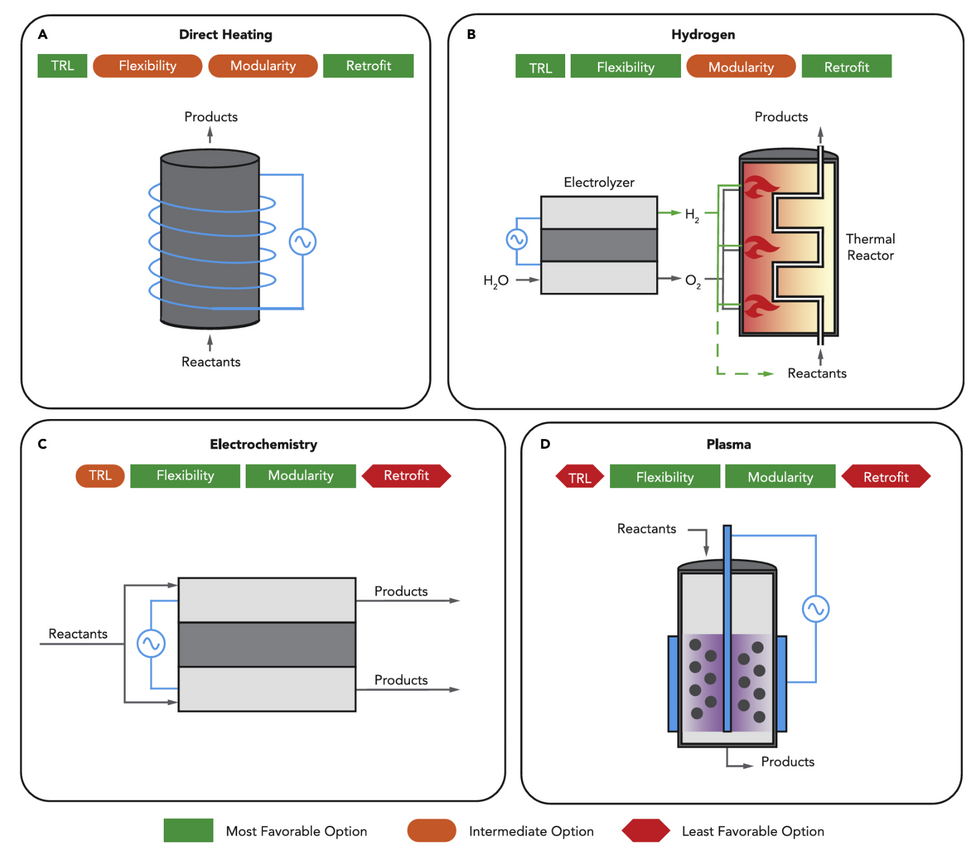 Of their evaluation of decarbonization strategies, DC-MUSE researchers recognized pathways together with resistive, microwave, and inductive heating methods. Labels embrace qualitative characterization of every pathway’s attributes throughout varied dimensions related for scalability, together with (1) know-how readiness ranges (TRLs), (2) course of flexibility, (3) modularity of chemical manufacturing course of as a complete, and (4) amenable for retrofitting for current manufacturing services.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
Of their evaluation of decarbonization strategies, DC-MUSE researchers recognized pathways together with resistive, microwave, and inductive heating methods. Labels embrace qualitative characterization of every pathway’s attributes throughout varied dimensions related for scalability, together with (1) know-how readiness ranges (TRLs), (2) course of flexibility, (3) modularity of chemical manufacturing course of as a complete, and (4) amenable for retrofitting for current manufacturing services.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
DC-MUSE has already begun laying the groundwork for this endeavor, using a multi-institution, collaborative strategy to analysis and outreach, with the assist of $1.2 million in grants from the Alfred P. Sloan Basis. The researchers laid out the challenges they’re going through in a paper within the journal Joule earlier this yr.
Within the paper, the researchers determine 4 technological pathways — starting from near-term choices to further-out applied sciences in want of quick analysis — with the purpose of analyzing how efficient they is likely to be in long-term efforts for decarbonization.
The primary two pathways straight substitute fossil fuel-produced warmth (which facilitates the reactions inherent in chemical manufacturing) with electrical energy or electrochemically generated hydrogen. The researchers counsel that each choices could possibly be deployed now and probably be used to retrofit current services.
Electrolytic hydrogen can also be highlighted as a chance to interchange fossil fuel-produced hydrogen (a course of that emits carbon dioxide) as a essential chemical feedstock. In 2020, fossil-based hydrogen provided almost all hydrogen demand (90 megatons) within the chemical and refining industries — hydrogen’s largest shoppers.
The subsequent two pathways launched — using electrochemistry and plasma — are much less technologically mature however have the potential to interchange energy- and carbon-intensive thermochemical processes presently used within the {industry}. By adopting electrochemical processes or plasma-driven reactions as an alternative, chemical transformations can happen at decrease temperatures and pressures, probably enhancing effectivity.
A big barrier to deep decarbonization of chemical manufacturing pertains to its complicated, multi-product nature. However, in response to the researchers, every of those electricity-driven pathways helps chemical {industry} decarbonization for varied feedstock decisions and end-of-life disposal selections.
Whatever the pathway chosen, the researchers stress the necessity for lively analysis and growth and deployment of those applied sciences. Additionally they emphasize the significance of workforce coaching and growth working in parallel to know-how growth.
New {industry} partnerships
Whereas DC-MUSE has made strides in decarbonization analysis, really transformative progress would require extra intensive and deeper partnerships with {industry} leaders. Because the researchers proceed their work in growing innovative applied sciences, the group has additionally been busy conducting outreach to potential companions within the {industry}.
Early this Fall, the DC-MUSE group gathered members of the {industry}, together with huge names from the pharmaceutical and power sectors, to collect concepts and assess industrial wants. One initiative is to ascertain an NSF Business-College Cooperative Analysis Heart (IUCRC) to develop an industry-driven analysis portfolio with the purpose of catalyzing the decarbonization of the chemical sector.
“We have to work along with {industry} to determine essentially the most useful path for decarbonization,” says Simon Mashala, Heart Managing Director. “Particularly for American corporations, investments in long-term decarbonization methods haven’t been substantial. In Europe, the place shoppers are typically extra unforgiving of corporations who hurt the atmosphere, the {industry} has a head begin. For America’s chemical sector to keep up its competitiveness, huge adjustments must be made.”
“Strong investments in long-term decarbonization options can guarantee the way forward for the sector, and that’s the place partnerships with DC-MUSE can transformationally change the outlook of the {industry},” he provides.
Business-university collaborations have huge potential to speed up innovation and deployment of decarbonization applied sciences
The NSF IUCRC program offers a construction for educational researchers to conduct elementary, pre-competitive analysis of shared curiosity to {industry} and authorities organizations. Taking part organizations pay membership charges in order that they will collectively envision and fund analysis, with at the least 90 p.c of member funds allotted to the direct prices of shared analysis tasks.
For DC-MUSE companions, the advantages they obtain embrace accessing data, services, tools, and mental property in a extremely cost-efficient mannequin; leveraging Heart analysis outcomes of their future proprietary tasks; interacting in a casual, collaborative means with different personal sector and authorities entities with shared pursuits; and figuring out and recruiting expertise. DC-MUSE is presently within the strategy of recruiting members, who will be capable to get in on the bottom ground of the chance.
Business-university collaborations have huge potential to speed up innovation and deployment of decarbonization applied sciences. When educational researchers and firm scientists work carefully collectively, they will higher perceive real-world issues and constraints. And analysis might be quickly translated into industrial options. Nevertheless, these partnerships have been missing within the decarbonization house. DC-MUSE goals to alter that via collaborative initiatives just like the NSF IUCRC.
A college-wide dedication to sustainable engineering
Whereas DC-MUSE is a collaboration between a number of establishments, its coronary heart is at NYU Tandon. And NYU Tandon has created an area the place sustainability infuses a big portion of the work produced there.
For instance, in 2022 Miguel Modestino was named the director of a brand new Sustainable Engineering Initiative (SEI) at NYU Tandon, which is dedicated to growing complete and tangible engineering strategies of addressing the huge array of environmental challenges now going through the world.
Modestino, the Donald F. Othmer Affiliate Professor of Chemical Engineering, is himself a member of DC-MUSE, and Taylor is a member of the Sustainable Engineering Initiative. The initiative’s researchers, who embrace school throughout a number of departments, shall be targeted on a framework they name AMRAd: avoiding emissions and pollution every time doable; mitigating them when complete avoidance isn’t doable; remediating in circumstances the place mitigation is inadequate, similar to when coping with conditions that developed earlier than Nineteen Seventies-era environmental protections have been put into place; and, lastly, growing engineering variations to conditions past human management, similar to when localized flooding happens, virtually inevitably carrying contaminants.
Whereas nonetheless new, the initiative is ramping up its actions. It presently has a number of openings for school members and researchers to affix the group, and new lab areas are being arrange as a way to accommodate the brand new analysis.
Modestino and the opposite researchers concerned are making use of the framework to a wide range of areas, similar to clear transportation, industrial decarbonization, environment friendly and resilient energy grids, catastrophe threat evaluation, environmental justice, and others.
Whereas nonetheless new, the initiative is ramping up its actions. It presently has a number of openings for school members and researchers to affix the group, and new lab areas are being arrange as a way to accommodate the brand new analysis.
Past analysis, SEI has a powerful academic platform. An interdisciplinary group of college members, led by Professor Ingrid Paredes, have began to combine sustainability into the first-year engineering curriculum at NYU Tandon, together with Common Engineering, arithmetic, physics, expository writing, and extra. Even one thing so simple as framing examination questions as sustainability issues may help recruit these younger engineers into tackling a number of the planet’s most cussed points.
 Miguel Modestino, Director of the Sustainable Engineering Initiative at NYU Tandon and a member of DC-MUSE.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
Miguel Modestino, Director of the Sustainable Engineering Initiative at NYU Tandon and a member of DC-MUSE.NYU Tandon College of Engineering
“Engineering selections are usually not made in a vacuum — they’re formed by and might form the environment, and that may be a accountability that our engineering neighborhood holds,” says Paredes. “We hope for our college students to grasp this accountability early of their educational years, and to think about sustainability as a key a part of engineering design processes.”
Past the College, Modestino has been establishing connections with native green-tech industries. AIR COMPANY — a Brooklyn-based firm that makes use of CO2 to create sustainable chemical compounds and fuels that may be utilized to a wide range of shopper and industrial merchandise — now has entry to a moist laboratory incubation houseon campus. And the Initiative has introduced in native entrepreneurs to show Tandon college students about the right way to create and assist startups within the inexperienced tech house.
“We hope to have many different sustainable engineering corporations becoming a member of us sooner or later, since we now have really distinctive services and a vibrant innovation ecosystem to supply them. With enhanced industry-university collaboration, speedy progress might be made. It’s time for extra corporations to companion with educational initiatives like DC-MUSE and SEI to decarbonize chemical manufacturing and construct a sustainable future,” Modestino says. “In the end, our purpose is to forge fruitful collaborations and assist New York Metropolis change into a world cleantech innovation hub.”
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net


