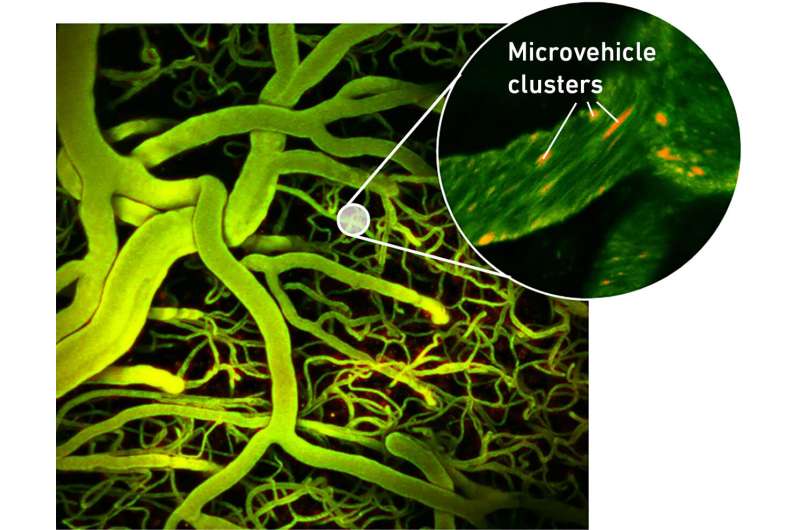
ETH Zurich researchers have proven for the primary time that microvehicles will be steered by means of blood vessels within the brains of mice utilizing ultrasound. They hope that this may ultimately result in remedies able to delivering medicine with pinpoint precision. Their research is printed in Nature Communications.
Mind tumors, mind hemorrhages and neurological and psychological circumstances are sometimes laborious to deal with with treatment. And even when efficient medicine can be found, these are likely to have extreme negative effects as a result of they flow into all through the mind and never simply the world they’re meant to deal with.
In gentle of this case, researchers have excessive hopes of someday with the ability to present a extra focused strategy that may ship medicines to very particularly outlined areas. To this finish, they’re within the technique of creating mini-transporters that may be guided by means of the dense maze of blood vessels.
Researchers at ETH Zurich, the College of Zurich and the College Hospital Zurich have now managed for the primary time to information microvehicles by means of the blood vessels within the mind of an animal utilizing ultrasound.
Ultrasound as an alternative of magnetism
In comparison with various navigation applied sciences similar to these based mostly on magnetic fields, ultrasound provides sure advantages. Daniel Ahmed, Professor of Acoustic Robotics at ETH Zurich and supervisor of the research, explains, “Along with being extensively used within the medical subject, ultrasound is secure and penetrates deep into the physique.”
For his or her microvehicle, Ahmed and his colleagues used gas-filled microbubbles coated in lipids—the identical substances that organic cell membranes are product of. The bubbles have a diameter of 1.5 micrometers and are presently used as distinction materials in ultrasound imaging.
Because the researchers have now proven, these microbubbles will be guided by means of blood vessels. “Since these bubbles, or vesicles, are already permitted to be used in people, it is seemingly that our expertise can be permitted and utilized in remedies for people extra shortly than different forms of microvehicles presently in growth,” Ahmed says.
One other good thing about the ultrasound-guided microbubbles is that they dissolve within the physique as soon as they’ve executed their job. When utilizing one other strategy, magnetic fields, the microvehicles must be magnetic, and it isn’t simple to develop biodegradable microvehicles. Furthermore, the microbubbles developed by the ETH Zurich researchers are small and clean. “This makes it simple for us to information them alongside slim capillaries,” says Alexia Del Campo Fonseca, a doctoral scholar in Ahmed’s group and lead creator of the research.
Going in opposition to the circulate
Over the previous few years, Ahmed and his group have been working within the lab to develop their methodology for guiding microbubbles by means of slim vessels. Now, in collaboration with researchers from the College of Zurich and College Hospital Zurich, they’ve examined this methodology on blood vessels within the brains of mice. The researchers injected the bubbles into the rodents’ circulatory system, the place they’re swept alongside within the bloodstream with none outdoors assist.
Nonetheless, the researchers managed to make use of ultrasound to carry the bubbles in place and information them by means of the mind vessels in opposition to the route of blood circulate. The researchers have been even in a position to information the bubbles by means of convoluted blood vessels or get them to vary route a number of occasions so as to steer them into the narrowest branches of the bloodstream.
To manage the microvehicles’ actions, the researchers additionally connected 4 small transducers to the skin of every mouse’s cranium. These units generate vibrations within the ultrasonic vary, which unfold by means of the mind as waves. At sure factors within the mind, the waves emitted by two or extra transducers can both amplify one another or cancel one another out. The researchers information the bubbles utilizing a complicated methodology of adjusting the output of every particular person transducer. Actual-time imaging reveals them what route the bubbles are transferring in.
To create the imaging for this research, the researchers used two-photon microscopy. Sooner or later, additionally they wish to use ultrasound itself for imaging and plan to reinforce ultrasound expertise for this function.
On this research, the microbubbles weren’t geared up with medicines. The researchers first needed to indicate that they may information the microvehicles alongside blood vessels and that this expertise is appropriate to be used within the mind. That is the place there are promising medical purposes, together with within the therapy of most cancers, stroke and psychological circumstances.
The researchers’ subsequent step can be to connect drug molecules to the skin of the bubble casing for transport. They wish to improve the whole methodology to the purpose at which it may be utilized in people, hoping it should someday present the idea for the event of recent remedies.
Extra data:
Alexia Del Campo Fonseca et al, Ultrasound trapping and navigation of microrobots within the mouse mind vasculature, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41557-3
Quotation:
Researchers steer microvehicles by means of blood vessels within the mouse mind utilizing ultrasound (2023, December 7)
retrieved 7 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-microvehicles-blood-vessels-mouse-brain.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


