Having labored in a wide range of cybersecurity roles for big firms and startups for twenty years, Toptal cybersecurity advisor Ilia Tivin has a deep understanding of the sector—previous, current, and future. This Q&A is a abstract of a current ask-me-anything-style Slack discussion board wherein Tivin fielded questions on synthetic intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity from different Toptal engineers and safety professionals around the globe.
Editor’s be aware: Some questions and solutions have been edited for readability and brevity.
Present and Future Makes use of of AI in Cybersecurity
Do you assume trendy cybersecurity requires AI options?
—Ok.S., Montreal, Canada
Sure, I do assume AI will probably be required sooner or later. To be frank, AI’s capability for creating exploits is pretty weak in the present day. However that’s going to escalate over time—and so ought to our defenses.
Did you ever encounter a enterprise case wherein AI was used to seek out safety breaches?
—J.O., Fortaleza, Brazil
The reply is dependent upon the way you outline a safety breach. AI that’s correctly programmed to look and sift by code can positively be used to establish vulnerabilities. You may as well have AI generate very persuasive phishing emails that incorporate particular particulars regarding your group. I haven’t but seen something outdoors of phishing emails, however that doesn’t imply it hasn’t occurred.
What are the downsides of AI in cybersecurity?
—Ok.B., Bergerac, France
The downsides of AI in cybersecurity are the identical because the downsides of AI in each different area. After we apply AI, we delegate a layer of decision-making to a robotic. However generally we can not absolutely perceive how the robotic arrives at its selections. If AI decides wrongly about safety automations, checks, or compliance, for instance, it will possibly result in vital regulatory fines, safety compromises, or lack of mental property.
What new cybersecurity dangers would possibly trendy AI (e.g., generative AI) create?
—R.L., Lake Oswego, United States
A threat that involves thoughts is overreliance on AI, even when it advantages from the newest developments. As builders transfer to make use of AI to code, in addition to to examine their code utilizing that very same AI, they might inadvertently introduce safety vulnerabilities to the code.
How would possibly AI enhance cybersecurity sooner or later?
—N.H., Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina
First, AI will hopefully cease supplying mistaken info and errors. I see a transfer towards extra automation worldwide. I additionally predict the enhancement of inspection strategies, contingent on the nations and jurisdictions wherein the assorted AI firms function. Inspection enhancement is much less prone to be carried out in Europe, as a result of its sturdy regulatory frameworks.
Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
|
Upsides |
Downsides |
|---|---|
|
|
AI in Cybersecurity Examples
Do you employ any AI cybersecurity instruments and, in that case, which of them would you advocate?
—M.D., Seattle, United States
To enrich the safety afforded by purchasers’ normal safety merchandise, I take advantage of the AironWorks phishing simulation platform, the place custom-made phishing simulations are generated for organizations to examine the preparedness and safety consciousness of their workers. However at the moment, from a testing perspective, I don’t assume that AI is nicely positioned to be of a lot assist in cybersecurity. Positive, all the large firms declare to have adopted AI for cybersecurity of their product choices, however the extent to which it’s usable varies.
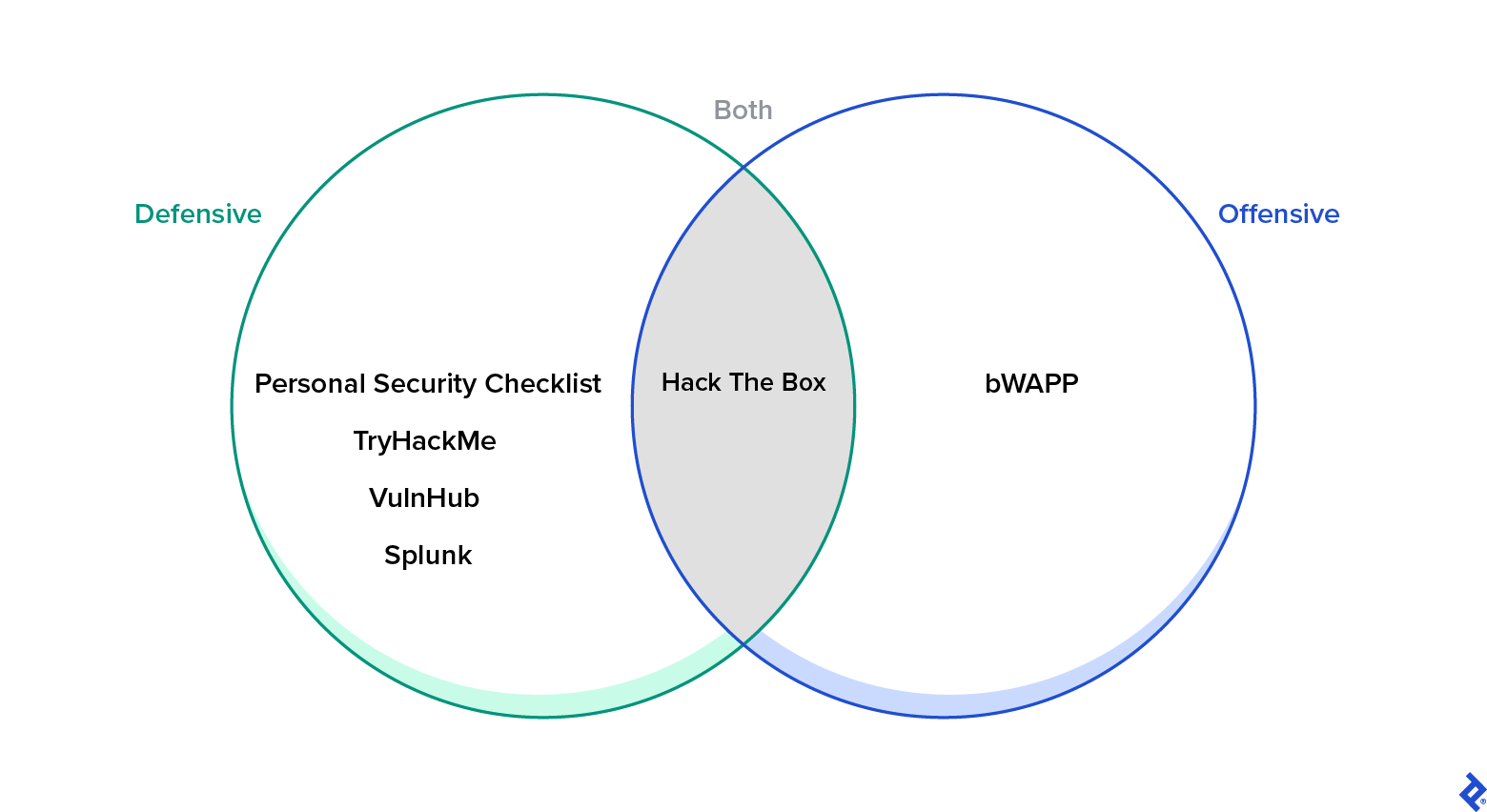
Are you able to recommend a enjoyable web site the place safety hobbyists can mess around with and uncover totally different subjects of offensive or defensive safety?
—J.O., Fortaleza, Brazil
I, for one, am a giant fan of private safety. From a defensive perspective, I at all times advocate the Private Safety Guidelines, a GitHub listing of 300-plus ideas for safeguarding digital safety and privateness. You need to use TryHackMe as a option to get began in safety, and even compete in a few of its on-line challenges. VulnHub is superior even when it’s not recurrently up to date. Challenges at Splunk—which seems prepared for a refresh—come to thoughts. From an offensive perspective, bWAPP is an effective Docker container that lets you attempt to exploit an online utility for your self. And there’s additionally Hack The Field, which incorporates each defensive and offensive parts.
I hear conflicting views relating to Mac safety: Some say that Mac is already safe, whereas others really feel that you may’t be too cautious. What’s your opinion?
—M.Z., Santa Clarita, United States
Properly, there are considerably fewer Mac customers than PC customers, which may clarify why a majority of cyberattacks are geared toward PCs. Nevertheless, on common, Mac customers spend far extra money on their computer systems than PC customers do—so you possibly can see how Mac additionally makes for a well-liked goal. Judging by the numerous OS safety fixes launched these days, it appears to me—and likewise to Wired, which printed an article on this matter—as if Apple agrees that elevated Mac concentrating on is an actual risk.
Would you advocate enhancing safety on Mac computer systems with antivirus instruments like Avast, or are these a waste of cash?
—M.Z., Santa Clarita, United States
You may at all times go free with ClamAV together with retaining your software program up to date. Additionally, Microsoft Defender is now accessible for Mac.
The editorial workforce of the Toptal Engineering Weblog extends its gratitude to Marco Jardim for reviewing the technical content material offered on this article.