Researchers on the Institute of Bodily Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS) have demonstrated that inexperienced tea–silver nanoparticles as a robust instrument in opposition to pathogens corresponding to micro organism and yeast. Their work is revealed in Nanoscale Advances.
Their aim was to develop an environment friendly technique to fight micro organism which are in any other case unaffected by antimicrobial brokers, corresponding to antibiotics.
The overuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of resistance to those compounds, changing into one of many greatest well being threats worldwide.
In consequence, antibiotic resistance has emerged sooner than the development of antibiotics, a phenomena researched by the group of scientists from the IPC PAS below the supervision of Prof. Jan Paczesny, who proposed new nanoformulations to be used in opposition to widespread and difficult pathogens corresponding to ESKAPE micro organism (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter spp.) and different problematic yeast pathogens corresponding to Candida auris or Cryptococcus neoformans.
These microorganisms, handled with commercially accessible antibiotics, quickly develop antibiotic resistance. Researchers selected ESKAPE because the goal group since these pathogens result in severe illnesses, from sepsis to even most cancers.
Just a few months in the past, Paczesny’s group determined to attempt combining silver nanoparticles, that are recognized for his or her antimicrobial and antifungal properties, and tea extracts wealthy in polyphenols that possess antioxidant properties. The idea was constructed to boost broad-spectrum efficacy in opposition to pathogens utilizing inexperienced hybrid silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), that are considerably simpler than all substances and much more efficient than sure antibiotics.
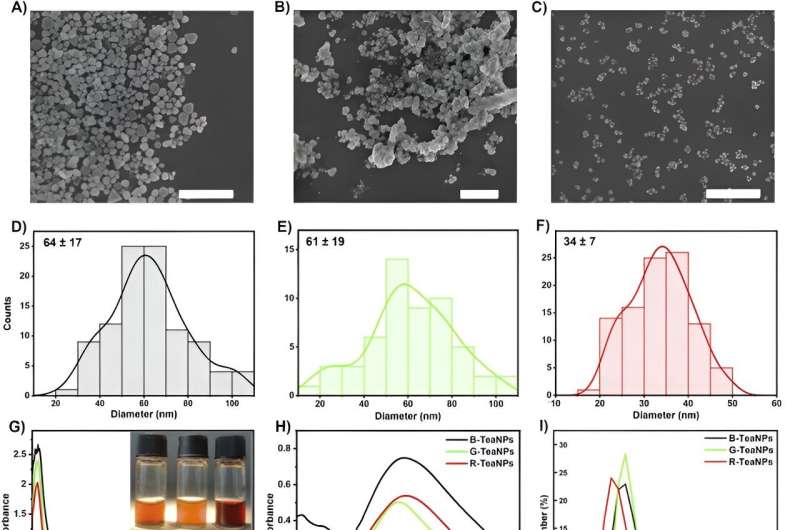
Why are these hybrid particles so particular? Of their work, three well-known tea varieties: black tea (B-Tea), inexperienced tea (G-Tea) and Pu-erh tea (R-Tea) have been used as a capping agent, which acts as a stabilizer to guard the synthesized particles from aggregation. On this manner, the particles provide a excessive energetic floor space in comparison with different formulations. Moreover, such synthesis is eco-friendly for the usage of pure substances throughout precipitation.
The constructions produced fluctuate in form and dimension from 34 to 65 nm, relying on the kind of tea used throughout synthesis, and present totally different reactivity in the direction of microorganisms.
Initially, silver nanoparticles produced within the presence of tea extracts (B-TeaNPs, G-TeaNPs and R-TeaNPs) have been used to deal with Gram-negative (E. coli) and Gram-positive (E. faecium) bacterial strains to check the impact on strains with totally different cell envelope morphologies. They regarded on the interactions between the manufactured nanoparticles and the pathogens to find out efficacy, evaluating the outcomes with commercially accessible antibiotics.
The ESKAPE pathogens have been then examined in keeping with a protocol for the best focus and composition of the particles, revealing as much as a 25% lower within the variety of bacterial cells in E. faecium and a 90% lower within the case of E. cloacae. Apparently, the inexperienced silver nanoparticles additionally confirmed antifungal exercise, resulting in an 80% lower within the variety of viable cells of C. auris and a few 90% lower for C. neoformans.
Sada Raza, the research’s first creator, claims, “What’s extra, the dimensions of nanoparticles is normally associated to the cytotoxic impact of nanomaterials, with smaller particles being extra cytotoxic. This could favor management AgNPs and R-TeaNPs over G-TeaNPs and B-TeaNPs in our experiments. This was not the case. In most experiments, C-AgNPs and R-TeaNPs confirmed the bottom antimicrobial efficacy. That is in step with different research, which demonstrated that dimension just isn’t a main issue affecting the antimicrobial exercise of AgNPs.”
The antibacterial and antifungal properties of silver nanoparticles made with tea extracts are higher than these of silver nanoparticles alone as a result of their excessive content material of phenolic compounds, isoflavonoids (particularly catechins corresponding to epigallocatechin (EGC) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)). These mixtures, utilizing biologically energetic tea extracts and smaller quantities of silver nanoparticles, seem like a possible option to fight a spread of infections and even exchange antibiotics in some purposes.
“We established that silver nanoparticles synthesized with tea extracts have larger antibacterial properties than silver nanoparticles alone. Subsequently, decrease dosages of TeaNPs might be used (0.1 mg mL−1). We confirmed that in some instances, the synergistic impact of tea extracts and silver nanoparticles allowed for efficacy larger than that of antibiotics (ampicillin) when examined on the identical concentrations (0.1 mg mL−1) and after a comparatively brief publicity time of three hours,” says Mateusz Wdowiak, co-author of this work.
The researchers discovered that the antimicrobial hybrid nanoparticles resulted in a big discount in micro organism in comparison with antibiotics or compounds individually. Though not all micro organism have been killed, it is a vital enchancment that would assist the therapy of superbugs utilizing a lot decrease doses than different commercially accessible compounds.
The quantity of hybrid silver nanoparticles wanted to beat micro organism or fungal infections is extraordinarily low, making them cost-effective, so the important thing to utilizing them effectively just isn’t solely performance, but additionally the low value of utility.
It’s an method that will also be tailored to fight different difficult-to-treat bacterial infections. The brand new nanoparticles developed by researchers on the IPC PAS might convey us one step nearer to successfully killing lethal drug-resistant superbugs, offering a substitute for antibiotics in opposition to Gram-negative and Gram-positive micro organism. This research additionally reveals how way more work there may be to be executed on this area. Compounds used individually have been a lot much less efficient than the inexperienced hybrid.
Sooner or later, the researchers’ important aim is to make use of nanoparticles in on a regular basis life, beginning with agricultural purposes. On a bigger scale, the proposed materials may be utilized in biomedical purposes, corresponding to an additive for wound dressings to guard in opposition to Gram-negative and Gram-positive micro organism. Additionally they hope to make use of nanotechnology to develop extra focused remedies for drug-resistant superbugs.
Extra info:
Sada Raza et al, Enhancing the antimicrobial exercise of silver nanoparticles in opposition to ESKAPE micro organism and rising fungal pathogens by utilizing tea extracts, Nanoscale Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3NA00220A
Offered by
Polish Academy of Sciences
Quotation:
Enhancing the antimicrobial exercise of silver nanoparticles in opposition to pathogens by utilizing tea extracts (2023, November 17)
retrieved 18 November 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-11-antimicrobial-silver-nanoparticles-pathogens-tea.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


