Researchers who’re working to search out alternate options to lithium-ion batteries have turned their consideration to potassium-ion batteries. Potassium is an considerable useful resource, and the know-how capabilities in a lot the identical approach as lithium-ion batteries, however these batteries haven’t been developed at a big scale as a result of the ionic radius causes issues in power storage and substandard electrochemical efficiency.
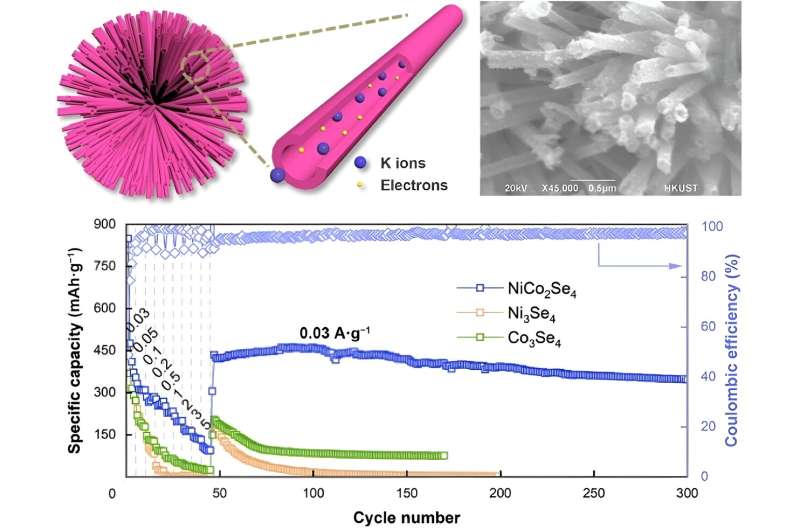
To resolve this drawback, researchers are contemplating NiCo2Se4, a bimetallic selenide, to create sphere-shaped electrodes. The spheres are constructed with NiCo2Se4 nanotubes, which enhance the electrochemical reactivity for sooner switch and storage of potassium ions.
The analysis was introduced in a paper printed in Vitality Supplies and Gadgets on 14 September.
“Bimetallic selenides mix the ameliorating options of two metals, which synergize by displaying wealthy redox response websites and excessive electrochemical actions. One bimetallic selenide, NiCo2Se4, was beforehand studied for sodium storage, supercapacitors, and electrocatalysts and presents appreciable potential for potassium ion storage.
“By synthesizing NiCo2Se4 utilizing a two-step hydrothermal course of, a nanotube construction with flower-like clusters develops, creating handy channels for potassium ion/electron switch,” stated Mingyue Wang, a researcher on the Engineering Analysis Heart of Vitality Storage Supplies and Gadgets at Xi’an Jiaotong College in Xi’an, China.
Initially, Ni-Co precursor spheres with strong nanoneedles are ready. These spheres have a well-defined crystalline construction that’s then uncovered to selenide throughout a course of known as selenization. This course of introduces selenium to the Ni-Co precursor, growing the NiCo2Se4 nanotube shell.
The hole tubes type due to a phenomenon known as the Kirkendall impact, which is when two metals transfer due to the distinction within the diffusion charges of their atoms. These nanotubes are round 35 nanometers large, giving sufficient area for the potassium ions and electrons to switch.
By quite a lot of assessments and evaluation, the researchers have been in a position to affirm how nicely the NiCo2Se4 anodes may transfer and retailer potassium ions and electrons. They discovered that NiCo2Se4 has extra lively websites than different electrode supplies, had uniformly distributed parts, and outperformed different electrodes that have been examined throughout analysis.
“The NiCo2Se4 nanotube electrode introduced a significantly better electrochemical efficiency when it comes to cyclic stability and charge functionality than different examined electrodes, together with Ni3Se4 and Co3Se4. It is because the distinctive nanotube construction of NiCo2Se4 and the synergy supplied by the co-presence of two metals,” stated Wang.
These monometallic counterparts, Ni3Se4 and Co3Se4 weren’t as profitable because the bimetallic NiCo2Se4, merely due to the way in which the 2 metals (Ni and Co) work together collectively. NiCo2Se4 additionally had the next capability, which could be very helpful for sustaining cyclic stability and high-rate efficiency.
“This work presents new insights into the design of micro/nano-structured binary steel selenides as anodes for potassium-ion batteries with extraordinary potassium ion storage efficiency,” stated Wang.
Extra info:
Mingyue Wang et al, Conversion mechanism of NiCo 2Se 4 nanotube sphere anodes for potassium-ion batteries, Vitality Supplies and Gadgets (2023). DOI: 10.26599/EMD.2023.9370001
Supplied by
Tsinghua College Press
Quotation:
Electrodes with hole nanotubes enhance efficiency of potassium-ion batteries (2023, October 27)
retrieved 27 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-electrodes-hollow-nanotubes-potassium-ion-batteries.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


