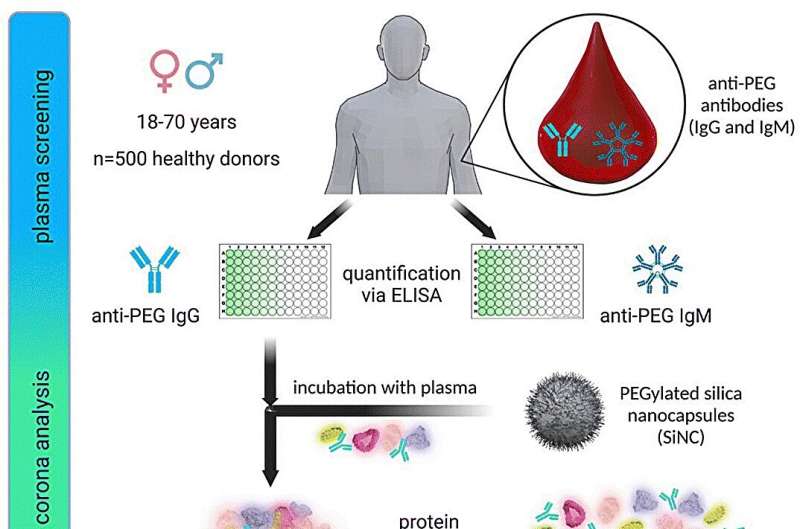
It has lengthy been recognized that folks can kind defenses and thus antibodies towards viruses. However antibodies can even develop towards polyethylene glycol (PEG), a substance utilized in cosmetics, meals and medication. These affect the effectiveness of medicine.
A staff of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Analysis has now investigated how widespread these antibodies already are in German society and the way they could affect medical therapies utilizing nanocarriers. They’ve printed their present ends in Nanoscale Horizons.
A virus invades the physique and the immune system begins to work: Antibodies develop that battle the an infection. On the similar time, an immune reminiscence builds up in order that antibodies will be shortly made obtainable within the occasion of a brand new an infection. Surprisingly, antibodies can even kind towards polyethylene glycol (PEG), a molecule with a reasonably easy construction.
Along with beauty merchandise—from lotions, perfumes and lotions to lipstick—polyethylene glycol can also be utilized in medication. Right here, it serves as a form of camouflage coat towards the physique’s personal immune system, thus rising the circulation time of an lively ingredient within the blood.
“For us, PEG is fascinating for coating nano-sized drug carriers with it,” says Svenja Morsbach, group chief in Katharina Landfester’s division on the MPI for Polymer Analysis. On this method, the researchers obtain an extended circulation time for the drug capsules, that are solely nanometers in dimension and may very well be an essential part in novel most cancers therapies sooner or later, for instance.
Of their research, the staff led by Morsbach and Landfester examined greater than 500 blood samples from sufferers taken in 2019. “The antibodies shaped towards PEG connect themselves to the coated nanocarriers, thus counteracting the impact that’s really desired: the nanocarrier turns into seen to the immune system and is eliminated earlier than it could exert its impact,” explains Katharina Landfester, director of the division.
The researchers led by Morsbach and Landfester assume that therapies must be tailored sooner or later to reply to this habits of the immune system. Of their statistical research of blood samples, they discovered that PEG antibodies have been already detectable in 83% of the samples examined.
The focus of PEG antibodies within the blood correlates anti-proportionally with the age of the individual examined: the older the individual, the less PEG antibodies have been current. “We presently assume that that is as a result of rising use of PEG in numerous areas of life solely lately and the variation of the immune system in age,” says Morsbach.
In additional research, the researchers would now wish to learn how future therapies may very well be tailored to compensate for the lowered camouflage of the nanocarriers. “Concepts would come with whether or not PEG will be changed or probably distributed with altogether,” Morsbach stated. However figuring out the antibody focus in a affected person’s blood and individually adjusting the quantity of lively ingredient may be an alternate.
Extra data:
Mareike F. S. Deuker et al, Anti-PEG antibodies enriched within the protein corona of PEGylated nanocarriers impression the cell uptake, Nanoscale Horizons (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3NH00198A
Offered by
Max Planck Society
Quotation:
Nanocarriers research exhibits antibodies towards polyethylene glycol in 83% of the German inhabitants (2023, October 20)
retrieved 23 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-nanocarriers-antibodies-polyethylene-glycol-german.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


