Google’s web site: operator limits search outcomes to a single area. It is among the oldest and most useful instruments for SEO.
To make use of, kind web site: adopted by the specified URL (no house) in Google’s search field — e.g., web site:sampledomain.com.
Listed here are 5 key website positioning duties with web site:.
Utilizing the web site: Operator
1. Discover inner pages to hyperlink to
The web site: operator is helpful for finding related inner pages shortly.
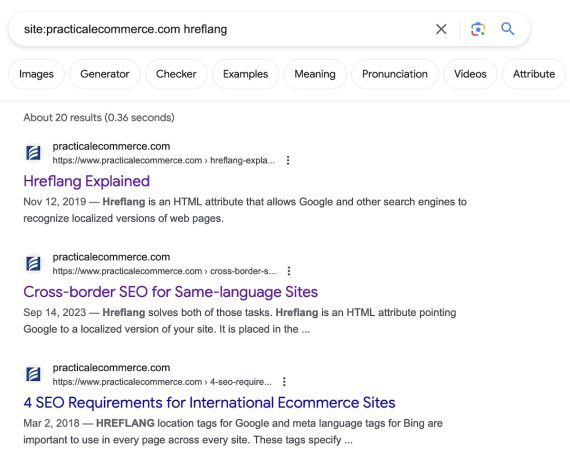
The web site: operator locates related inner pages shortly. This instance searches for “hreflang” articles.
Search optimizers as soon as used the operator to know which pages Google prioritized for any question. However that’s not dependable as a result of outcomes for web site: will not be based mostly on intent, earlier searches, and even freshness — as is the case for different queries.
Nonetheless, the web site: operator sometimes surfaces a search-optimized web page for every question, so I proceed utilizing it for inner hyperlink choices.
2. Find URLs that shouldn’t be listed
Google’s Search Console is one of the best ways to establish pages that ought to and shouldn’t be listed. Nevertheless it’s not good. Generally Search Console lists unindexed URLs which can be really listed. So use Search Console and web site: to search out listed pages that needs to be blocked, redirected, or canonicalized.
Even higher, run a number of web site: operators to verify correctly listed pages, guaranteeing:
- Tag pages will not be listed: web site:area.com inurl:tag
- Backend, admin pages will not be listed: web site:area.com inurl:admin
- Solely https URLs are listed: web site:area.com inurl:http or web site:area.com -inurl:https
From there, use Search Console’s URL inspection software to search out the explanations for improper indexation.
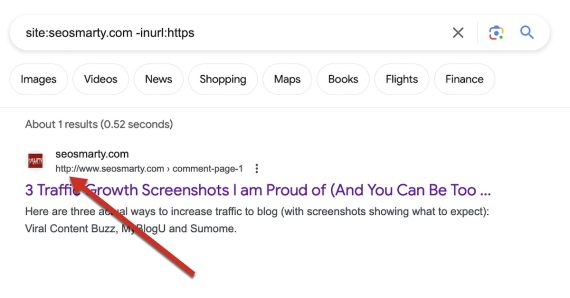
A seek for web site:seosmarty.com -inurl:https features a minus signal to exclude https pages from the outcomes.
3. Entry Google’s cache
Google’s cache exhibits how the search engine sees all parts of a web page. A web site: search can entry the cache model of a web page by clicking the three vertical dots subsequent to the title within the outcomes. The following “Extra choices” pop-up card may also state how lengthy Google has listed the web page.
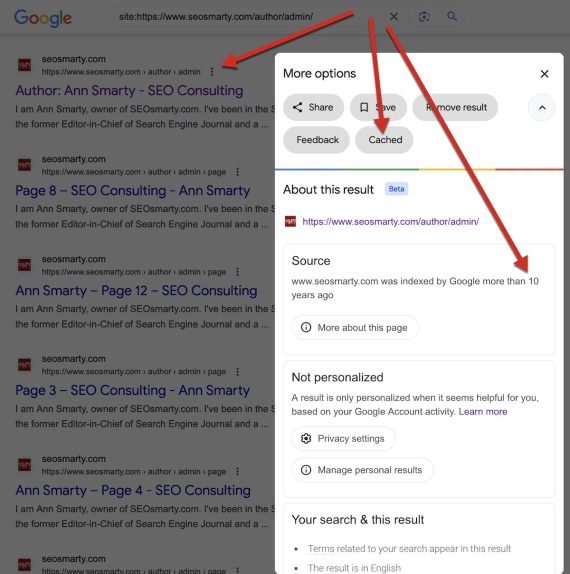
Entry the cached model of a web page through a web site: search after which clicking the three vertical dots subsequent to the title within the outcomes.
4. Preview a site’s search snippets
The content material of natural search snippets is query-dependent. Relying on the search time period, Google might rewrite the web page title, extract on-page content material as an alternative of the meta description, and show web site names as an alternative of URLs.
Nonetheless, the web site: operator will present:
- The place a snippet is tranсated.
- The web page’s publish date, per Google.
Right here’s a web page preview utilizing the web site: operator:
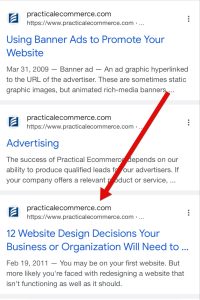
Right here’s what it seems like in a typical search. Observe the date and the title look the identical, however the query-driven snippet beneath has a distinct description and web site title. It additionally contains a picture.
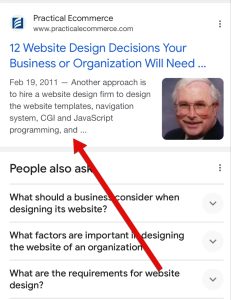
Regular snippets — with out utilizing the web site: operator — embrace a picture, amongst different variations.
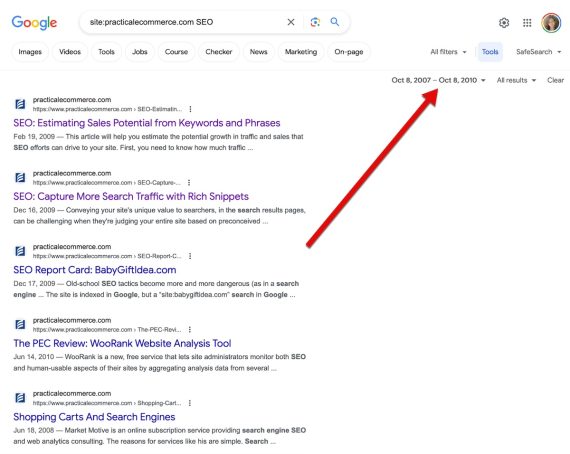
5. Discover pages to replace
Google provides a helpful date search possibility that hides behind the “Instruments” hyperlink in search outcomes. Select a date vary to search out all pages Google listed throughout that interval. It’s a fast option to discover articles to replace, particularly when publishing a associated subject.
Browser Extensions
I’m conscious of two browser extensions to entry the web site: operator shortly.
- Search Web site WE (Firefox). Spotlight any phrases on a web page and right-click. The extension will seek for these phrases on the present area or subdomain.
- Search the present web site (Google Chrome). Click on the extension icon and kind any phrase to provoke Google’s web site: seek for the present area.