Oct 12, 2023
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers have developed a brand new method to watch the habits of particular person molecules in actual time.
Key Takeaways
A brand new technique utilizing gold nanorods can lure and observe particular person molecules in real-time utilizing dynamic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (D-SERS).
Developed by the Hefei Institutes of Bodily Science in China, this system presents each sensitivity and stability for extended molecular remark.
The strategy demonstrated its effectiveness by trapping extraordinarily dilute crystal violet dye molecules, observing them for as much as 4 minutes repeatedly.
The method permits researchers to know the habits of molecules in tight nano-spaces, providing useful insights for fields like chemistry and biophysics.
This method guarantees potential for observing atomic-scale processes with out altering the molecule, offering a pure view into reactions and processes.
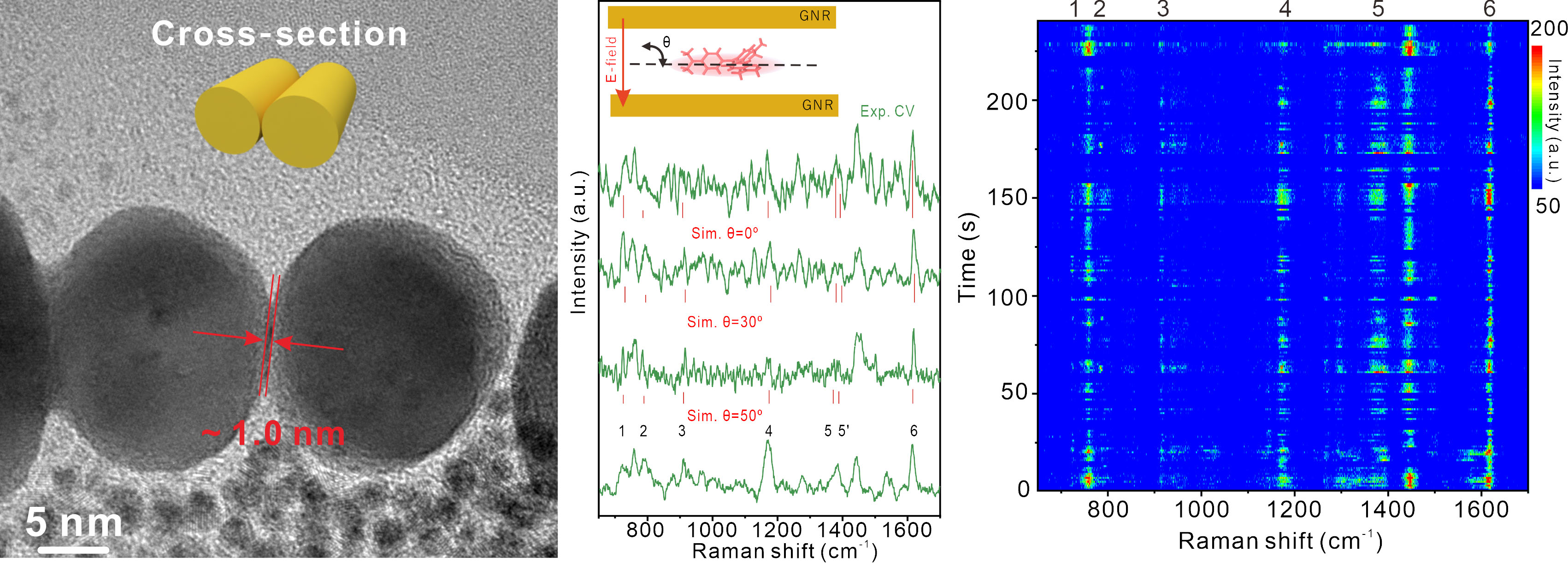
Left: Transmission electron micrograph of the cross-section of laser reconfigured gold nanorods; Center: outcomes of the detection and evaluation of single-molecule diffusion habits; Proper: outcomes of SERS-mapping of crystalline violet molecules in 4 min. (Picture: YAN Wuwen)
The Analysis
The strategy, outlined in a paper revealed within the
Journal of Bodily Chemistry Letters (
“ARTIKEL”), leverages the distinctive properties of gold nanorods to create tiny gaps that may “lure” single molecules. Monitoring the trapped molecules with an imaging method known as dynamic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (D-SERS) permits researchers to comply with the random orientations a molecule adopts in a particularly restricted house.
Although many methods can detect single molecules, steady monitoring stays difficult. The gold nanorod platform devised by chemists on the Hefei Institutes of Bodily Science in China offers the sensitivity and stability wanted for extended remark.
Gold nanorods are useful instruments in chemistry and biomedical analysis due to their robust mild absorption and scattering properties. The Chinese language researchers discovered that by alternating laser pulses of excessive and low depth, they might immediate the nanorods to attract collectively into clusters with nanoscale gaps between them.
These tiny crevices primarily function cages that isolate particular person visitor molecules whereas enhancing spectroscopic indicators. “We’ve constructed a extremely enhanced hotspot house of ~1.0 nm for long-term sustainable single-molecule remark with D-SERS,” mentioned principal investigator Dr. Liangbao Yang.
To show the method, the researchers trapped crystal violet dye molecules within the gaps. Although crystal violet concentrations have been extraordinarily dilute – only one molecule per laser spot – the spectroscopic signature remained robust sufficient to repeatedly monitor for as much as 4 minutes.
The spectra confirmed the telltale blinking sample that reveals single molecule detection. By buying fast measurements, the researchers may discern the molecule flipping to totally different orientations within the confined house. Evaluating experimental knowledge to laptop simulations, they decided essentially the most secure poses preserve the molecule comparatively flat, between 50-90 levels relative to the gold floor.
This orientation desire seemingly stems from the ultra-narrow gaps created by the method. The outcomes present new perception on the habits of molecules in restrictive nano-environments.
Whereas earlier strategies can briefly maintain a molecule in a single place, the gold nanorod platform permits remark for vastly prolonged intervals. The sturdy encapsulation protects fragile molecules from environmental disturbances.
Co-author Dr. Hyun-Dangle Shin defined the importance: “These benefits could be leveraged to additional examine the basic mechanisms of SERS and the mechanisms of chemical reactions on the single-molecule degree whatever the chemical species of the reactant.”
The researchers counsel their method may very well be tailored to include ultrafast SERS capabilities that function on the femtosecond scale. By upgrading to greater pace measurements, delicate molecular fluctuations could turn out to be perceptible.
The research demonstrates delicate real-time monitoring of an remoted biomolecule with out chemical modification or tethering. The passive trapping method may present a window into atomic-scale processes related to chemistry, biophysics, and supplies science. Optical traps that constrain however do not actively manipulate single molecules will allow researchers to comply with reactions as they naturally unfold.
 Left: Transmission electron micrograph of the cross-section of laser reconfigured gold nanorods; Center: outcomes of the detection and evaluation of single-molecule diffusion habits; Proper: outcomes of SERS-mapping of crystalline violet molecules in 4 min. (Picture: YAN Wuwen)
Left: Transmission electron micrograph of the cross-section of laser reconfigured gold nanorods; Center: outcomes of the detection and evaluation of single-molecule diffusion habits; Proper: outcomes of SERS-mapping of crystalline violet molecules in 4 min. (Picture: YAN Wuwen)
 Left: Transmission electron micrograph of the cross-section of laser reconfigured gold nanorods; Center: outcomes of the detection and evaluation of single-molecule diffusion habits; Proper: outcomes of SERS-mapping of crystalline violet molecules in 4 min. (Picture: YAN Wuwen)
Left: Transmission electron micrograph of the cross-section of laser reconfigured gold nanorods; Center: outcomes of the detection and evaluation of single-molecule diffusion habits; Proper: outcomes of SERS-mapping of crystalline violet molecules in 4 min. (Picture: YAN Wuwen)